Additives are substances added to materials like concrete to enhance properties such as strength or workability, while admixtures specifically refer to chemical components that modify the material's behavior during mixing, setting, or curing. Understanding the difference helps you select the right product to improve your construction project's durability and performance.
Table of Comparison
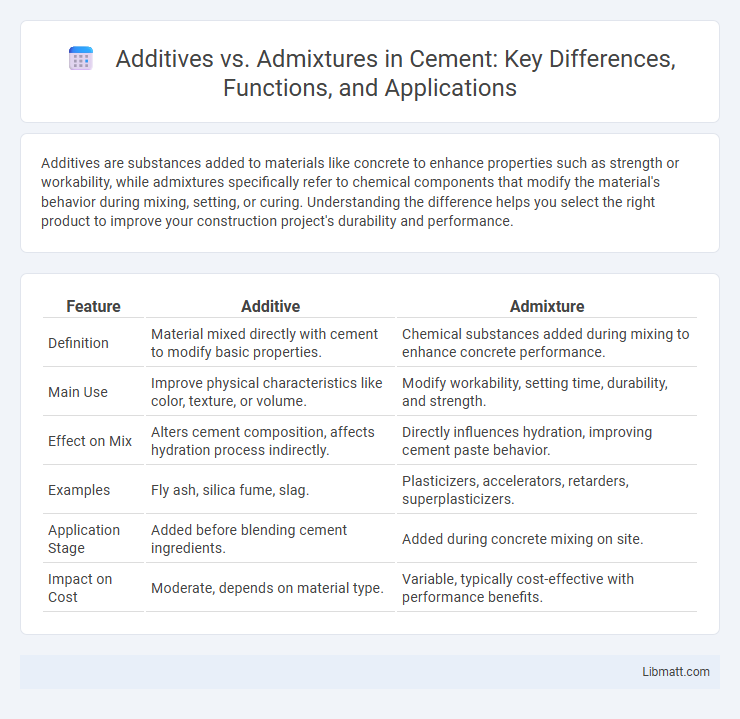
| Feature | Additive | Admixture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Material mixed directly with cement to modify basic properties. | Chemical substances added during mixing to enhance concrete performance. |
| Main Use | Improve physical characteristics like color, texture, or volume. | Modify workability, setting time, durability, and strength. |
| Effect on Mix | Alters cement composition, affects hydration process indirectly. | Directly influences hydration, improving cement paste behavior. |
| Examples | Fly ash, silica fume, slag. | Plasticizers, accelerators, retarders, superplasticizers. |
| Application Stage | Added before blending cement ingredients. | Added during concrete mixing on site. |
| Impact on Cost | Moderate, depends on material type. | Variable, typically cost-effective with performance benefits. |
Introduction to Concrete Modification
Additive and admixture are both essential components in concrete modification, enhancing the material's properties to meet specific construction needs. Additives, typically in solid form, are mixed directly with cement to alter the concrete's mechanical attributes, while admixtures are liquid chemicals added during mixing to improve workability, set time, or durability. Understanding the differences between these modifications allows you to optimize concrete performance for varied applications and environmental conditions.
Defining Additives in Construction
Additives in construction are substances incorporated into building materials to enhance specific properties such as durability, workability, or setting time. Unlike admixtures, which are typically liquids mixed into concrete or mortar, additives can be solid or powdered compounds added to alter the chemical or physical characteristics of materials. Common additives include pigments for color, fibers for reinforcement, and waterproofing agents to improve moisture resistance.
Understanding Admixtures in Concrete
Admixtures in concrete are specialized substances added to the mix to enhance specific properties such as workability, durability, and curing time, differing from general additives that may alter only basic characteristics. These chemical or mineral agents improve concrete performance by modifying setting times, reducing water content, or increasing resistance to environmental factors. Understanding admixtures allows you to optimize concrete mixtures for tailored construction needs, ensuring strength and longevity in various applications.
Key Differences: Additive vs Admixture
Additives and admixtures both enhance concrete properties but serve distinct roles; additives are raw materials mixed to improve specific concrete characteristics, while admixtures are chemical agents added in small quantities to modify fresh or hardened concrete behavior. Additives often alter the basic composition or volume, such as cement or aggregates, whereas admixtures influence workability, setting time, strength, or durability without changing the fundamental mix proportions. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate component to achieve desired performance in construction and concrete technology.
Types of Common Additives
Common additives in concrete include accelerators, which speed up the curing process; retarders, which delay setting time for extended workability; plasticizers that improve flow without extra water; and air-entraining agents, which introduce tiny air bubbles to enhance freeze-thaw durability. Each type of additive modifies the concrete's properties to meet specific construction needs. Your choice of additive depends on project requirements such as climate conditions, workability, and structural performance.
Popular Admixture Categories
Popular admixture categories in concrete include water-reducing agents, which enhance workability and strength, and accelerators, designed to speed up the curing process for quicker construction timelines. Retarders delay setting time for hot-weather concreting, while air-entraining agents improve durability by creating microscopic air bubbles to resist freeze-thaw cycles. Understanding these categories helps you select appropriate admixtures tailored to your specific project requirements, ensuring optimal concrete performance.
Effects on Concrete Performance
Additives and admixtures both influence concrete performance by altering its physical and chemical properties, but admixtures provide targeted enhancements like improved workability, setting time, and durability, while additives generally modify the concrete matrix composition. Your concrete's strength, resistance to environmental factors, and curing behavior can be significantly optimized using admixtures such as plasticizers, accelerators, or retarders. Selecting the right type ensures tailored performance improvements for specific construction needs.
Application Methods and Timing
Additives are typically mixed directly with raw materials during production, ensuring uniform distribution throughout the mixture, while admixtures are usually introduced at the batching plant or on-site just before or during mixing to modify concrete properties. The timing of additive incorporation is crucial for achieving desired effects like accelerated curing or enhanced durability, whereas admixtures can be adjusted based on environmental conditions such as temperature or humidity. Your choice between additives and admixtures affects application efficiency and the final performance of construction materials.
Advantages and Limitations of Each
Additives enhance concrete properties such as strength, durability, and workability, providing benefits like improved setting time and resistance to environmental factors, but may increase costs and require precise dosage control. Admixtures offer targeted improvements like reduced water content, increased hydration, and better freeze-thaw resistance while allowing flexibility in mix design; however, they can introduce compatibility issues with certain cement types and may affect long-term durability if not properly balanced. Understanding the chemical composition and intended effect of each additive or admixture is critical for optimizing concrete performance and ensuring structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Option for Your Project
Selecting the right option between additives and admixtures depends on your project's specific requirements, including desired concrete properties and environmental conditions. Additives typically refer to substances that alter fresh or hardened concrete properties, while admixtures are carefully formulated chemical agents enhancing performance factors like workability, durability, or curing time. Understanding the differences ensures your construction achieves optimum strength, longevity, and cost-effectiveness tailored to your project's demands.
Additive vs Admixture Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com