Embedded HMI integrates directly into machinery, offering seamless control and real-time data visualization within a single device, enhancing system efficiency and reliability. Standalone HMI operates independently, providing flexible installation options and easy maintenance, ideal for applications requiring diverse or upgradeable interfaces.
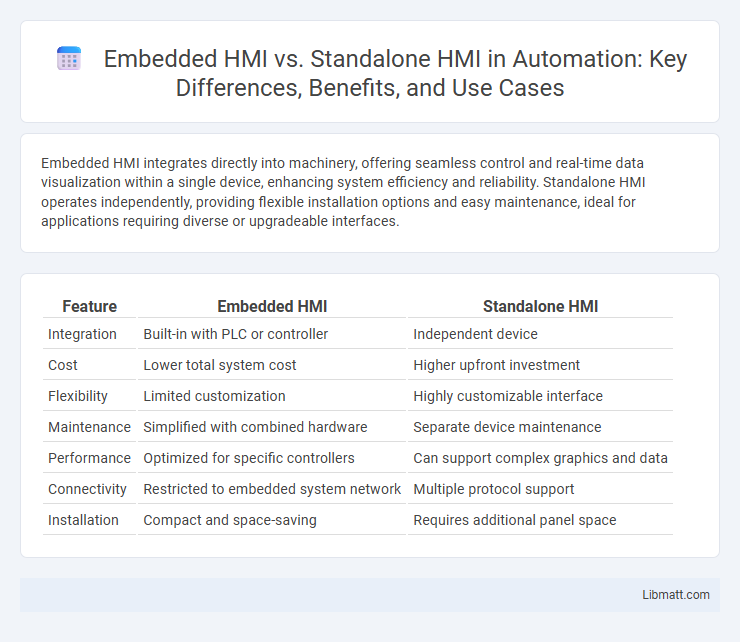
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Embedded HMI | Standalone HMI |
|---|---|---|
| Integration | Built-in with PLC or controller | Independent device |
| Cost | Lower total system cost | Higher upfront investment |
| Flexibility | Limited customization | Highly customizable interface |
| Maintenance | Simplified with combined hardware | Separate device maintenance |
| Performance | Optimized for specific controllers | Can support complex graphics and data |
| Connectivity | Restricted to embedded system network | Multiple protocol support |
| Installation | Compact and space-saving | Requires additional panel space |
Introduction to HMI Systems
Embedded HMI systems integrate directly within industrial machinery, offering seamless control and real-time data exchange, while standalone HMI devices function independently, providing flexibility and ease of installation. Your choice between embedded and standalone HMI depends on the complexity of operations and the level of integration required for monitoring and controlling processes. Optimizing system performance involves evaluating factors such as reliability, scalability, and user interface customization essential for effective human-machine interaction.
Defining Embedded HMI
Embedded HMI refers to human-machine interface systems integrated directly into a control device or machinery, offering seamless interaction without the need for external hardware. These interfaces are optimized for specific applications, ensuring faster response times, reduced latency, and enhanced reliability compared to standalone HMIs. Embedded HMIs typically feature tailored software and hardware designed to fit within the operational parameters of the host system, delivering real-time monitoring and control capabilities.
Understanding Standalone HMI
Standalone HMI (Human-Machine Interface) operates independently with a dedicated processor and display, enabling direct control and monitoring of machines without requiring external connections. Your system benefits from increased reliability and flexibility since Standalone HMIs can function in environments with limited network infrastructure. These interfaces often support advanced features such as customizable touchscreens, data logging, and local alarm management, improving operational efficiency and user interaction.
Key Differences Between Embedded and Standalone HMI
Embedded HMI systems are integrated directly into machinery or devices, providing seamless control and real-time data access within the equipment's existing hardware, while standalone HMI units operate independently and often offer more flexibility with customizable interfaces and broader connectivity options. Embedded HMIs typically consume less power and occupy less space, making them ideal for compact industrial applications, whereas standalone HMIs are favored for complex environments requiring advanced processing and multiple protocol support. Your choice between embedded and standalone HMI should consider factors like installation space, system integration needs, and scalability.
Performance and Speed Comparison
Embedded HMIs offer superior performance and faster response times due to direct integration with control systems, reducing latency and communication overhead. Standalone HMIs, while flexible and easier to upgrade, may experience slower data processing speeds because of indirect communication with controllers via external networks. Real-time performance in embedded HMIs enhances operational efficiency in critical industrial applications compared to the comparatively delayed processing in standalone devices.
Integration and Compatibility Considerations
Embedded HMI systems offer seamless integration by being directly built into machinery controllers, ensuring high compatibility with existing hardware and software platforms. Standalone HMI devices require additional communication protocols and interfaces, which may introduce compatibility challenges but offer greater flexibility for multi-vendor environments. Your choice should weigh the ease of integration with existing systems against the adaptability needs of your operational setup.
Scalability and Flexibility of HMI Solutions
Embedded HMI systems offer limited scalability as they are integrated into specific devices, restricting your ability to upgrade or customize the interface independently. Standalone HMI solutions provide greater flexibility, allowing for easy expansion and adaptation across various equipment or production lines without hardware redesign. Choosing standalone HMI ensures smoother scalability and more versatile control in evolving industrial environments.
Cost Implications: Embedded vs Standalone HMI
Embedded HMI solutions typically reduce overall system costs by integrating directly with existing control hardware, minimizing the need for additional components and wiring. Standalone HMIs often incur higher expenses due to separate hardware units, increased installation complexity, and maintenance requirements. Cost efficiency in embedded HMIs arises from consolidated design and lower energy consumption compared to standalone alternatives.
Security Features and Vulnerabilities
Embedded HMI systems offer enhanced security through direct integration with control devices, reducing attack surfaces by limiting external connectivity and enabling real-time monitoring of system status. Standalone HMIs, while flexible and easier to update, present higher vulnerability risks due to their reliance on network communications and potential exposure to unauthorized access or malware. Advanced encryption protocols, user authentication, and firmware integrity checks are critical security measures implemented in both systems to mitigate threats and protect industrial control processes.
Choosing the Right HMI for Your Application
Choosing the right Human-Machine Interface (HMI) depends on your application's complexity and integration needs. Embedded HMIs offer seamless integration with control systems, providing real-time data visualization and reduced hardware footprint. Standalone HMIs deliver greater flexibility and easier upgrades but require separate mounting and connectivity, making them ideal for versatile or retrofit projects.
Embedded HMI vs Standalone HMI Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com