Alternative fuels offer cleaner combustion and reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fuels, promoting environmental sustainability. Your choice of fuel impacts air quality and energy independence, making alternative options a viable solution for future transportation and energy needs.
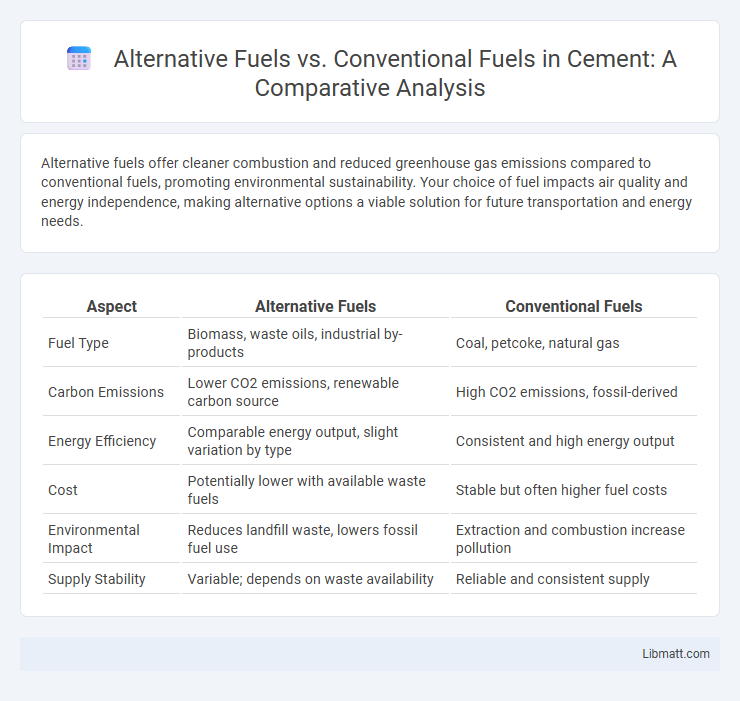
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Alternative Fuels | Conventional Fuels |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Type | Biomass, waste oils, industrial by-products | Coal, petcoke, natural gas |
| Carbon Emissions | Lower CO2 emissions, renewable carbon source | High CO2 emissions, fossil-derived |
| Energy Efficiency | Comparable energy output, slight variation by type | Consistent and high energy output |
| Cost | Potentially lower with available waste fuels | Stable but often higher fuel costs |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste, lowers fossil fuel use | Extraction and combustion increase pollution |
| Supply Stability | Variable; depends on waste availability | Reliable and consistent supply |
Introduction to Alternative and Conventional Fuels
Alternative fuels such as biofuels, hydrogen, and electricity offer sustainable energy solutions with lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fuels like gasoline and diesel, which are derived from finite fossil fuel reserves. Conventional fuels remain dominant due to established infrastructure and higher energy density but contribute significantly to air pollution and climate change. The transition to alternative fuels aims to reduce environmental impact while maintaining energy security and supporting advancements in vehicle technology.
Types of Alternative Fuels
Alternative fuels include biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel, hydrogen fuel, natural gas, and electricity, offering cleaner and renewable energy sources compared to conventional fuels like gasoline and diesel. These alternative fuels reduce greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fossil fuels, enhancing environmental sustainability. Your choice of alternative fuel can significantly impact vehicle performance, emission levels, and energy efficiency.
Common Conventional Fuels Explained
Common conventional fuels include gasoline, diesel, and natural gas, which are derived primarily from fossil fuels and widely used for transportation and energy production. These fuels release significant amounts of carbon dioxide and other pollutants when burned, contributing to environmental concerns such as climate change and air quality degradation. Understanding the limitations of conventional fuels can help you make informed decisions when considering more sustainable alternatives for your energy needs.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Alternative fuels such as biodiesel, ethanol, and hydrogen significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fossil fuels by producing fewer pollutants like carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. Lifecycle analyses reveal that alternative fuels typically generate lower carbon footprints, especially when sourced sustainably, minimizing the impact on air quality and climate change. Conventional fuels, derived from crude oil combustion, contribute extensively to environmental degradation through high emissions and resource depletion, exacerbating global warming and ecosystem harm.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Factors
Alternative fuels such as biodiesel, ethanol, and electric power offer varying cost efficiencies compared to conventional fuels like gasoline and diesel, often influenced by production scale and technological advancements. Economic factors including fuel price volatility, government subsidies, and infrastructure investment significantly impact the overall cost-effectiveness and market adoption of alternative fuels. Lifecycle cost analysis reveals that alternative fuels can reduce dependence on imported oil, stabilizing long-term fuel expenses despite higher initial infrastructure costs.
Energy Efficiency and Performance
Alternative fuels such as electric, hydrogen, and biofuels often demonstrate higher energy efficiency compared to conventional fossil fuels by converting a greater percentage of stored energy into usable power. Performance metrics reveal that electric motors provide instant torque and smoother acceleration, while hydrogen fuel cells offer longer range and faster refueling times relative to gasoline and diesel engines. Despite these advantages, some alternative fuels face challenges in energy density and infrastructure availability, impacting widespread adoption and consistent engine performance.
Availability and Infrastructure
Alternative fuels such as hydrogen, biodiesel, and electricity often face limited availability and underdeveloped infrastructure compared to conventional fuels like gasoline and diesel, which benefit from extensive global distribution networks and refueling stations. Investment in charging stations, hydrogen refueling points, and biodiesel production facilities remains crucial to expanding the accessibility of alternative fuels. Conventional fuels dominate the market due to existing infrastructure, but ongoing advancements aim to bridge this gap to support sustainable energy transitions.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in promoting alternative fuels by offering tax credits, subsidies, and grants aimed at reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. Conventional fuels often face increasing regulatory pressures, such as carbon pricing and stricter emission standards, which encourage the transition to cleaner energy sources. You can benefit from these policies by choosing alternative fuels that qualify for financial incentives and support sustainable energy use.
Future Trends in Fuel Technology
Future trends in fuel technology emphasize the shift from conventional fossil fuels to alternative fuels such as hydrogen, biofuels, and electric batteries, driven by the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. Advanced research in renewable energy sources and improved fuel efficiency promises to enhance the sustainability and affordability of transportation and industrial sectors. Your adoption of vehicles powered by alternative fuels can significantly contribute to a cleaner environment and accelerate the transition toward a low-carbon future.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Fuel Option
Selecting the best fuel option depends on factors like environmental impact, availability, and vehicle compatibility. Alternative fuels such as biodiesel, ethanol, and hydrogen offer reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional fuels like gasoline and diesel. Your choice should balance sustainability goals with practical considerations like infrastructure and cost-efficiency.
Alternative Fuels vs Conventional Fuels Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com