A redundant power supply ensures continuous operation by automatically switching to a backup power source within your device if the primary supply fails, preventing downtime without external intervention. A UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) provides battery backup power and surge protection during outages, allowing your equipment to safely shut down or continue running temporarily when the main power is lost.
Table of Comparison
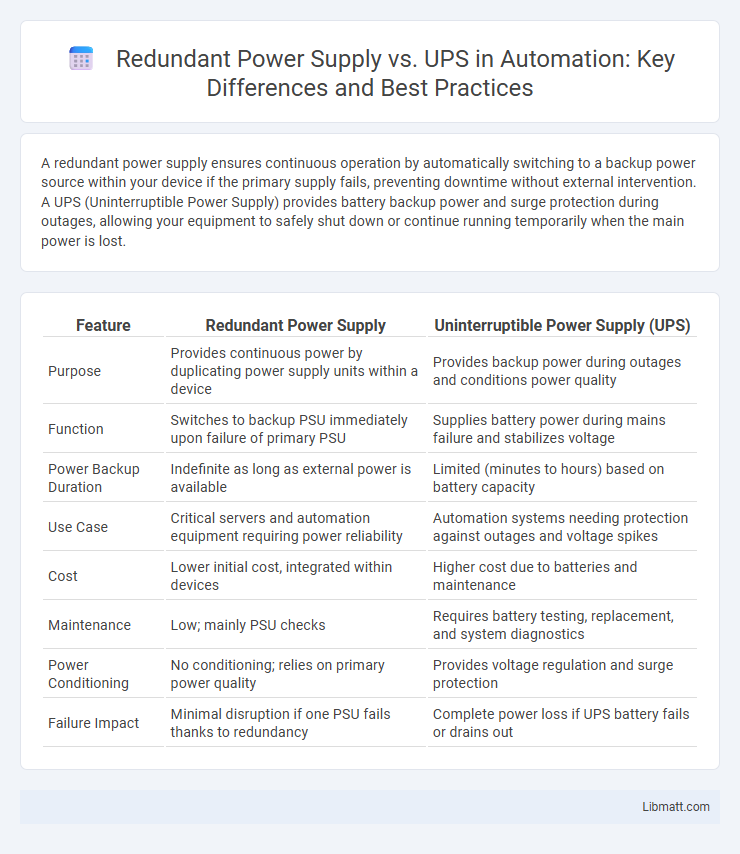
| Feature | Redundant Power Supply | Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides continuous power by duplicating power supply units within a device | Provides backup power during outages and conditions power quality |
| Function | Switches to backup PSU immediately upon failure of primary PSU | Supplies battery power during mains failure and stabilizes voltage |
| Power Backup Duration | Indefinite as long as external power is available | Limited (minutes to hours) based on battery capacity |
| Use Case | Critical servers and automation equipment requiring power reliability | Automation systems needing protection against outages and voltage spikes |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, integrated within devices | Higher cost due to batteries and maintenance |
| Maintenance | Low; mainly PSU checks | Requires battery testing, replacement, and system diagnostics |
| Power Conditioning | No conditioning; relies on primary power quality | Provides voltage regulation and surge protection |
| Failure Impact | Minimal disruption if one PSU fails thanks to redundancy | Complete power loss if UPS battery fails or drains out |
Introduction to Power Backup Solutions
Redundant power supply systems ensure continuous operation by using multiple power sources to prevent downtime during a single power failure, making them ideal for critical infrastructure. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) provide immediate temporary power through battery backup during outages, allowing your equipment to stay online while switching or shutting down safely. Both solutions are essential for maintaining power reliability and protecting sensitive electronics from unexpected interruptions.
What is a Redundant Power Supply?
A Redundant Power Supply (RPS) is a hardware configuration designed to provide continuous power to devices by using multiple power supply units running in parallel, ensuring system operation even if one power source fails. Unlike an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) that offers battery backup during outages, an RPS minimizes downtime by instantly switching to a backup unit within the same device. This setup is essential in critical environments like data centers and servers where power reliability is crucial.
Understanding Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) deliver immediate, short-term backup power during electrical outages, ensuring continuous operation and protecting sensitive equipment from data loss or hardware damage. Unlike redundant power supplies, which provide internal backup by duplicating power units within a system for constant availability, UPS units combine battery backup and surge protection to handle external power interruptions. Key UPS components include batteries, inverters, and transformers, designed to switch seamlessly to battery power the moment utility power fails, maintaining critical system uptime.
Key Differences: Redundant Power Supply vs UPS
A Redundant Power Supply (RPS) provides backup power within a device by using multiple power units to ensure continuous operation if one unit fails, primarily for internal hardware protection. An Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) offers external battery backup and surge protection to maintain power during outages and voltage fluctuations, supporting multiple devices or systems. While RPS prevents downtime due to internal power module failure, UPS safeguards against broader power disruptions, making them complementary solutions in critical infrastructure.
Advantages of Using Redundant Power Supply
Redundant power supply systems provide continuous and reliable power to critical equipment by automatically switching to backup units during power failures or component malfunctions, minimizing downtime and data loss. Your infrastructure benefits from increased system availability and improved operational efficiency due to reduced risk of power interruptions. These systems also reduce maintenance complexity and ensure smooth network performance compared to relying solely on uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
Benefits of Implementing a UPS System
Implementing a UPS system provides uninterrupted power during outages, protecting critical equipment from sudden shutdowns and data loss. It stabilizes voltage fluctuations and delivers backup power long enough to safely shut down devices or switch to a secondary power source. UPS systems enhance overall network reliability and reduce downtime, which is essential for businesses requiring continuous operation.
Common Use Cases for Redundant Power Supply
Redundant power supplies are commonly used in critical server environments, data centers, and network equipment to ensure continuous operation by providing backup power within the same device. They are essential for telecom systems, storage arrays, and medical equipment, where hardware failure can lead to significant downtime or data loss. Unlike UPS systems, redundant power supplies prevent interruptions caused by internal power unit failures without the need for external battery backup.
Typical Applications for UPS Systems
UPS systems are commonly employed in data centers, healthcare facilities, and critical infrastructure to provide uninterrupted power during outages, ensuring operational continuity and protection of sensitive equipment. They are essential for maintaining power stability in environments with frequent voltage fluctuations or short-term interruptions. These systems support mission-critical applications where even brief power loss can result in data loss, equipment damage, or operational downtime.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Redundant Power Supply and UPS
When choosing between a Redundant Power Supply (RPS) and an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS), assess the criticality of your equipment's uptime and the potential impact of power failures. Consider the duration of power outages you need to cover; RPS provides immediate backup within the device itself, while UPS offers external battery backup for longer-term power continuity. Your decision should align with the specific power protection requirements, load capacity, and maintenance complexity of your infrastructure.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Power Protection Solution
Choosing between a redundant power supply and an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) depends on your specific power reliability needs and infrastructure. Redundant power supplies provide hardware-level fault tolerance by duplicating power sources within devices, ensuring continuous operation during component failures. Your decision should factor in the criticality of uninterrupted power, backup duration, and budget constraints to select the most effective power protection solution.
Redundant Power Supply vs UPS Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com