Servo drives offer precise control of position, speed, and torque, making them ideal for applications requiring high performance and accuracy, while VFDs (Variable Frequency Drives) efficiently control motor speed and energy consumption in standard industrial processes. Choosing between a servo drive and a VFD depends on your need for precision versus simple motor speed regulation.
Table of Comparison
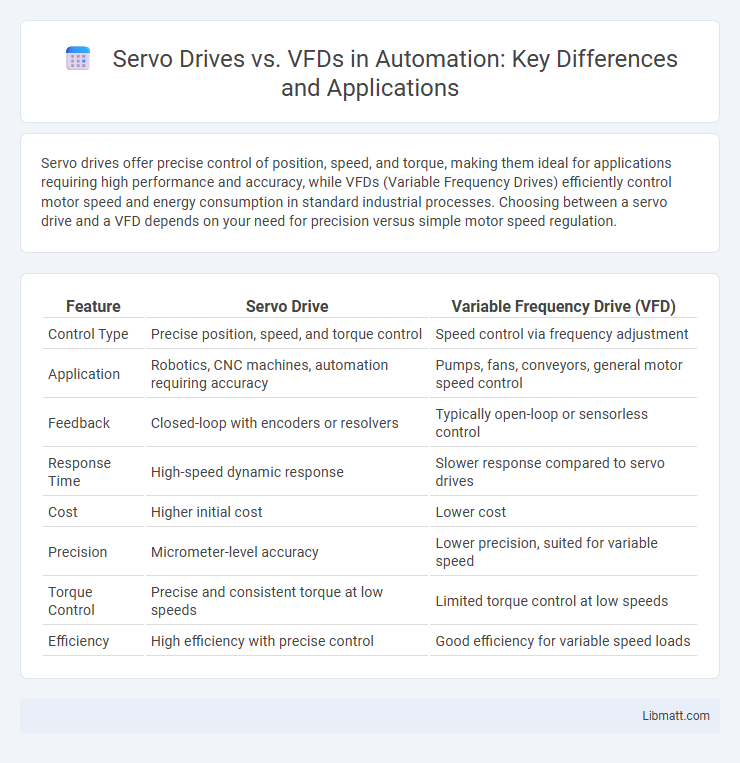
| Feature | Servo Drive | Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) |
|---|---|---|
| Control Type | Precise position, speed, and torque control | Speed control via frequency adjustment |
| Application | Robotics, CNC machines, automation requiring accuracy | Pumps, fans, conveyors, general motor speed control |
| Feedback | Closed-loop with encoders or resolvers | Typically open-loop or sensorless control |
| Response Time | High-speed dynamic response | Slower response compared to servo drives |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost |
| Precision | Micrometer-level accuracy | Lower precision, suited for variable speed |
| Torque Control | Precise and consistent torque at low speeds | Limited torque control at low speeds |
| Efficiency | High efficiency with precise control | Good efficiency for variable speed loads |
Introduction to Motion Control Systems
Motion control systems are essential for precise control of mechanical movements in automation and robotics, where Servo Drives and Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) serve distinct functions. Servo Drives provide high-accuracy positioning and dynamic response by controlling the motor's position, speed, and torque through feedback mechanisms, making them ideal for robotic arms and CNC machines. VFDs regulate the speed of AC motors by adjusting the frequency and voltage of the power supply, optimizing energy consumption and reducing mechanical stress in pumps, fans, and conveyors within your industrial processes.
What is a Servo Drive?
A Servo Drive is a specialized electronic device that precisely controls the position, velocity, and torque of servo motors in automation systems. It uses feedback from encoders or resolvers to adjust motor performance, ensuring accurate motion control in applications such as robotics, CNC machinery, and manufacturing equipment. Unlike Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), Servo Drives offer high dynamic response and precise load handling for complex motion tasks.
What is a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)?
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is an electronic device designed to control the speed and torque of an AC motor by varying the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor. VFDs improve energy efficiency and process control in applications such as pumps, fans, conveyors, and HVAC systems. Your choice between a VFD and a servo drive depends on the precision and dynamic response required by your specific industrial automation needs.
Key Differences Between Servo Drives and VFDs
Servo drives offer precise motion control with high torque at low speeds, ideal for applications requiring accurate positioning, while VFDs primarily control the speed of induction motors for variable frequency and voltage. Servo drives incorporate feedback systems like encoders for real-time adjustments, enhancing accuracy and responsiveness compared to VFDs, which typically operate without direct position feedback. Your choice depends on whether precise motion control or efficient speed variation is the priority in your industrial system.
Performance and Precision: Servo Drive vs VFD
Servo drives deliver superior performance and precision by providing accurate position, speed, and torque control through closed-loop feedback systems, making them ideal for applications requiring high dynamic response and repeatability. VFDs (Variable Frequency Drives) control motor speed by varying frequency and voltage, offering efficient energy use but with less precise positioning and slower response times compared to servo drives. Your choice between servo drive and VFD depends on the need for fine motion control versus general speed regulation in industrial automation.
Application Areas: Where Each Excels
Servo drives excel in precision control applications such as robotics, CNC machinery, and automated manufacturing where exact position, speed, and torque control are critical. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are ideal for pumping systems, HVAC equipment, and conveyor belts where energy efficiency and adjustable speed control of induction motors are prioritized. Servo drives provide higher dynamic response and accuracy, while VFDs offer cost-effective solutions for variable speed operations in less demanding control environments.
Cost Comparison: Servo Drive vs VFD
Servo drives generally have a higher upfront cost compared to Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) due to their advanced precision and control capabilities suited for complex motion applications. VFDs offer a more cost-effective solution for general motor speed control, making them ideal for applications where precise positioning is not critical. Your choice between a servo drive and a VFD should weigh initial investment against performance requirements and long-term operational efficiency.
Energy Efficiency and Maintenance
Servo drives typically offer higher energy efficiency than VFDs due to precise motor control, reducing power wastage during variable loads. Maintenance requirements for servo drives are generally lower because of advanced diagnostics and fewer mechanical parts subject to wear. VFDs may require more frequent upkeep due to thermal stress and simpler control mechanisms that can lead to less optimized energy consumption.
Selecting the Right Drive for Your Application
Choosing between a Servo Drive and a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) depends on the precision and control requirements of your application. Servo Drives excel in applications demanding high torque accuracy, dynamic response, and position control, making them ideal for robotics and CNC machinery. VFDs are more cost-effective for controlling induction motors with variable speed, suitable for pumps, fans, and conveyors where speed regulation without precise position control is sufficient.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Choice
Choosing between a Servo Drive and a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) depends on your specific application requirements, with Servo Drives offering precise control and high dynamic response for position and speed, while VFDs provide efficient motor speed control for general-purpose AC motors. Servo Drives excel in automation tasks requiring accuracy and rapid changes, whereas VFDs are more cost-effective for controlling motor speed and improving energy efficiency in less demanding scenarios. Evaluating your system's precision, speed control needs, and budget will help you make an informed decision that optimizes performance and cost.
Servo Drive vs VFD Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com