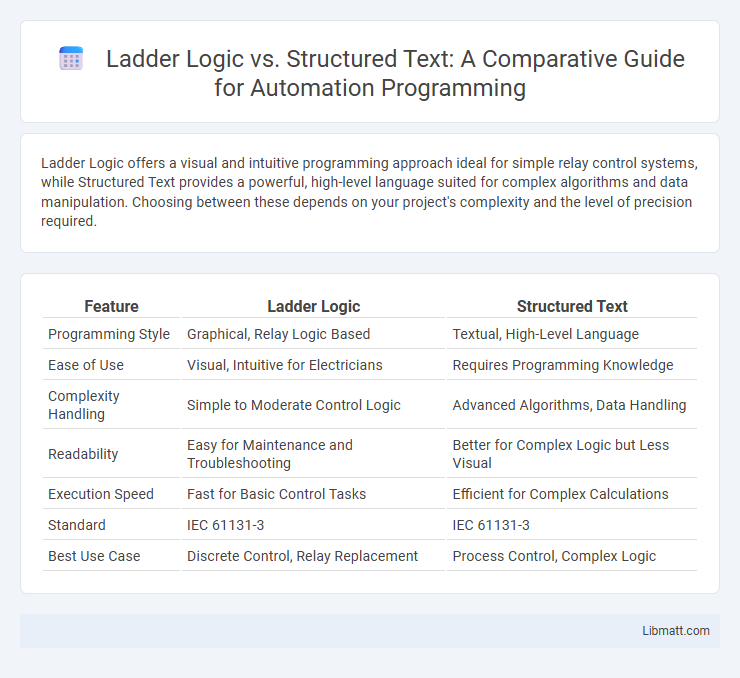
Ladder Logic offers a visual and intuitive programming approach ideal for simple relay control systems, while Structured Text provides a powerful, high-level language suited for complex algorithms and data manipulation. Choosing between these depends on your project's complexity and the level of precision required.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ladder Logic | Structured Text |
|---|---|---|
| Programming Style | Graphical, Relay Logic Based | Textual, High-Level Language |
| Ease of Use | Visual, Intuitive for Electricians | Requires Programming Knowledge |
| Complexity Handling | Simple to Moderate Control Logic | Advanced Algorithms, Data Handling |
| Readability | Easy for Maintenance and Troubleshooting | Better for Complex Logic but Less Visual |
| Execution Speed | Fast for Basic Control Tasks | Efficient for Complex Calculations |
| Standard | IEC 61131-3 | IEC 61131-3 |
| Best Use Case | Discrete Control, Relay Replacement | Process Control, Complex Logic |
Introduction to Ladder Logic and Structured Text
Ladder Logic is a graphical programming language commonly used in programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that represents electrical relay logic through interconnected rungs and contacts, making it intuitive for engineers with electrical backgrounds. Structured Text is a high-level, text-based programming language resembling Pascal, enabling complex algorithms and data handling with greater flexibility and precision. Both languages are standardized under IEC 61131-3 and serve different purposes depending on application complexity and programmer expertise.
Historical Background and Development
Ladder Logic, developed in the 1960s, originated as a graphical programming language modeled after electrical relay logic diagrams, making it accessible for electricians and technicians in industrial automation. Structured Text emerged in the 1970s as part of IEC 61131-3 standardization, designed to provide a high-level, text-based programming language resembling Pascal for more complex control algorithms. Both languages evolved to address different industrial programming needs, with Ladder Logic favoring simplicity and visualization, while Structured Text supports advanced functions and scalability in programmable logic controllers (PLCs).
Core Principles and Syntax Comparison
Ladder Logic uses graphical representation resembling electrical relay circuits, emphasizing intuitive visualization and ease of troubleshooting for control engineers. Structured Text employs high-level programming syntax similar to Pascal, allowing complex algorithms and data manipulation with conditional statements and loops. While Ladder Logic excels in straightforward control tasks with contact and coil symbols, Structured Text offers enhanced flexibility for advanced functions through code blocks and structured programming.
User Interface and Programming Environment
Ladder Logic offers a visual programming environment resembling electrical schematics, making it intuitive for technicians and engineers familiar with relay logic, with drag-and-drop functionality for ease of use. Structured Text provides a text-based interface akin to high-level programming languages, featuring syntax highlighting, code completion, and debugging tools that enhance development efficiency for software-oriented users. Both environments are supported by major PLC platforms like Siemens TIA Portal and Rockwell Studio 5000, but Ladder Logic emphasizes graphical clarity while Structured Text delivers greater flexibility for complex algorithms.
Visual Representation vs Textual Coding
Ladder Logic offers a visual representation of control processes using graphical symbols resembling electrical relay diagrams, making it intuitive for technicians familiar with circuit design. Structured Text uses a high-level textual coding language that supports complex mathematical operations and algorithms, offering greater flexibility for programming intricate control logic. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize clear visual debugging or advanced, scalable code development.
Ease of Learning and User Adoption
Ladder Logic offers intuitive visual representation through relay-like diagrams, making it easier for electricians and technicians with a background in electrical control to learn and adopt quickly. Structured Text, resembling traditional programming languages, requires familiarity with syntax and coding concepts, presenting a steeper learning curve for users without programming experience. User adoption of Ladder Logic remains higher in industrial automation environments due to its simplicity and alignment with existing skill sets.
Application Suitability and Industry Use Cases
Ladder Logic excels in discrete manufacturing and control systems, offering intuitive graphical representation ideal for relay logic and sequential control tasks in industries like automotive assembly and packaging. Structured Text is suited for complex mathematical computations, data handling, and process control, widely used in chemical processing, energy management, and advanced automation systems requiring detailed algorithmic control. Both languages integrate within IEC 61131-3 standards, enabling versatile application across diverse industrial automation scenarios depending on system complexity and user expertise.
Troubleshooting and Debugging Features
Ladder Logic offers intuitive visual troubleshooting through easily recognizable symbols and real-time monitoring of relay states, simplifying fault identification in control systems. Structured Text provides advanced debugging tools including breakpoints, step-by-step execution, and variable watch windows, enabling detailed analysis of complex logic and data flow. Both languages enhance troubleshooting efficiency, with Ladder Logic favoring hardware-oriented diagnostics and Structured Text supporting software-centric problem-solving.
Performance, Flexibility, and Scalability
Ladder Logic offers fast execution and intuitive visualization for simple control tasks, but it lacks the flexibility needed for complex algorithms and large-scale automation projects. Structured Text excels in performance by enabling advanced data manipulation and modular programming, making it highly scalable for extensive industrial systems. Its textual format supports greater flexibility, allowing developers to implement complex function blocks and reuse code efficiently across diverse automation environments.
Choosing the Right Language: Key Considerations
Choosing the right programming language for PLCs involves evaluating your project's complexity, scalability, and maintenance needs. Ladder Logic excels in simplicity and ease of troubleshooting, making it ideal for straightforward control systems and technicians familiar with electrical diagrams, while Structured Text offers advanced capabilities for complex algorithms, data handling, and modular code, suitable for experienced programmers. Your decision should weigh these factors alongside team expertise and long-term system requirements to optimize performance and maintainability.
Ladder Logic vs Structured Text Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com