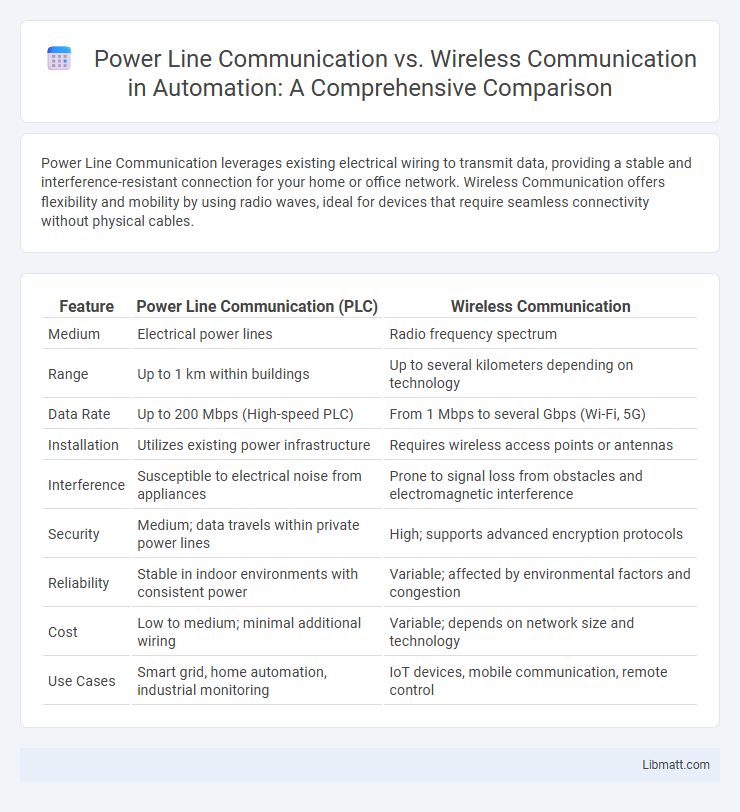
Power Line Communication leverages existing electrical wiring to transmit data, providing a stable and interference-resistant connection for your home or office network. Wireless Communication offers flexibility and mobility by using radio waves, ideal for devices that require seamless connectivity without physical cables.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Power Line Communication (PLC) | Wireless Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Electrical power lines | Radio frequency spectrum |
| Range | Up to 1 km within buildings | Up to several kilometers depending on technology |
| Data Rate | Up to 200 Mbps (High-speed PLC) | From 1 Mbps to several Gbps (Wi-Fi, 5G) |
| Installation | Utilizes existing power infrastructure | Requires wireless access points or antennas |
| Interference | Susceptible to electrical noise from appliances | Prone to signal loss from obstacles and electromagnetic interference |
| Security | Medium; data travels within private power lines | High; supports advanced encryption protocols |
| Reliability | Stable in indoor environments with consistent power | Variable; affected by environmental factors and congestion |
| Cost | Low to medium; minimal additional wiring | Variable; depends on network size and technology |
| Use Cases | Smart grid, home automation, industrial monitoring | IoT devices, mobile communication, remote control |
Introduction to Power Line Communication (PLC) and Wireless Communication
Power Line Communication (PLC) uses existing electrical wiring to transmit data, offering reliable and cost-effective networking without additional cabling. Wireless Communication enables data transfer through radio waves, providing mobility and flexibility in connections across various devices. Your choice between PLC and Wireless Communication depends on factors like environment, range, and interference tolerance.
How Power Line Communication Works
Power Line Communication (PLC) transmits data by superimposing digital signals onto existing electrical power lines, utilizing the same infrastructure that delivers electricity to homes and businesses. This method leverages modulation techniques such as Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) to encode information onto high-frequency carrier signals without disrupting electrical power supply. PLC offers reliable connectivity in environments where wireless signals face interference, enabling smart grid applications and home automation systems through broadband over power lines.
Fundamentals of Wireless Communication Technologies
Wireless communication technologies rely on electromagnetic waves to transmit data through the air, utilizing frequency bands such as LTE, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth for different applications. Key components include antennas, transceivers, and modulation schemes like QAM and OFDM that enhance signal quality and data rates. These technologies enable mobility, flexibility, and ease of deployment compared to Power Line Communication, which uses existing electrical wiring for data transfer but faces challenges with noise and limited range.
Key Advantages of Power Line Communication
Power Line Communication (PLC) leverages existing electrical wiring, providing a cost-effective solution with easy installation and reduced infrastructure needs. It offers high reliability and stability for data transmission, as it is less prone to interference compared to wireless communication in congested environments. Your network benefits from consistent connectivity and extended reach, especially in buildings where wireless signals struggle to penetrate walls or floors.
Core Benefits of Wireless Communication
Wireless communication offers unparalleled mobility and ease of installation by transmitting data through radio waves, eliminating the need for physical cables. It enables seamless connectivity over wide areas, supporting devices in dynamic environments such as smartphones, IoT sensors, and remote monitoring systems. Enhanced scalability and flexibility make wireless technologies ideal for smart cities, industrial automation, and consumer electronics.
PLC vs Wireless: Speed and Data Transfer Rates
Power Line Communication (PLC) offers data transfer rates typically ranging from 1 Mbps to 200 Mbps, depending on the technology generation and network conditions. Wireless communication technologies like Wi-Fi and 5G provide significantly higher speeds, with Wi-Fi 6 reaching up to 9.6 Gbps and 5G networks offering theoretical speeds over 10 Gbps. Despite generally lower throughput, PLC benefits from stable connections over existing electrical infrastructure, making it suitable for scenarios where wireless signals face interference or range limitations.
Reliability and Interference: PLC versus Wireless
Power Line Communication (PLC) offers superior reliability compared to wireless communication by utilizing existing electrical wiring, which reduces susceptibility to signal fading and obstacles common in wireless environments. Wireless communication often faces interference from physical barriers, electromagnetic signals, and crowded frequency spectrums, impacting performance in dense urban or industrial settings. Your choice between PLC and wireless should consider these factors, as PLC provides more stable connectivity where electromagnetic interference and physical obstructions challenge wireless transmission.
Security Considerations: Power Line vs Wireless Networks
Power Line Communication (PLC) offers enhanced security advantages due to its reliance on existing electrical wiring, limiting signal propagation beyond physical premises and reducing eavesdropping risks compared to Wireless Communication, which transmits over airwaves vulnerable to interception. Wireless networks require robust encryption protocols like WPA3 and frequent firmware updates to mitigate hacking and unauthorized access, whereas PLC networks benefit from inherent isolation but must still address vulnerabilities via secure modulation and authentication methods. Both technologies demand rigorous security frameworks, but the physical constraints of PLC provide a narrower attack surface relative to the more exposed nature of wireless signals.
Typical Use Cases and Applications
Power Line Communication (PLC) is widely used in smart grid management, home automation, and industrial monitoring where existing electrical wiring facilitates data transmission without additional infrastructure. Wireless Communication excels in mobile connectivity, IoT devices, and remote sensing applications, offering flexibility and broad coverage in environments lacking physical cabling. Both technologies support smart metering and building automation, yet PLC is favored for stable, high-security environments while wireless suits dynamic, large-scale deployments.
Future Trends in PLC and Wireless Communication
Future trends in Power Line Communication (PLC) highlight advancements in broadband capacity and enhanced noise mitigation techniques, enabling more reliable data transmission over existing electrical grids. Wireless communication is rapidly evolving with 5G and upcoming 6G technologies, focusing on ultra-low latency, massive device connectivity, and higher data rates to support IoT and smart city applications. Your choice between PLC and wireless solutions will depend on specific requirements such as infrastructure availability, cost-efficiency, and desired coverage range.
Power Line Communication vs Wireless Communication Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com