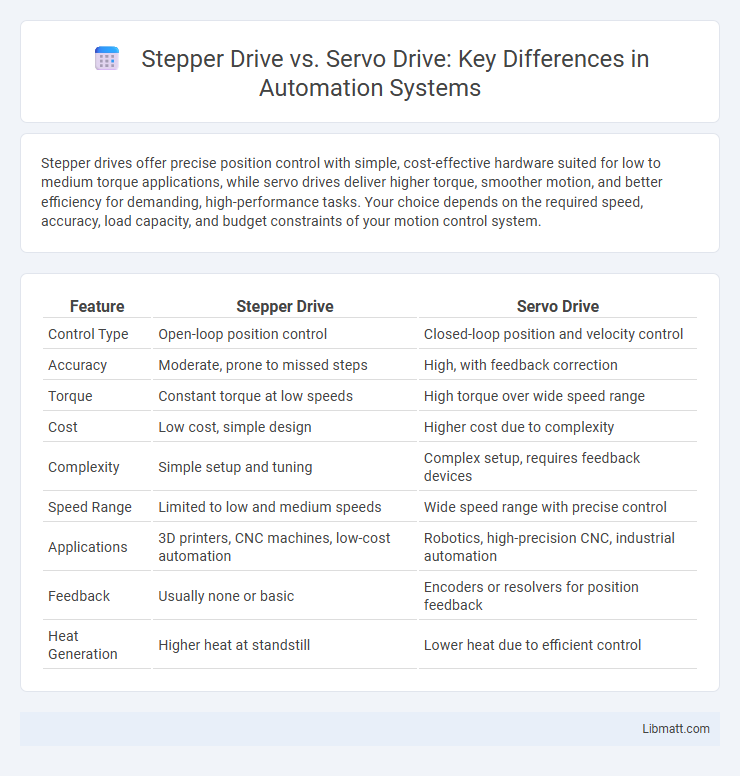
Stepper drives offer precise position control with simple, cost-effective hardware suited for low to medium torque applications, while servo drives deliver higher torque, smoother motion, and better efficiency for demanding, high-performance tasks. Your choice depends on the required speed, accuracy, load capacity, and budget constraints of your motion control system.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stepper Drive | Servo Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Control Type | Open-loop position control | Closed-loop position and velocity control |
| Accuracy | Moderate, prone to missed steps | High, with feedback correction |
| Torque | Constant torque at low speeds | High torque over wide speed range |
| Cost | Low cost, simple design | Higher cost due to complexity |
| Complexity | Simple setup and tuning | Complex setup, requires feedback devices |
| Speed Range | Limited to low and medium speeds | Wide speed range with precise control |
| Applications | 3D printers, CNC machines, low-cost automation | Robotics, high-precision CNC, industrial automation |
| Feedback | Usually none or basic | Encoders or resolvers for position feedback |
| Heat Generation | Higher heat at standstill | Lower heat due to efficient control |
Introduction to Stepper and Servo Drives
Stepper drives control stepper motors by sending discrete pulse signals, enabling precise position control without feedback sensors, commonly used in applications requiring simple, open-loop motion control. Servo drives regulate servo motors using continuous feedback from encoders or resolvers, providing high torque, speed, and accuracy for dynamic, closed-loop positioning systems. The choice between stepper and servo drives depends on the application's precision, speed, and load requirements.
Basic Principles of Stepper Drives
Stepper drives operate by sending precise electrical pulses to stepper motors, causing them to move in fixed angular increments called steps. Each pulse corresponds to a discrete movement, allowing for accurate open-loop position control without the need for feedback systems. This basic principle makes stepper drives ideal for applications requiring precise positioning and repeatability at low to moderate speeds.
Basic Principles of Servo Drives
Servo drives operate by continuously monitoring the position, velocity, and torque of the motor through feedback devices like encoders or resolvers, enabling precise control of motion. They use closed-loop control systems to adjust current supplied to the motor, ensuring accurate and smooth movement with high responsiveness. This feedback mechanism distinguishes servo drives from open-loop stepper drives by providing superior dynamic performance and position accuracy.
Key Differences Between Stepper and Servo Drives
Stepper drives offer precise, open-loop control with fixed step increments, making them ideal for simple, low-speed applications requiring straightforward positioning. Servo drives provide closed-loop control with feedback systems, delivering higher torque, speed, and accuracy for complex, dynamic tasks. Your choice depends on the need for precision, torque requirements, and system complexity.
Performance Comparison: Stepper vs Servo Drives
Servo drives offer superior performance in terms of speed, precision, and torque control compared to stepper drives, making them ideal for high-demand industrial automation applications. Stepper drives excel in cost-effective, low to moderate speed tasks with simpler control requirements but suffer from reduced accuracy and torque at higher speeds. The choice between stepper and servo drives depends on the specific application's performance needs, with servo systems preferred for complex motion control and stepper systems favored for budget-sensitive, less demanding environments.
Precision and Accuracy Considerations
Stepper drives offer high positional accuracy through fixed step increments, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent repeatability without feedback systems. Servo drives provide superior precision by utilizing continuous feedback from encoders, enabling dynamic correction and smoother motion control with minimal overshoot. For tasks demanding fine-tuned accuracy and adaptability to varying loads, servo drives outperform stepper drives in maintaining precise positioning and speed.
Application Suitability: Where Each Drive Excels
Stepper drives excel in applications requiring precise positioning at low speeds and hold torque without feedback, such as 3D printers, CNC routers, and simple automation tasks. Servo drives are better suited for high-speed, high-torque applications requiring dynamic response and closed-loop control, commonly found in robotics, industrial automation, and CNC machining. Selecting the appropriate drive depends on factors like load inertia, speed requirements, and precision needed for the specific application.
Cost Analysis: Stepper vs Servo Solutions
Stepper drives generally offer a lower initial cost compared to servo drives, making them suitable for budget-conscious applications with moderate performance requirements. Servo drives typically incur higher upfront expenses due to advanced feedback systems and precision control but provide greater efficiency, speed, and torque capabilities, which can reduce long-term operational costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership involves considering factors like maintenance, energy consumption, and application complexity, where servo drives often justify their higher price through improved performance and reliability.
Energy Efficiency and Maintenance
Stepper drives consume more energy due to constant current draw, whereas servo drives optimize power usage by adjusting current based on load, resulting in higher energy efficiency. Maintenance requirements for stepper drives are generally lower, with fewer components susceptible to wear, while servo drives demand regular monitoring and servicing of feedback systems and motors to ensure optimal performance. The choice between these drives depends on balancing energy savings with the complexity and frequency of maintenance tasks.
Choosing the Right Drive for Your Application
Selecting the right drive for your application depends on factors like precision, speed, and torque requirements. Stepper drives excel in cost-effective, open-loop control for moderate precision tasks, while servo drives offer higher accuracy, dynamic response, and efficiency for complex or high-load operations. Understanding your application's demands ensures you choose the optimal drive that balances performance and budget.
Stepper Drive vs Servo Drive Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com