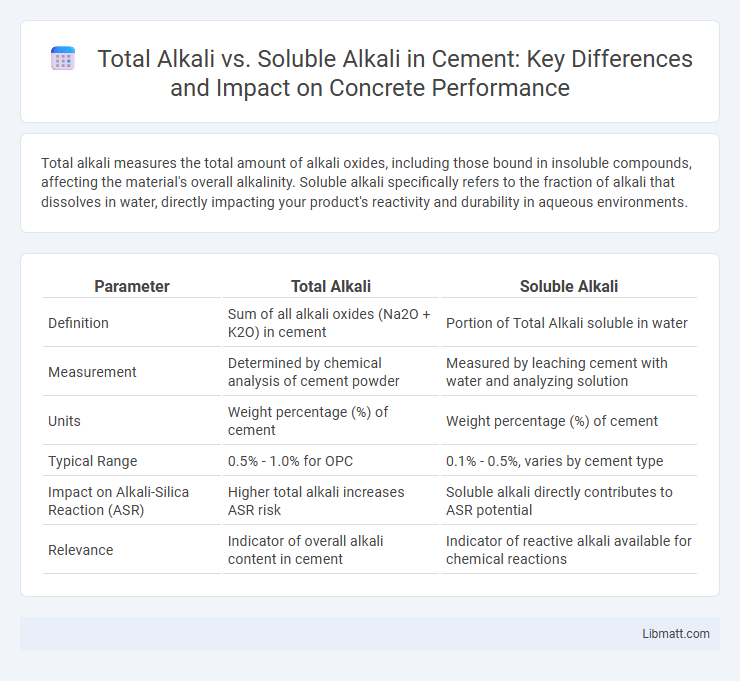
Total alkali measures the total amount of alkali oxides, including those bound in insoluble compounds, affecting the material's overall alkalinity. Soluble alkali specifically refers to the fraction of alkali that dissolves in water, directly impacting your product's reactivity and durability in aqueous environments.
Table of Comparison
| Parameter | Total Alkali | Soluble Alkali |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sum of all alkali oxides (Na2O + K2O) in cement | Portion of Total Alkali soluble in water |
| Measurement | Determined by chemical analysis of cement powder | Measured by leaching cement with water and analyzing solution |
| Units | Weight percentage (%) of cement | Weight percentage (%) of cement |
| Typical Range | 0.5% - 1.0% for OPC | 0.1% - 0.5%, varies by cement type |
| Impact on Alkali-Silica Reaction (ASR) | Higher total alkali increases ASR risk | Soluble alkali directly contributes to ASR potential |
| Relevance | Indicator of overall alkali content in cement | Indicator of reactive alkali available for chemical reactions |
Introduction to Alkali Content in Materials
Alkali content in materials is crucial for understanding their chemical behavior, especially in cement and concrete applications. Total alkali represents the overall concentration of alkaline oxides, primarily sodium and potassium, while soluble alkali refers specifically to those alkali components that readily dissolve in water, impacting material reactivity and durability. Your assessment of these alkali levels helps control potential alkali-silica reactions and optimize performance in construction materials.
Defining Total Alkali and Its Significance
Total alkali refers to the combined concentration of all alkali metals, primarily sodium (Na2O) and potassium (K2O), present in a material, crucial for assessing its chemical reactivity and processing behavior. It plays a significant role in industries like cement manufacturing, where total alkali content influences clinker formation, cement durability, and resistance to alkali-silica reaction (ASR). Understanding total alkali levels helps optimize raw material selection and ensures compliance with quality standards to enhance the performance and lifespan of construction materials.
What Are Soluble Alkalis?
Soluble alkalis refer to alkali compounds that readily dissolve in water, including sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, and sodium carbonate. These compounds increase the pH level in solutions, making them highly reactive and useful in various industrial applications such as detergent manufacturing and chemical processing. Understanding the difference between total alkali and soluble alkali is crucial for controlling chemical reactions and ensuring product quality in processes where your formulations require specific alkalinity levels.
Key Differences: Total Alkali vs Soluble Alkali
Total Alkali represents the combined concentration of all alkali metals, including potassium, sodium, and lithium, present in a sample, while Soluble Alkali measures only the fraction of alkali metals that dissolve in water. Total Alkali is often determined through complete digestion methods, providing a comprehensive view of alkali content, whereas Soluble Alkali reflects the bioavailable or reactive portion important for soil and water chemistry. Understanding the distinction between Total and Soluble Alkali is critical in fields like agriculture, environmental science, and materials engineering, where precise alkali measurement affects quality control and ecological impact assessments.
Methods for Measuring Total Alkali
Total Alkali is primarily measured through gravimetric analysis or titration techniques such as acid-base titration with hydrochloric acid to quantify hydroxides, carbonates, and bicarbonates. Soluble Alkali, in contrast, is assessed by first filtering the sample and then performing titration on the filtrate to measure alkali content dissolved in water. Precise control of pH and careful sample preparation is critical in methods measuring Total Alkali to ensure accurate determination of all alkalinity components.
Techniques to Determine Soluble Alkali
Techniques to determine soluble alkali include water extraction methods followed by titration using acid-base indicators or potentiometric titration to quantify alkalinity levels. Ion chromatography offers precise measurement by separating and detecting alkali ions in the extract solution. Spectrophotometric analysis can also be employed, utilizing specific reagents that react with soluble alkali ions to produce measurable color changes.
Impact on Material Performance and Durability
Total alkali content in materials measures the sum of all alkali metals present, influencing the overall chemical reactivity and potential for degradation within concrete and ceramics. Soluble alkali specifically refers to the portion of alkalis that readily dissolve in water, directly affecting the material's interaction with moisture and susceptibility to alkali-silica reaction (ASR), which compromises structural integrity. Understanding the distinction between total and soluble alkali is critical for predicting long-term durability and optimizing formulations to enhance resistance against alkali-induced damage.
Alkali Contribution to Concrete Reactions
Total alkali represents the overall concentration of sodium and potassium oxides in cement, which directly influences the potential for alkali-silica reaction (ASR) in concrete. Soluble alkali, the portion of total alkali that dissolves in pore water, plays a critical role in concrete durability by actively participating in ASR, leading to expansion and cracking. Understanding your concrete mix's soluble alkali content helps mitigate harmful reactions and enhances the long-term performance of your structures.
Industry Standards for Alkali Content
Industry standards for alkali content distinguish Total Alkali, which includes all soluble and insoluble alkali components, from Soluble Alkali, representing only the alkali dissolved in water. Total Alkali measurements are critical for assessing the overall alkaline composition in raw materials and finished products, ensuring compliance with regulations set by organizations like ASTM and ISO. Your quality control processes should prioritize Soluble Alkali levels to prevent corrosion and maintain product durability according to stringent industrial benchmarks.
Practical Implications: Selecting the Right Alkali Metrics
Total alkali measures the complete alkali content in a material, including both soluble and insoluble forms, while soluble alkali specifically quantifies only the water-extractable alkali fraction. Selecting the right alkali metric is critical in industries like cement manufacturing and concrete production, where soluble alkali plays a key role in alkali-silica reaction (ASR) management and durability performance. Using soluble alkali data allows for more accurate prediction of ASR risk, guiding formulation adjustments to improve long-term structural integrity and durability.
Total Alkali vs Soluble Alkali Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com