A bag filter fan is designed to maintain air pressure and flow through dust collection systems, effectively controlling dust emissions by supporting the bag filter's operation. Your choice between a bag filter fan and an ID fan depends on the specific requirements for controlling air pollution and maintaining proper airflow within industrial processes.
Table of Comparison
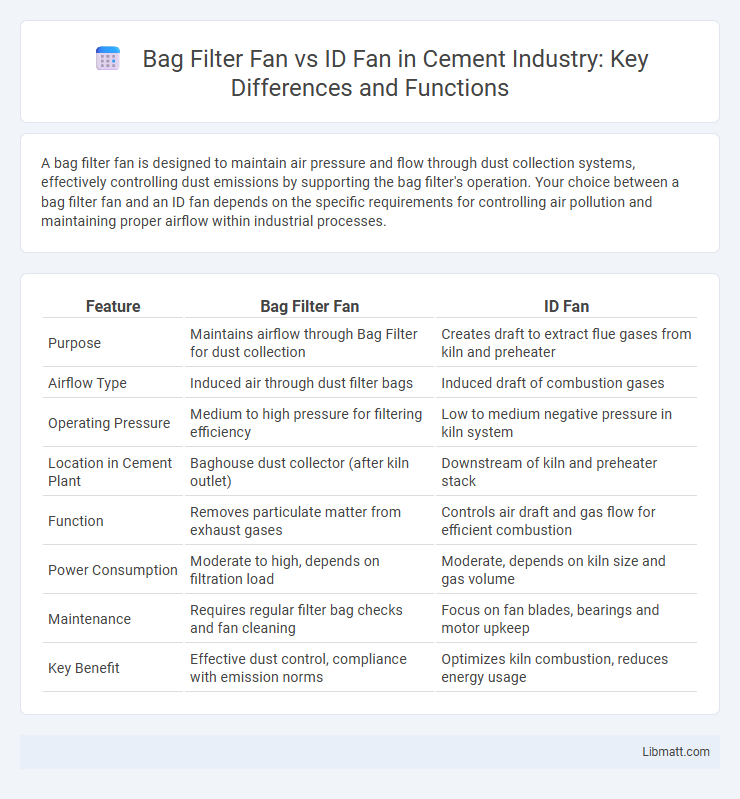
| Feature | Bag Filter Fan | ID Fan |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Maintains airflow through Bag Filter for dust collection | Creates draft to extract flue gases from kiln and preheater |
| Airflow Type | Induced air through dust filter bags | Induced draft of combustion gases |
| Operating Pressure | Medium to high pressure for filtering efficiency | Low to medium negative pressure in kiln system |
| Location in Cement Plant | Baghouse dust collector (after kiln outlet) | Downstream of kiln and preheater stack |
| Function | Removes particulate matter from exhaust gases | Controls air draft and gas flow for efficient combustion |
| Power Consumption | Moderate to high, depends on filtration load | Moderate, depends on kiln size and gas volume |
| Maintenance | Requires regular filter bag checks and fan cleaning | Focus on fan blades, bearings and motor upkeep |
| Key Benefit | Effective dust control, compliance with emission norms | Optimizes kiln combustion, reduces energy usage |
Introduction to Bag Filter Fans and ID Fans
Bag filter fans and ID fans serve distinct roles in industrial air pollution control systems. Bag filter fans are designed to maintain the required pressure and airflow through baghouse filters, ensuring efficient particulate matter removal from industrial emissions. ID fans, or induced draft fans, create negative pressure to draw flue gases from boilers or furnaces through the entire pollution control system, supporting your facility's compliance with emission standards.
Basic Working Principles of Bag Filter Fans
Bag filter fans operate by drawing contaminated air through fabric filter bags, capturing dust particles while allowing clean air to pass through. These fans maintain a consistent airflow and pressure to ensure efficient filtration and prevent filter clogging, enhancing air quality in industrial settings. Your system's performance depends on the proper selection and maintenance of a bag filter fan to optimize dust removal and air circulation.
Key Functions of Induced Draft (ID) Fans
Induced Draft (ID) Fans play a crucial role in maintaining negative pressure within industrial boilers, ensuring efficient combustion by extracting flue gases from the furnace and pushing them through pollution control equipment like bag filters. They optimize airflow to prevent backflow and enhance the performance of air pollution control systems by drawing exhaust gases out of the combustion chamber. Unlike bag filter fans that specifically support dust collection by creating suction in filtration units, ID fans manage the overall flue gas movement critical for boiler efficiency and emission control.
Differences in Design: Bag Filter Fan vs ID Fan
Bag filter fans are designed primarily to maintain the required airflow through dust collection systems, featuring backward-curved or forward-curved blades optimized for low pressure and medium airflow. In contrast, ID (Induced Draft) fans handle higher pressure drops and larger air volumes, often incorporating robust construction with radial or axial blades to manage flue gas extraction in industrial processes. Understanding these design differences helps you select the appropriate fan type based on airflow requirements and system pressure conditions.
Application Areas: Where Each Fan is Used
Bag filter fans are primarily used in industrial dust collection systems to maintain airflow through baghouse filters, ensuring efficient particulate removal in cement plants, power stations, and steel mills. ID fans, or induced draft fans, are mainly applied to extract flue gases from boilers and maintain negative pressure in furnaces across power plants and chemical processing facilities. Understanding the specific airflow requirements of your system will help determine whether a bag filter fan or an ID fan best suits your application needs.
Performance Efficiency: Comparing Bag Filter and ID Fans
Bag filter fans are designed to maintain high static pressure and consistent airflow to effectively capture particulate matter in filtration systems, ensuring optimal bag filter performance. ID fans (Induced Draft fans) primarily handle flue gas extraction by creating negative pressure in combustion systems, prioritizing volume handling over fine filtration efficiency. Performance efficiency varies as bag filter fans optimize for pressure stability and dust collection, while ID fans maximize gas volume movement with moderate pressure support.
Energy Consumption: Bag Filter Fan vs ID Fan
Bag filter fans typically consume more energy than ID fans due to higher static pressure requirements for filtering particulate matter from industrial gases. ID (Induced Draft) fans operate with lower static pressure and focus primarily on maintaining airflow through boilers or furnaces, resulting in comparatively lower energy consumption. Optimizing fan selection based on specific process needs can significantly reduce operational costs and improve energy efficiency in industrial ventilation systems.
Maintenance Requirements for Both Fan Types
Bag filter fans typically require more frequent maintenance due to the need for regular cleaning of filter bags and inspection of fan blades to prevent clogging and ensure efficient airflow. ID fans, used to maintain negative pressure in systems, generally have simpler maintenance routines focused on motor checks, bearing lubrication, and vibration monitoring. Understanding these maintenance requirements helps you optimize fan performance and extend equipment lifespan.
Cost Implications: Initial and Operational Costs
Bag filter fans generally have higher initial costs due to their complex design and requirement for precise airflow control, while ID fans are typically more affordable upfront with simpler construction. Operational costs for bag filter fans increase because of the frequent maintenance and energy consumption linked to filtering dust-laden air, whereas ID fans tend to have lower operational costs since they primarily handle flue gas exhaust with less particulate load. Long-term expenses for bag filter fans include bag replacement and cleaning cycles, making their lifecycle cost notably higher compared to the maintenance-focused expenses of ID fans.
Choosing the Right Fan for Your Industrial Needs
Bag filter fans are designed to provide the precise air volume and pressure required for dust collection systems, ensuring efficient particulate removal and maintaining system integrity. ID (Induced Draft) fans excel in creating negative pressure to draw flue gases through boilers, furnaces, or other industrial processes, supporting combustion efficiency and environmental compliance. Choosing the right fan depends on your need for dust control capacity or gas draft performance, balancing airflow, pressure demands, and operational conditions to optimize industrial ventilation.
Bag filter fan vs ID fan Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com