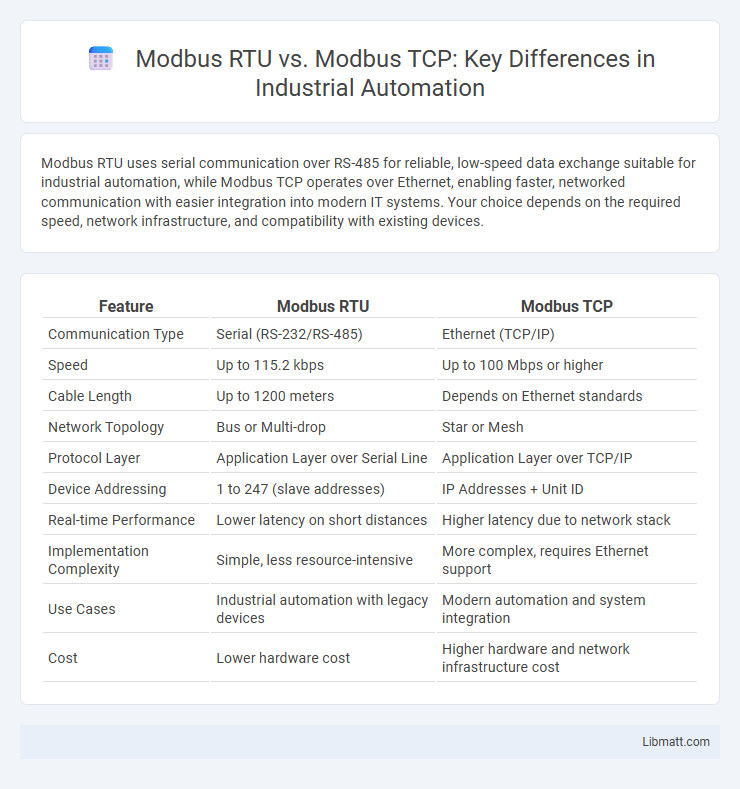
Modbus RTU uses serial communication over RS-485 for reliable, low-speed data exchange suitable for industrial automation, while Modbus TCP operates over Ethernet, enabling faster, networked communication with easier integration into modern IT systems. Your choice depends on the required speed, network infrastructure, and compatibility with existing devices.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Modbus RTU | Modbus TCP |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Type | Serial (RS-232/RS-485) | Ethernet (TCP/IP) |
| Speed | Up to 115.2 kbps | Up to 100 Mbps or higher |
| Cable Length | Up to 1200 meters | Depends on Ethernet standards |
| Network Topology | Bus or Multi-drop | Star or Mesh |
| Protocol Layer | Application Layer over Serial Line | Application Layer over TCP/IP |
| Device Addressing | 1 to 247 (slave addresses) | IP Addresses + Unit ID |
| Real-time Performance | Lower latency on short distances | Higher latency due to network stack |
| Implementation Complexity | Simple, less resource-intensive | More complex, requires Ethernet support |
| Use Cases | Industrial automation with legacy devices | Modern automation and system integration |
| Cost | Lower hardware cost | Higher hardware and network infrastructure cost |
Introduction to Modbus Protocols
Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP are communication protocols used in industrial automation for data exchange between devices. Modbus RTU operates over serial communication (RS-485) with compact binary messages, while Modbus TCP uses Ethernet for faster and more scalable network connections. Your choice between these protocols depends on the network infrastructure and speed requirements of your control system.
What is Modbus RTU?
Modbus RTU is a serial communication protocol used for transmitting data between electronic devices over RS-485 or RS-232 interfaces, employing binary encoding for efficient and compact data exchange. It is widely implemented in industrial automation for connecting programmable logic controllers (PLCs), sensors, and actuators in real-time control systems. Modbus RTU operates with a master-slave architecture, where the master device initiates commands and multiple slave devices respond sequentially.
What is Modbus TCP?
Modbus TCP is a communication protocol that utilizes Ethernet networks to transmit Modbus messages over TCP/IP, enabling faster and more efficient data exchange compared to traditional serial methods. It supports simultaneous multiple client connections, enhancing network scalability and integration in industrial automation systems. Modbus TCP eliminates the need for serial-to-Ethernet conversion, simplifying network architecture while maintaining compatibility with existing Modbus registers and function codes.
Communication Differences Explained
Modbus RTU uses serial communication via RS-485 or RS-232 protocols, transmitting data in a compact binary format suited for short-distance, real-time industrial applications. Modbus TCP operates over Ethernet networks, encapsulating Modbus messages within TCP/IP packets, enabling high-speed, long-distance communication and easier integration with modern IT infrastructure. The key difference lies in the physical layer and transport protocol, with RTU optimized for simplicity and reliability in wired serial environments and TCP designed for versatile networked systems.
Speed and Performance Comparison
Modbus TCP offers faster communication speeds and lower latency compared to Modbus RTU due to its use of Ethernet networks, supporting data rates up to 100 Mbps or more, while Modbus RTU typically operates on serial lines at speeds up to 115.2 Kbps. This increased speed in Modbus TCP enhances your system's performance, especially for applications requiring rapid data exchange and real-time monitoring. However, Modbus RTU remains reliable for slower, simpler communication setups or environments where Ethernet infrastructure is unavailable.
Network Topologies: RTU vs TCP
Modbus RTU primarily supports serial communication using point-to-point or multi-drop bus topologies ideal for short-distance and simple device networks. Modbus TCP operates over Ethernet networks utilizing star and mesh topologies, enabling high-speed, scalable communication across extensive industrial systems. The difference in physical and network layer protocols dictates the choice of topology, influencing system complexity, speed, and flexibility.
Hardware Requirements
Modbus RTU requires a serial communication interface such as RS-485 or RS-232 hardware, making it suitable for legacy industrial equipment with limited networking capabilities. Modbus TCP runs over standard Ethernet hardware, allowing seamless integration into modern LAN infrastructures and supporting higher data transfer rates. Understanding your hardware setup is critical, as it determines whether your system can handle serial connections for Modbus RTU or Ethernet for Modbus TCP.
Scalability and Flexibility
Modbus TCP offers superior scalability by supporting network expansions through standard Ethernet infrastructure, allowing seamless integration of multiple devices across long distances without significant performance degradation. Modbus RTU, while reliable for smaller, localized systems, is limited by serial communication constraints and slower data rates, restricting flexibility in complex or large-scale industrial environments. Choosing Modbus TCP enhances your system's adaptability and growth potential, making it ideal for future-proofing industrial automation networks.
Security Features
Modbus TCP offers enhanced security features compared to Modbus RTU, including support for TLS encryption and improved authentication mechanisms to protect data integrity and prevent unauthorized access. Modbus RTU, operating over serial communication, lacks built-in encryption or authentication, making it more vulnerable to interception and attacks in unsecured environments. When securing your industrial network, choosing Modbus TCP provides stronger safeguards against cyber threats due to its ability to integrate with modern network security protocols.
Choosing Between Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP
Choosing between Modbus RTU and Modbus TCP depends on communication infrastructure and application requirements, with Modbus RTU favored for serial communication over RS-485 networks offering simplicity and reliability, while Modbus TCP leverages Ethernet for faster data transfer and easier integration with modern network systems. Modbus TCP supports higher bandwidth and scalability, making it suitable for complex industrial environments requiring extensive device connectivity and remote management. Cost considerations, latency tolerance, and existing legacy systems also influence the decision, balancing performance needs against infrastructure investments.
Modbus RTU vs Modbus TCP Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com