Process instrumentation involves the measurement and monitoring of variables such as pressure, temperature, and flow within a system, while process control focuses on managing these variables to maintain desired operating conditions. Understanding the distinction between the two ensures your industrial processes are accurately measured and effectively regulated for optimal performance.
Table of Comparison
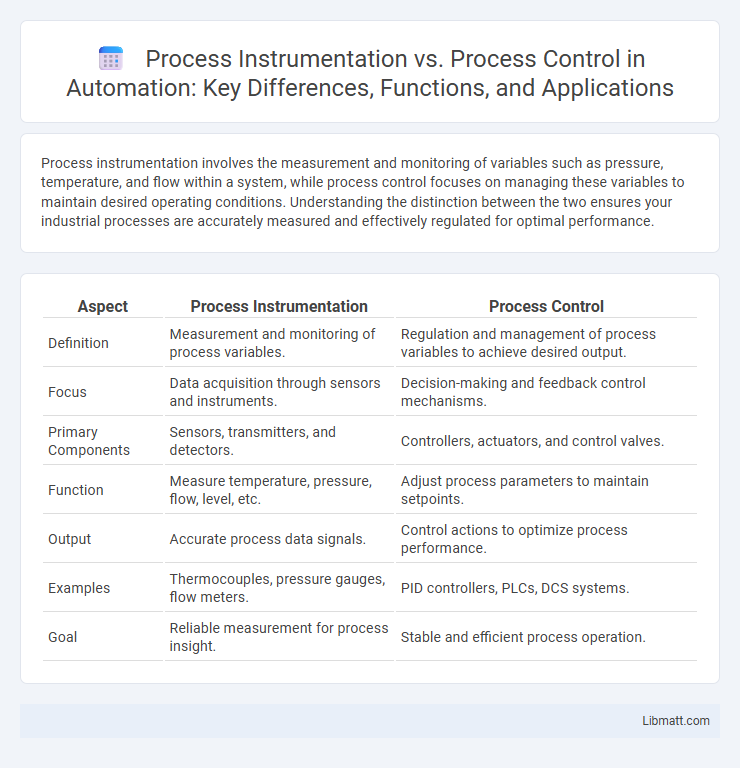
| Aspect | Process Instrumentation | Process Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measurement and monitoring of process variables. | Regulation and management of process variables to achieve desired output. |
| Focus | Data acquisition through sensors and instruments. | Decision-making and feedback control mechanisms. |
| Primary Components | Sensors, transmitters, and detectors. | Controllers, actuators, and control valves. |
| Function | Measure temperature, pressure, flow, level, etc. | Adjust process parameters to maintain setpoints. |
| Output | Accurate process data signals. | Control actions to optimize process performance. |
| Examples | Thermocouples, pressure gauges, flow meters. | PID controllers, PLCs, DCS systems. |
| Goal | Reliable measurement for process insight. | Stable and efficient process operation. |
Introduction to Process Instrumentation and Process Control
Process instrumentation involves the devices and sensors used to measure and monitor variables such as temperature, pressure, flow, and level within industrial processes. Process control refers to the methods and systems that use these measurements to regulate and maintain desired process conditions, ensuring stability and efficiency. Understanding how process instrumentation provides critical real-time data enables you to implement effective process control strategies for optimized performance.
Defining Process Instrumentation
Process instrumentation involves the measurement and monitoring of various physical parameters such as pressure, temperature, flow, and level within industrial processes to ensure accurate data collection. It utilizes sensors, transmitters, and analyzers to provide real-time feedback critical for process evaluation and safety. Process instrumentation forms the foundational layer that enables effective process control by delivering precise input data for automated systems.
Understanding Process Control
Process control involves regulating variables such as temperature, pressure, flow, and level within industrial systems to maintain desired operating conditions. It uses feedback from process instrumentation like sensors and transmitters to adjust actuators or control valves, ensuring stability and efficiency in manufacturing operations. Understanding process control helps optimize your system's performance by enabling precise adjustments based on accurate instrument measurements.
Key Components of Process Instrumentation
Process instrumentation involves key components such as sensors, transmitters, and signal conditioners that accurately measure variables like temperature, pressure, and flow in industrial processes. These instruments convert physical parameters into standardized signals for monitoring and diagnostics. Reliable data from process instrumentation ensures precise control actions in process control systems, optimizing operational efficiency and safety.
Core Elements of Process Control Systems
Process instrumentation involves measuring and detecting variables such as temperature, pressure, and flow, providing the essential data for effective process control systems. Core elements of process control systems include sensors, controllers, and actuators that work together to maintain desired process conditions by adjusting variables in real-time. Your ability to optimize these components enhances accuracy, efficiency, and safety in automated industrial operations.
Differences Between Process Instrumentation and Process Control
Process instrumentation involves the measurement and monitoring of process variables such as temperature, pressure, flow, and level through sensors and transmitters. Process control refers to the regulation and automation of these variables using controllers, control valves, and actuators to maintain desired process conditions. While instrumentation provides the data input, process control utilizes that data to execute corrective actions and ensure system stability.
Role of Instrumentation in Process Automation
Process instrumentation plays a critical role in process automation by providing accurate data measurement and monitoring of variables such as pressure, temperature, and flow. These instruments enable real-time feedback and control, ensuring processes operate within desired parameters to maintain efficiency and safety. Your automation system relies on precise instrumentation to detect changes and adjust control actions dynamically, enhancing overall process reliability.
How Process Control Enhances System Performance
Process control optimizes system performance by continuously monitoring process instrumentation data such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates, enabling real-time adjustments that maintain desired operational conditions. Advanced control algorithms use inputs from sensors and transmitters to regulate actuators and valves, reducing variability and improving consistency in output quality. You benefit from increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced safety through precise automation driven by integrated process instrumentation and control systems.
Integration of Instrumentation and Control in Industrial Settings
The integration of process instrumentation and process control in industrial settings enhances system accuracy by providing real-time data from sensors and transmitters directly to control systems such as PLCs and DCS. Effective integration enables seamless communication between measurement devices and control equipment, optimizing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. This synergy supports advanced automation strategies, predictive maintenance, and improved safety protocols in manufacturing and processing plants.
Future Trends in Process Instrumentation and Control
Future trends in process instrumentation and control emphasize the integration of advanced sensors with AI-driven analytics to enhance real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Smart instrumentation enables higher accuracy and efficiency in process control systems, reducing downtime and operational costs. Your facility can leverage these innovations to improve automation, data transparency, and adaptive control strategies for more resilient industrial processes.
Process Instrumentation vs Process Control Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com