De-dusting removes fine dust particles from materials to improve cleanliness and product quality, while conditioning adjusts moisture and temperature levels to enhance material handling and processing efficiency. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize dust reduction or optimal material consistency for your specific application.
Table of Comparison
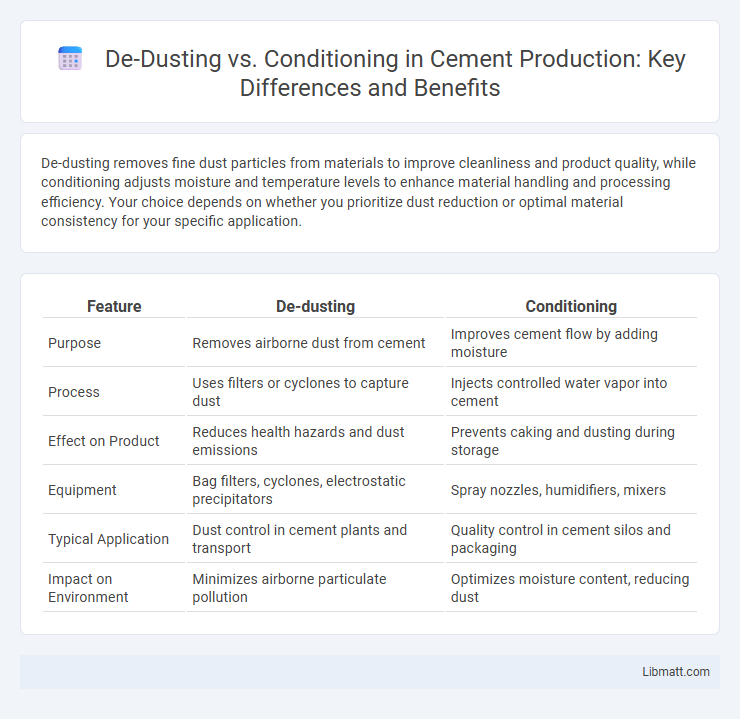
| Feature | De-dusting | Conditioning |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Removes airborne dust from cement | Improves cement flow by adding moisture |
| Process | Uses filters or cyclones to capture dust | Injects controlled water vapor into cement |
| Effect on Product | Reduces health hazards and dust emissions | Prevents caking and dusting during storage |
| Equipment | Bag filters, cyclones, electrostatic precipitators | Spray nozzles, humidifiers, mixers |
| Typical Application | Dust control in cement plants and transport | Quality control in cement silos and packaging |
| Impact on Environment | Minimizes airborne particulate pollution | Optimizes moisture content, reducing dust |
Introduction to De-dusting and Conditioning
De-dusting removes fine dust particles from materials, improving air quality and reducing equipment wear in industrial processes. Conditioning enhances material properties by adjusting moisture or temperature levels to optimize performance in manufacturing or storage. Your choice between de-dusting and conditioning depends on whether your priority is contamination control or material preparation.
Understanding the Need for Dust Control
Effective dust control is essential for improving air quality, enhancing worker safety, and maintaining equipment performance in industrial environments. De-dusting targets the removal of airborne particles using filters and scrubbers, whereas conditioning adjusts temperature and humidity to reduce dust generation and dispersion. Your choice between de-dusting and conditioning depends on the specific operational challenges, material characteristics, and regulatory standards governing your facility.
What is De-dusting?
De-dusting is the process of removing fine dust particles from materials, typically in industrial or agricultural settings, to improve product quality and reduce health hazards. This technique uses filters, cyclones, or air classifiers to separate dust from bulk materials such as grains, minerals, or powders. Effective de-dusting enhances your operational efficiency by minimizing contamination and equipment wear.
What is Conditioning?
Conditioning is a process in which materials are treated to improve their handling and processing properties by adjusting moisture content and temperature. This technique enhances the flowability, reduces static electricity, and prevents clumping, ensuring smooth operation in industrial applications. By optimizing material characteristics through conditioning, you can increase efficiency and product quality in manufacturing or processing environments.
Key Differences Between De-dusting and Conditioning
De-dusting primarily involves removing dust particles from raw materials to improve cleanliness and reduce contamination, whereas conditioning modifies moisture content or applies treatment to enhance material properties for better processing. De-dusting targets surface-level impurities using equipment like cyclones or filters, while conditioning impacts material texture and behavior through methods such as steaming or adding moisture. The key difference lies in de-dusting's emphasis on cleanliness versus conditioning's focus on preparing materials for optimal processing performance.
Advantages of De-dusting Systems
De-dusting systems improve air quality by efficiently removing dust particles from industrial environments, reducing health risks for workers. These systems enhance equipment longevity by preventing dust accumulation, which can lead to mechanical failures and increased maintenance costs. Their energy-efficient operation and compliance with environmental regulations also contribute to sustainable manufacturing processes.
Benefits of Conditioning Processes
Conditioning processes enhance material flowability and reduce dust generation by adding controlled moisture or binding agents, improving operational safety and air quality in industrial settings. By stabilizing fine particles, conditioning minimizes surface dust, leading to lower maintenance costs and decreased health risks for workers. These processes also facilitate efficient handling and storage, resulting in optimized production throughput and reduced equipment wear.
Choosing the Right Solution: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right solution between de-dusting and conditioning depends on the specific material properties and processing goals; de-dusting is ideal for removing fine particulate matter to improve product quality and reduce airborne contaminants, while conditioning enhances material flow and reduces static by adjusting moisture or adding binders. Consider factors such as the nature of the dust problem, the desired product consistency, and environmental regulations impacting your operation. Your choice should align with operational efficiency, product safety standards, and cost-effectiveness to achieve optimal results.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
De-dusting is extensively utilized in mining, food processing, and pharmaceuticals to eliminate airborne particles, improving air quality and worker safety, while conditioning is pivotal in the wood and fiber industries to adjust moisture content for optimal material handling and processing efficiency. Case studies reveal that de-dusting systems in cement plants reduce dust emissions by over 90%, significantly minimizing environmental impact and regulatory penalties. Conditioning techniques in paper manufacturing enhance product quality by stabilizing fiber moisture, leading to a 15% increase in production efficiency and reduced machine downtime.
Future Trends in Dust Management Technologies
Future trends in dust management technologies emphasize advanced real-time monitoring systems and AI-driven predictive maintenance to enhance efficiency and safety. Innovations in electrostatic precipitation and wet scrubber technologies promise higher dust capture rates with lower energy consumption. Integrating smart sensors with your dust control systems will enable proactive responses, reducing downtime and improving air quality compliance.
De-dusting vs Conditioning Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com