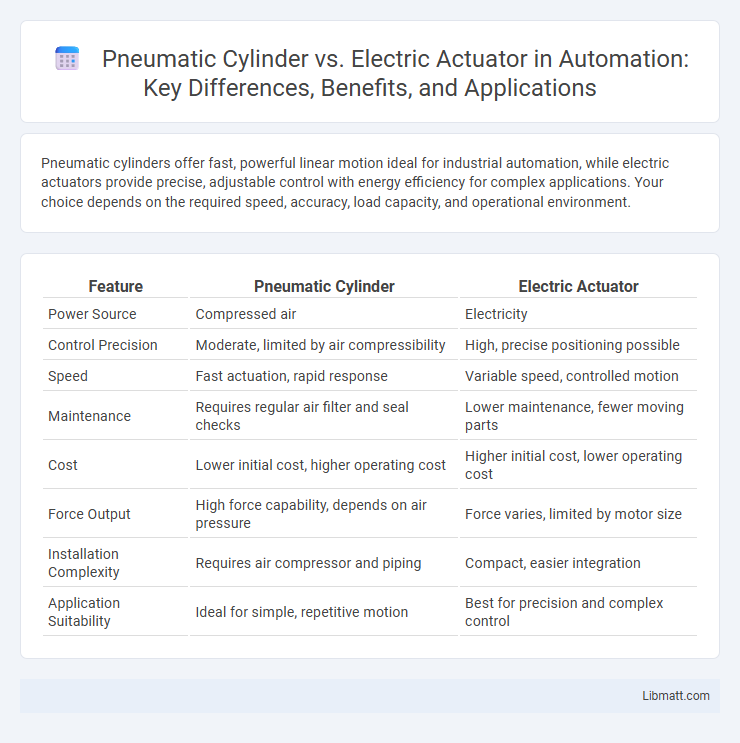
Pneumatic cylinders offer fast, powerful linear motion ideal for industrial automation, while electric actuators provide precise, adjustable control with energy efficiency for complex applications. Your choice depends on the required speed, accuracy, load capacity, and operational environment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pneumatic Cylinder | Electric Actuator |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Compressed air | Electricity |
| Control Precision | Moderate, limited by air compressibility | High, precise positioning possible |
| Speed | Fast actuation, rapid response | Variable speed, controlled motion |
| Maintenance | Requires regular air filter and seal checks | Lower maintenance, fewer moving parts |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, higher operating cost | Higher initial cost, lower operating cost |
| Force Output | High force capability, depends on air pressure | Force varies, limited by motor size |
| Installation Complexity | Requires air compressor and piping | Compact, easier integration |
| Application Suitability | Ideal for simple, repetitive motion | Best for precision and complex control |
Overview of Pneumatic Cylinders and Electric Actuators
Pneumatic cylinders utilize compressed air to create linear motion and force, commonly used in industrial automation for their speed and simplicity. Electric actuators convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, offering precise control and high repeatability ideal for applications requiring accuracy. Both devices serve as essential components in motion control systems, with pneumatic cylinders favored for robust, cost-effective performance and electric actuators preferred for advanced positioning and energy efficiency.
Working Principles: Pneumatic vs. Electric Motion
Pneumatic cylinders operate through compressed air to create linear force and motion, using air pressure to push and pull a piston within a sealed chamber. Electric actuators rely on electric motors converting electrical energy into mechanical motion, allowing precise control over speed, position, and force. The fundamental difference lies in pneumatic cylinders using air pressure for rapid, forceful movements, while electric actuators provide accurate, programmable motion with high energy efficiency.
Performance Comparison: Speed, Force, and Precision
Pneumatic cylinders provide rapid movement and high force, making them ideal for applications requiring quick and powerful strokes, though their precision can be limited by air compressibility. Electric actuators offer superior precision and controllability, enabling fine adjustments and repeatable positioning, but may have slower speeds and lower peak forces compared to pneumatics. Your choice depends on whether speed and force or accurate control and repeatability are the primary performance criteria in your application.
Energy Efficiency and Operational Costs
Pneumatic cylinders consume compressed air generated by energy-intensive compressors, leading to higher operational energy costs and lower overall efficiency compared to electric actuators. Electric actuators convert electrical energy directly into mechanical motion, offering precise control and significantly reduced energy consumption. Over time, electric actuators contribute to lower maintenance expenses and operational costs due to their superior energy efficiency and longer lifespan.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Pneumatic cylinders require regular inspection for air leaks, seal replacements, and lubrication to maintain optimal performance, typically leading to more frequent maintenance cycles. Electric actuators have fewer moving parts, resulting in lower maintenance demands and longer operational lifespans due to reduced wear and tear. Longevity of electric actuators often surpasses pneumatic cylinders by several years, especially in applications with precise control and variable motion requirements.
Control Flexibility and Integration
Electric actuators offer superior control flexibility with precise positioning, variable speed, and easy programmability through digital interfaces, enabling seamless integration into automated systems and industrial networks. Pneumatic cylinders provide simpler, less expensive solutions but have limited control options, typically operating in binary states with less precise positioning, making them less adaptable for complex automation tasks. Integration of electric actuators with IoT and Industry 4.0 technologies enhances real-time monitoring and adaptive control, outperforming pneumatic systems in modern manufacturing environments.
Application Suitability Across Industries
Pneumatic cylinders excel in industries requiring fast, repetitive motion and high force output, such as automotive manufacturing and packaging. Electric actuators provide precise control and energy efficiency ideal for medical devices, robotics, and semiconductor production. Selecting between these actuators depends on industry-specific needs for speed, accuracy, and environmental conditions.
Environmental Considerations and Safety
Pneumatic cylinders operate using compressed air, producing minimal heat and emissions, making them suitable for environments requiring clean operation, but they can pose risks from air leaks or high-pressure failures. Electric actuators offer precise control and do not rely on fluids, reducing the risk of leaks and contamination, which enhances safety in sensitive applications. Your choice should weigh the environmental impact of energy consumption and the safety standards required for your specific industrial setting.
Initial Investment and Long-Term ROI
Pneumatic cylinders generally require a lower initial investment due to simpler designs and lower material costs, making them cost-effective for basic automation tasks. Electric actuators demand higher upfront expenses driven by advanced electronics and precision components but offer superior energy efficiency and reduced maintenance costs over time. Long-term ROI favors electric actuators as their durability, programmability, and lower operational costs lead to significant savings compared to pneumatic systems reliant on compressed air infrastructure.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Needs
Pneumatic cylinders offer rapid, powerful linear motion ideal for applications requiring high force and simplicity, while electric actuators provide precise control, energy efficiency, and easy integration with automation systems. Your choice depends on factors like load requirements, environmental conditions, control precision, and maintenance preferences. Evaluating the specific demands of your project ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Pneumatic Cylinder vs Electric Actuator Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com