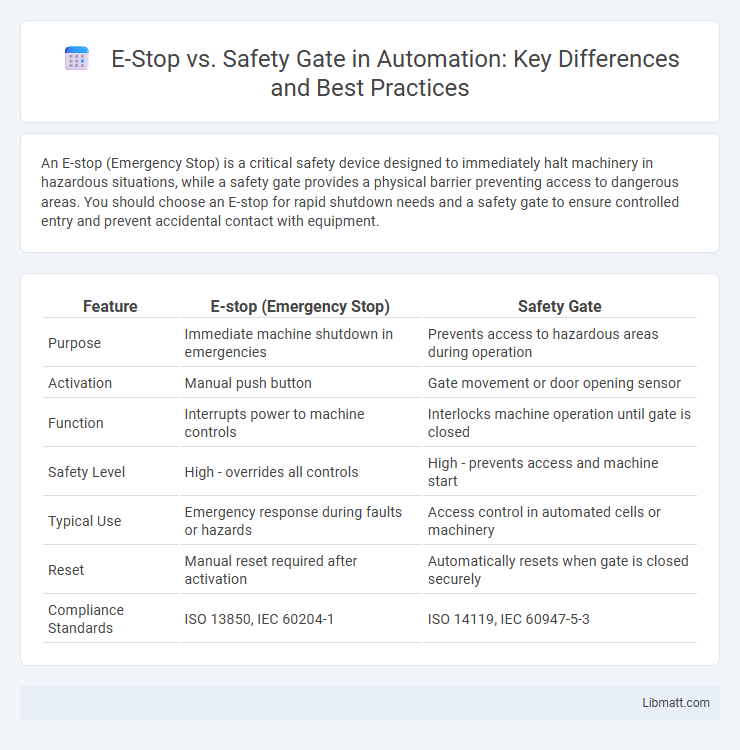
An E-stop (Emergency Stop) is a critical safety device designed to immediately halt machinery in hazardous situations, while a safety gate provides a physical barrier preventing access to dangerous areas. You should choose an E-stop for rapid shutdown needs and a safety gate to ensure controlled entry and prevent accidental contact with equipment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | E-stop (Emergency Stop) | Safety Gate |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Immediate machine shutdown in emergencies | Prevents access to hazardous areas during operation |
| Activation | Manual push button | Gate movement or door opening sensor |
| Function | Interrupts power to machine controls | Interlocks machine operation until gate is closed |
| Safety Level | High - overrides all controls | High - prevents access and machine start |
| Typical Use | Emergency response during faults or hazards | Access control in automated cells or machinery |
| Reset | Manual reset required after activation | Automatically resets when gate is closed securely |
| Compliance Standards | ISO 13850, IEC 60204-1 | ISO 14119, IEC 60947-5-3 |
Introduction to E-Stop and Safety Gate Systems
E-stop and safety gate systems are critical components in industrial automation designed to protect operators and machinery from hazards. The E-stop (emergency stop) provides an immediate shutdown of equipment when pressed, halting all operations to prevent accidents. Safety gates incorporate interlocking mechanisms that stop machines when the gate is opened, ensuring safe access to hazardous areas without interrupting overall production flow.
Defining E-Stop: Purpose and Mechanism
An E-stop, or emergency stop, is a safety device designed to immediately halt machinery operation to prevent accidents or injuries. It works by breaking the power supply or stopping the machine's motion through a simple, clearly identifiable button or pull cord. Your quick activation of an E-stop ensures rapid response during hazardous situations, minimizing potential harm.
Understanding Safety Gates: Functionality and Role
Safety gates serve as physical barriers designed to prevent unauthorized access to hazardous areas, automatically stopping machinery when opened to enhance workplace safety. These gates are integrated with sensors that detect entry attempts, triggering immediate machine shutdown to protect operators from injury. Understanding the functionality of safety gates helps ensure Your environment complies with safety regulations and minimizes accident risks.
Key Differences Between E-Stops and Safety Gates
E-Stops provide immediate machine shutdown during emergencies by cutting power instantly, ensuring rapid hazard mitigation. Safety Gates act as physical barriers that prevent access to dangerous areas and typically incorporate interlocking mechanisms that stop operations when opened. Your choice between these safety devices depends on whether instant emergency stopping or controlled access to hazardous zones is prioritized.
Safety Standards and Compliance Requirements
Emergency Stop (E-stop) devices and Safety Gates serve distinct roles in industrial safety systems, each governed by specific safety standards and compliance requirements. E-stops must comply with ISO 13850 and IEC 60204-1 standards, ensuring rapid machine shutdown in emergencies, while Safety Gates adhere to ISO 14119 and ISO 14120 standards, focusing on access control and hazard prevention through interlocking mechanisms. Compliance with these standards guarantees effective risk reduction, legal conformity, and enhanced workplace safety in automated and machinery environments.
Application Scenarios: When to Use E-Stop vs Safety Gate
E-stop devices are essential in emergency situations where immediate machine shutdown is critical to prevent injury or equipment damage, often used in high-risk environments like manufacturing lines and heavy machinery. Safety gates are better suited for controlled access scenarios, ensuring operators cannot enter hazardous areas while machinery is active, common in automated production cells and robotic workstations. Understanding your facility's specific risk factors helps determine whether an E-stop or a safety gate is the most effective safety solution.
Integration with Automation and Control Systems
E-stop devices provide immediate manual shutdown capability, integrating with automation and control systems via hardwired or programmable logic controller (PLC) inputs for rapid emergency response. Safety gates are equipped with interlock switches that communicate with automation systems to prevent machine operation when the gate is open, ensuring operator protection through controlled access points. Both systems require seamless integration to maintain operational safety and comply with industry safety standards such as ISO 13850 and ISO 14119.
Maintenance and Testing Procedures
E-stop systems require frequent functional tests to ensure immediate machine shutdown during emergencies, involving regular inspections of button activation, wiring integrity, and reset mechanisms. Safety Gates demand thorough verification of interlocking devices and sensor alignment to prevent machine operation when open, with periodic testing of locking forces and signal feedback. Maintaining your equipment involves documenting all test results and promptly addressing any faults to comply with safety standards and minimize operational risks.
Common Mistakes in Implementing Machine Safety
Common mistakes in implementing machine safety include confusing the E-stop with safety gates, leading to improper use and increased risk of injury. E-stops are designed for immediate machine shutdown during emergencies, while safety gates prevent access to hazardous areas and should be interlocked to stop machine operation only when opened. Ensuring your safety system differentiates these functions correctly enhances protection and compliance with industry safety standards.
Choosing the Right Safety Solution for Your Facility
Selecting the right safety solution for your facility depends on the specific risk levels and operational requirements; an Emergency Stop (E-stop) system provides rapid machine shutdown during emergencies, while Safety Gates create physical barriers to prevent access to hazardous areas. Evaluating machinery hazards, workflow, and compliance with standards like ISO 13850 or ISO 14119 is essential to determine whether an E-stop or safety gate better enhances worker protection and operational efficiency. Integrating both solutions can offer comprehensive safety by combining immediate stop functions with controlled access to dangerous zones.
E-stop vs Safety Gate Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com