Ambient curing allows concrete to harden naturally at room temperature, promoting gradual strength gain without the need for external heat sources. Steam curing, by contrast, accelerates the curing process through controlled heat and moisture, enabling faster setting and early strength development ideal for time-sensitive projects.
Table of Comparison
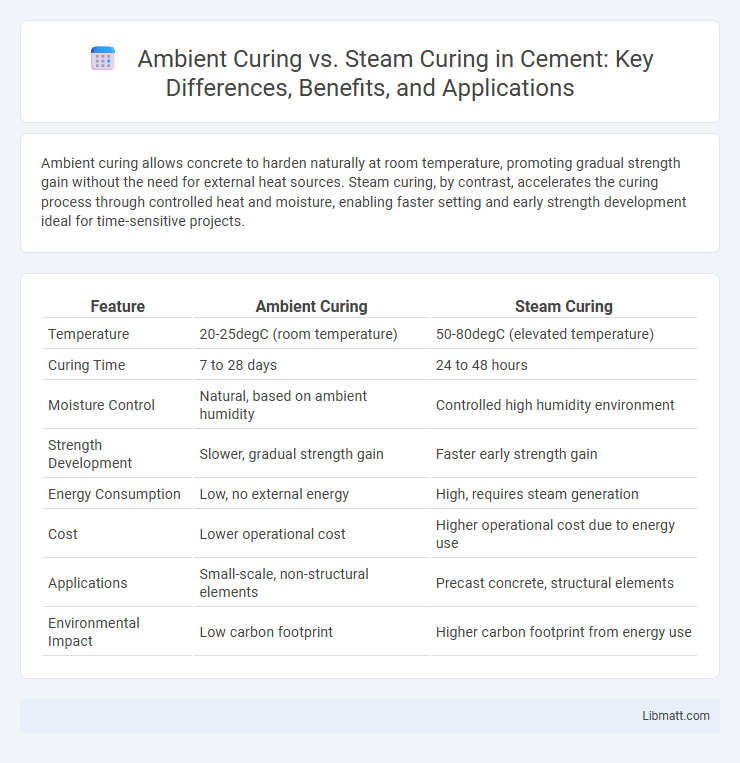
| Feature | Ambient Curing | Steam Curing |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 20-25degC (room temperature) | 50-80degC (elevated temperature) |
| Curing Time | 7 to 28 days | 24 to 48 hours |
| Moisture Control | Natural, based on ambient humidity | Controlled high humidity environment |
| Strength Development | Slower, gradual strength gain | Faster early strength gain |
| Energy Consumption | Low, no external energy | High, requires steam generation |
| Cost | Lower operational cost | Higher operational cost due to energy use |
| Applications | Small-scale, non-structural elements | Precast concrete, structural elements |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint | Higher carbon footprint from energy use |
Introduction to Concrete Curing Methods
Concrete curing methods impact the strength and durability of construction projects significantly. Ambient curing relies on natural temperature and humidity, allowing concrete to harden gradually over time, ideal for non-urgent applications and moderate climates. Steam curing accelerates hydration using controlled heat and moisture, reducing curing time and increasing early strength, making it suitable for precast or high-production environments where faster turnaround is essential.
What Is Ambient Curing?
Ambient curing refers to the process of allowing concrete or other materials to harden and gain strength naturally at room temperature without external heat application. This method relies on the surrounding environmental conditions, typically between 20degC to 25degC (68degF to 77degF), and can take several days to achieve the desired strength. Ambient curing is energy-efficient and suitable for projects where time constraints are less critical compared to steam curing, which accelerates the curing process using elevated temperature and humidity.
Understanding Steam Curing
Steam curing accelerates the concrete hydration process by applying heat and moisture, which enhances early strength development and reduces curing time. This method is especially beneficial in precast concrete production, where faster turnaround is critical for maintaining project schedules. By understanding steam curing, you can optimize curing conditions to achieve improved durability and early load-bearing capacity.
Key Differences Between Ambient and Steam Curing
Ambient curing relies on natural temperature and humidity conditions to harden concrete, resulting in slower strength development and longer curing times. Steam curing accelerates the hydration process using controlled heat and moisture, significantly enhancing early-age strength and reducing curing duration. Key differences include temperature control, curing speed, and impact on concrete microstructure and durability.
Advantages of Ambient Curing
Ambient curing offers significant energy savings by eliminating the need for external heat sources, making it environmentally friendly and cost-effective for concrete curing. This method enhances the long-term strength and durability of concrete through slow, natural hydration processes, reducing the risk of thermal cracking compared to steam curing. Ideal for on-site applications, ambient curing requires minimal equipment, simplifying logistics and enabling continuous curing in various environmental conditions.
Benefits of Steam Curing
Steam curing accelerates concrete strength development by providing a controlled high-temperature, high-humidity environment, which significantly reduces construction time. This method enhances early strength gain, improving project efficiency and allowing faster formwork removal. You benefit from improved durability and consistent quality when using steam curing compared to ambient curing, especially in precast concrete production.
Limitations of Ambient Curing
Ambient curing faces limitations such as slower strength development and extended curing times compared to steam curing. This method depends heavily on environmental conditions, making it less reliable in low temperatures or dry climates. Your concrete may experience reduced durability and increased susceptibility to cracking under ambient curing due to insufficient moisture retention.
Drawbacks of Steam Curing
Steam curing accelerates the concrete hydration process but can lead to drawbacks such as thermal cracking due to rapid temperature changes and excessive moisture loss, which compromises structural integrity. The higher energy consumption and increased operational costs make steam curing less sustainable compared to ambient curing methods. You should consider these factors when selecting a curing technique to ensure long-term durability and cost-efficiency.
Application Scenarios for Each Method
Ambient curing is ideal for projects where consistent temperature and humidity levels can be maintained naturally, such as outdoor construction during mild weather or precast concrete elements stored in controlled environments. Steam curing suits precast concrete production and cold weather conditions, as it accelerates strength development by providing elevated temperatures and moisture in factory or field settings. Your choice depends on project timelines and environmental control, with steam curing favored for rapid strength gain and ambient curing preferred when natural conditions are sufficient.
Choosing the Right Curing Method for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate curing method depends on project requirements, environmental conditions, and desired concrete properties. Ambient curing suits small-scale or outdoor projects with stable temperatures, promoting natural hydration and cost-effectiveness without specialized equipment. Steam curing accelerates strength development in precast or large-scale applications, using controlled heat and humidity to enhance early-age concrete performance but requires careful monitoring to prevent thermal cracking.
Ambient Curing vs Steam Curing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com