Manual valves require direct human operation to control fluid flow, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness in low-frequency use scenarios. Automated valves provide precise, remote, and programmable control, enhancing efficiency and safety in complex or high-demand systems.
Table of Comparison
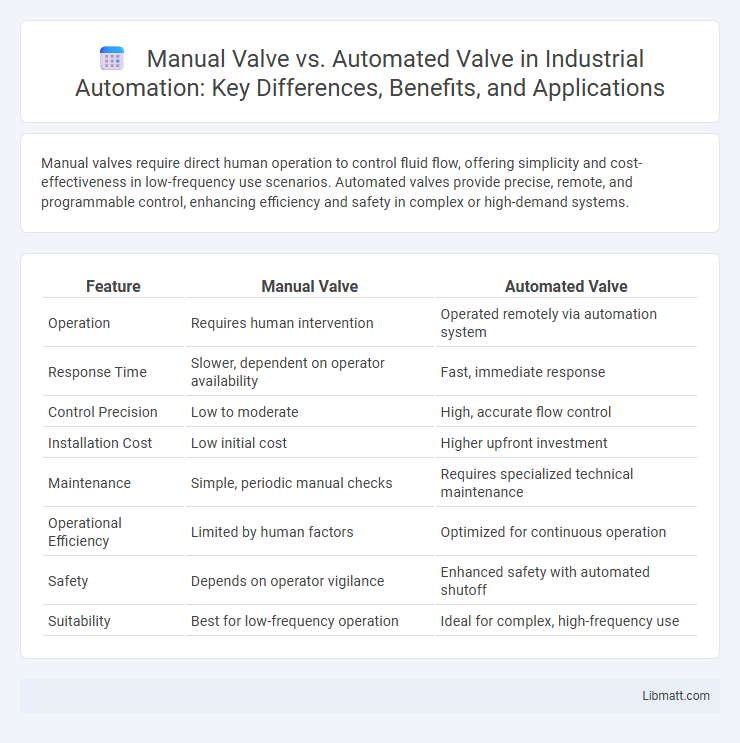
| Feature | Manual Valve | Automated Valve |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Requires human intervention | Operated remotely via automation system |
| Response Time | Slower, dependent on operator availability | Fast, immediate response |
| Control Precision | Low to moderate | High, accurate flow control |
| Installation Cost | Low initial cost | Higher upfront investment |
| Maintenance | Simple, periodic manual checks | Requires specialized technical maintenance |
| Operational Efficiency | Limited by human factors | Optimized for continuous operation |
| Safety | Depends on operator vigilance | Enhanced safety with automated shutoff |
| Suitability | Best for low-frequency operation | Ideal for complex, high-frequency use |
Introduction to Manual and Automated Valves
Manual valves require human intervention to regulate fluid flow, making them ideal for simple or infrequent adjustments in industrial processes. Automated valves use actuators and control systems to enable precise, remote, and real-time control of fluid flow, enhancing efficiency and safety in complex operations. These valves play a critical role in industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, and manufacturing by optimizing process control and reducing operational downtime.
Fundamental Differences Between Manual and Automated Valves
Manual valves require human intervention to operate, relying on physical mechanisms like handwheels or levers to control fluid flow. Automated valves utilize electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic actuators for remote and precise operation without manual effort. The fundamental difference lies in control method: manual valves depend on direct human action, while automated valves enable integration with control systems for real-time process management.
Key Components of Manual Valves
Manual valves consist primarily of a handwheel or lever, stem, valve body, and sealing elements like gaskets or O-rings, which work together to control fluid flow by physical operation. These components ensure precise control and reliable shut-off in applications where automation is unnecessary or impractical. Understanding these key parts can help you maintain and troubleshoot your manual valve system effectively.
Key Components of Automated Valves
Automated valves consist primarily of an actuator, which controls the valve's movement, a valve body that regulates flow, and a positioner that ensures precise valve positioning. These components work together to enable remote operation, faster response times, and improved process control compared to manual valves. Key actuator types include pneumatic, electric, and hydraulic, each offering distinct advantages depending on system requirements.
Operational Efficiency: Manual vs Automated Valves
Automated valves significantly enhance operational efficiency by enabling precise control and rapid response to changing process conditions, reducing downtime and human error compared to manual valves. Manual valves require physical intervention, leading to slower adjustments and increased labor costs, which can hinder real-time process optimization. Your choice between these valve types impacts overall system performance, maintenance frequency, and energy consumption, with automated valves offering superior efficiency in dynamic environments.
Cost Comparison: Manual vs Automated Valves
Manual valves generally have lower upfront costs and simpler installation requirements compared to automated valves, making them cost-effective for basic flow control applications. Automated valves incur higher initial expenses due to actuator components and control systems but offer long-term savings through improved efficiency, reduced labor, and precise operation. Your choice between manual and automated valves should consider both immediate budget constraints and potential maintenance and operational cost benefits over time.
Maintenance and Reliability Factors
Manual valves require regular physical inspections and lubrication to maintain optimal performance, often resulting in higher maintenance frequency compared to automated valves. Automated valves feature integrated sensors and self-diagnostic capabilities that enhance reliability by predicting failures and minimizing downtime. The choice between manual and automated valves depends on system complexity, with automated valves offering improved consistency and reduced human error in demanding applications.
Safety Considerations and Risk Management
Manual valves provide direct control and immediate shut-off capabilities during emergencies, reducing the risk of system failures caused by power loss or automation faults. Automated valves offer precise operation and remote control, enhancing safety in hazardous environments where manual intervention poses risk, but depend on reliable power and control systems to avoid malfunctions. Integrating safety protocols with regular maintenance and fail-safe designs is essential to mitigate risks associated with both manual and automated valve systems.
Industry Applications for Manual and Automated Valves
Manual valves are extensively used in industries with low-frequency operations or requiring precise human control, such as water treatment, small-scale chemical processing, and HVAC systems. Automated valves dominate high-demand sectors like oil and gas, power generation, and pharmaceuticals, where remote operation, quick response, and integration with control systems are critical. The choice between manual and automated valves hinges on factors like process complexity, safety requirements, and cost efficiency within specific industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Valve for Your System
Selecting the right valve for your system hinges on factors such as operational frequency, system complexity, and control requirements. Manual valves offer simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ease of maintenance, making them ideal for low-frequency or emergency shutoff applications. Automated valves provide precise control, remote operation, and integration with control systems, suiting high-frequency use and complex processes demanding accuracy and reliability.
Manual Valve vs Automated Valve Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com