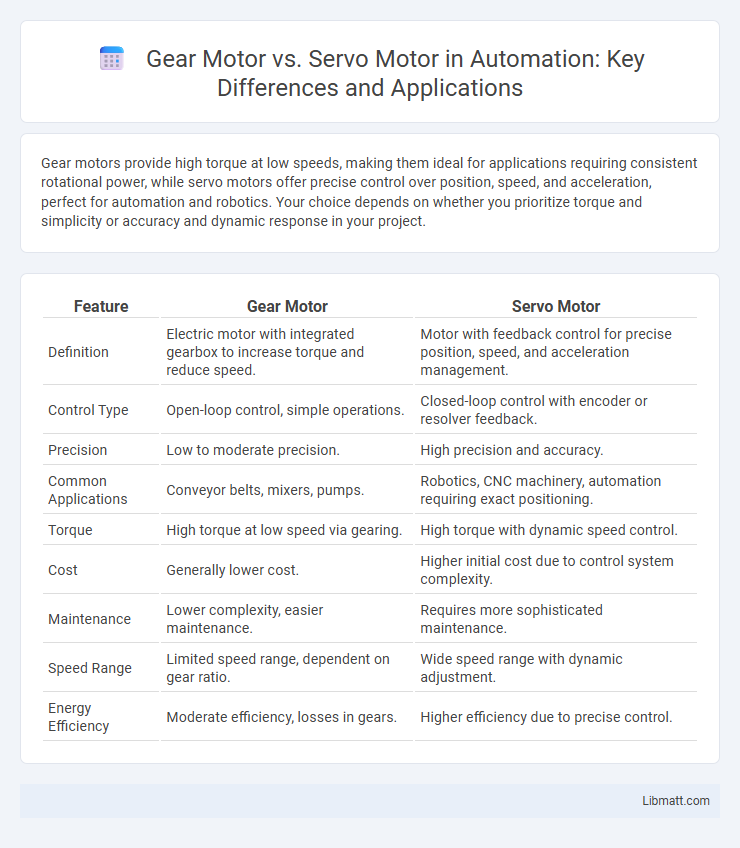
Gear motors provide high torque at low speeds, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent rotational power, while servo motors offer precise control over position, speed, and acceleration, perfect for automation and robotics. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize torque and simplicity or accuracy and dynamic response in your project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gear Motor | Servo Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electric motor with integrated gearbox to increase torque and reduce speed. | Motor with feedback control for precise position, speed, and acceleration management. |
| Control Type | Open-loop control, simple operations. | Closed-loop control with encoder or resolver feedback. |
| Precision | Low to moderate precision. | High precision and accuracy. |
| Common Applications | Conveyor belts, mixers, pumps. | Robotics, CNC machinery, automation requiring exact positioning. |
| Torque | High torque at low speed via gearing. | High torque with dynamic speed control. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost. | Higher initial cost due to control system complexity. |
| Maintenance | Lower complexity, easier maintenance. | Requires more sophisticated maintenance. |
| Speed Range | Limited speed range, dependent on gear ratio. | Wide speed range with dynamic adjustment. |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate efficiency, losses in gears. | Higher efficiency due to precise control. |
Introduction to Gear Motors and Servo Motors
Gear motors combine a standard motor with a gear reducer to enhance torque and control speed efficiently, making them ideal for applications requiring high torque at low speeds. Servo motors provide precise control of angular position, velocity, and acceleration through feedback mechanisms, offering high accuracy and dynamic response for robotics and automation. Understanding the distinct functions of gear motors and servo motors helps you select the right solution for your specific motion control needs.
Key Differences Between Gear Motors and Servo Motors
Gear motors combine a motor and gearbox to provide high torque at low speeds, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent power output and simple control. Servo motors offer precise position control, fast response, and high efficiency, driven by feedback systems to ensure accuracy in motion control tasks. Your choice depends on the need for either high torque with basic functionality or precise, dynamic motion control in robotics, CNC machines, or automation.
Working Principles of Gear Motors
Gear motors operate by combining an electric motor with a series of gears to increase torque while reducing speed, enabling precise mechanical movement in various applications. The motor generates rotational power, which is transmitted through the gear train that modifies output speed and torque according to the gear ratio. This working principle allows gear motors to provide efficient power transmission and controlled motion in robotics, conveyor systems, and automotive devices.
Working Principles of Servo Motors
Servo motors operate using feedback control systems that continuously adjust the motor's position, speed, and torque to achieve precise motion. A built-in encoder or resolver provides real-time data to the controller, enabling accurate position regulation and minimizing errors. Your applications benefit from the servo motor's ability to maintain consistent performance under varying loads and rapid response times.
Performance Comparison: Torque, Speed, and Precision
Gear motors deliver high torque at low speeds, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring substantial force. Servo motors excel in precision and speed control, offering rapid acceleration and accurate positioning with feedback systems. While gear motors provide robust torque, servo motors outperform in precision tasks due to their closed-loop control and higher speed capabilities.
Applications of Gear Motors
Gear motors are extensively used in industrial automation, conveyor systems, and robotics due to their ability to provide high torque at low speeds. Their applications include packaging machines, automotive seat adjustments, and agricultural machinery where precise speed control and power transmission are essential. You can rely on gear motors for cost-effective motion control solutions in various heavy-duty and precision-demanding environments.
Applications of Servo Motors
Servo motors are ideal for applications requiring precise control of position, speed, and torque, such as robotics, CNC machinery, and automated manufacturing systems. Their ability to provide accurate feedback and smooth motion makes them essential in camera autofocus mechanisms, conveyor systems, and aerospace technology. Your projects demanding high precision and dynamic response benefit significantly from the advanced capabilities of servo motors.
Cost and Efficiency Considerations
Gear motors generally offer lower upfront costs and simpler design, making them suitable for budget-conscious applications requiring moderate precision. Servo motors provide higher efficiency and precise control through advanced feedback mechanisms, but their initial investment and maintenance expenses are significantly higher. Evaluating cost-effectiveness requires balancing the need for accuracy and energy savings against the total lifecycle expenses of both motor types.
Maintenance and Durability Factors
Gear motors require regular lubrication and inspection of gears to ensure long-term durability, while servo motors demand precise calibration and periodic checks on feedback components for optimal maintenance. Servo motors generally offer higher durability in dynamic applications due to their closed-loop control, reducing wear from overloads compared to gear motors. Proper maintenance of your gear motor or servo motor directly impacts performance longevity, especially in industrial automation environments.
How to Choose Between Gear Motor and Servo Motor
Choosing between a gear motor and a servo motor depends on your application's requirements for precision, speed, and torque control. Gear motors are ideal for applications needing high torque at low speeds with simpler control, while servo motors provide precise positioning, speed, and acceleration control, making them suitable for robotics and automation systems. Assess your system's need for accuracy, load characteristics, and budget constraints to make the best decision for your project.
Gear Motor vs Servo Motor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com