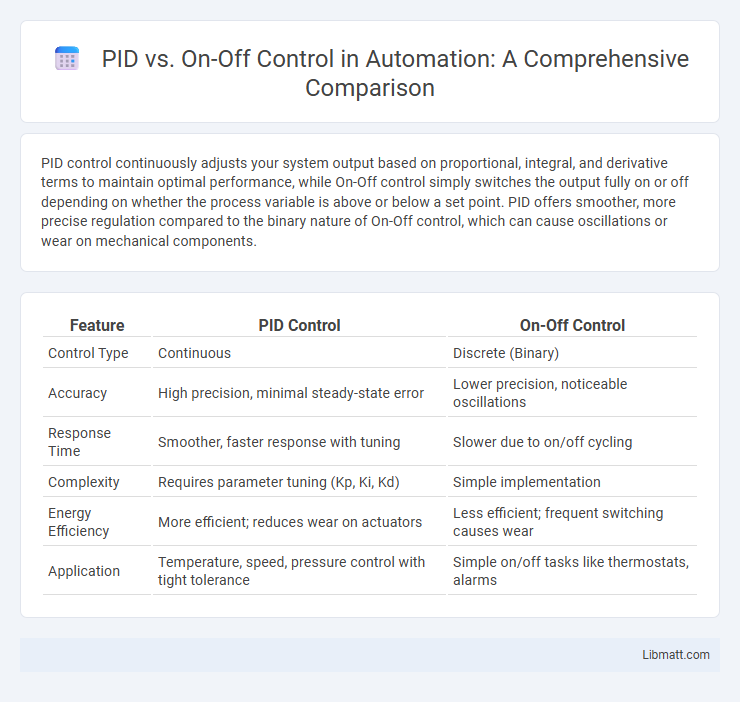
PID control continuously adjusts your system output based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms to maintain optimal performance, while On-Off control simply switches the output fully on or off depending on whether the process variable is above or below a set point. PID offers smoother, more precise regulation compared to the binary nature of On-Off control, which can cause oscillations or wear on mechanical components.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | PID Control | On-Off Control |
|---|---|---|
| Control Type | Continuous | Discrete (Binary) |
| Accuracy | High precision, minimal steady-state error | Lower precision, noticeable oscillations |
| Response Time | Smoother, faster response with tuning | Slower due to on/off cycling |
| Complexity | Requires parameter tuning (Kp, Ki, Kd) | Simple implementation |
| Energy Efficiency | More efficient; reduces wear on actuators | Less efficient; frequent switching causes wear |
| Application | Temperature, speed, pressure control with tight tolerance | Simple on/off tasks like thermostats, alarms |
Introduction to Control Systems
Control systems regulate the behavior of dynamic systems by using feedback mechanisms to achieve desired performance. PID control combines proportional, integral, and derivative actions to provide precise and stable control, while On-Off control operates with binary signals to switch the system fully on or off. Your choice between PID and On-Off control depends on system requirements for accuracy, response time, and complexity.
Understanding PID Control
PID control continuously adjusts the output by calculating proportional, integral, and derivative terms to minimize error, offering precise and stable system performance. Unlike On-Off control, which switches output fully on or off, PID control smooths responses and reduces oscillations in your processes. Understanding PID enables optimization of control systems for improved accuracy and efficiency in various industrial applications.
What is On-Off Control?
On-Off control is a basic control strategy that switches a system fully on or off based on a setpoint threshold, without any modulation of output intensity. It is commonly used in applications like thermostats, where the control variable alternates between two states to maintain the desired temperature range. The simplicity of On-Off control can lead to system oscillations and less precise regulation compared to PID control, which continuously adjusts output to minimize error.
Key Differences Between PID and On-Off Control
PID control continuously adjusts the output by calculating proportional, integral, and derivative terms to minimize error, providing smooth and precise control. On-Off control operates in a binary state, switching the output fully on or off based on a setpoint threshold, resulting in simpler but less precise regulation. Key differences include PID's ability to reduce overshoot and steady-state error, while On-Off control tends to cause oscillations and is more suitable for systems where precision is not critical.
Advantages of PID Control
PID control offers precise regulation of temperature, speed, and pressure by continuously adjusting output based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms, leading to minimal steady-state error and reduced system oscillations. Unlike On-Off control, PID provides smoother operation and better stability, enhancing process efficiency and product quality in complex industrial applications. By using PID control, your systems respond accurately to changes, improving overall performance and reducing wear on mechanical components.
Benefits and Limitations of On-Off Control
On-Off control offers simplicity and low cost, making it suitable for basic temperature and pressure regulation where precise control is unnecessary. Its main limitation lies in frequent cycling, leading to wear and tear on mechanical components and potential system instability. Unlike PID control, On-Off lacks the ability to provide smooth, continuous adjustments, resulting in oscillations around the setpoint.
Applications of PID Control
PID control is widely applied in industrial processes requiring precise regulation, such as temperature control in chemical reactors, speed control in electric motors, and pressure management in pneumatic systems. Its ability to continuously adjust the output based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms makes it ideal for maintaining stability and optimizing performance in dynamic environments. Your automation systems benefit from PID control by achieving smooth and accurate responses, minimizing overshoot and steady-state error.
Uses of On-Off Control in Industry
On-Off control is widely used in industrial applications where simple and cost-effective regulation is sufficient, such as temperature control in ovens, refrigerators, and boilers. This method excels in systems that do not require precise adjustment and where the system can tolerate oscillations around the setpoint. Your processes benefit from On-Off control when rapid switching and straightforward implementation are prioritized over fine-tuned control accuracy.
Choosing Between PID and On-Off Control
Choosing between PID and On-Off control depends on the required precision and system complexity; PID control offers continuous, proportional, integral, and derivative adjustments for accurate and stable output in dynamic processes. On-Off control provides a simpler, binary approach suitable for systems with less stringent accuracy demands or where cost and ease of implementation are priorities. Understanding process variables, response time, and tolerance to oscillations guides selection for optimal control performance.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Control Strategy
Selecting the right control strategy depends on the system's complexity and precision requirements. PID control offers continuous, fine-tuned adjustments by calculating proportional, integral, and derivative terms, making it ideal for processes needing stable and accurate regulation. On-Off control suits simpler, less sensitive systems where binary, threshold-based switching provides effective and cost-efficient operation.
PID vs On-Off Control Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com