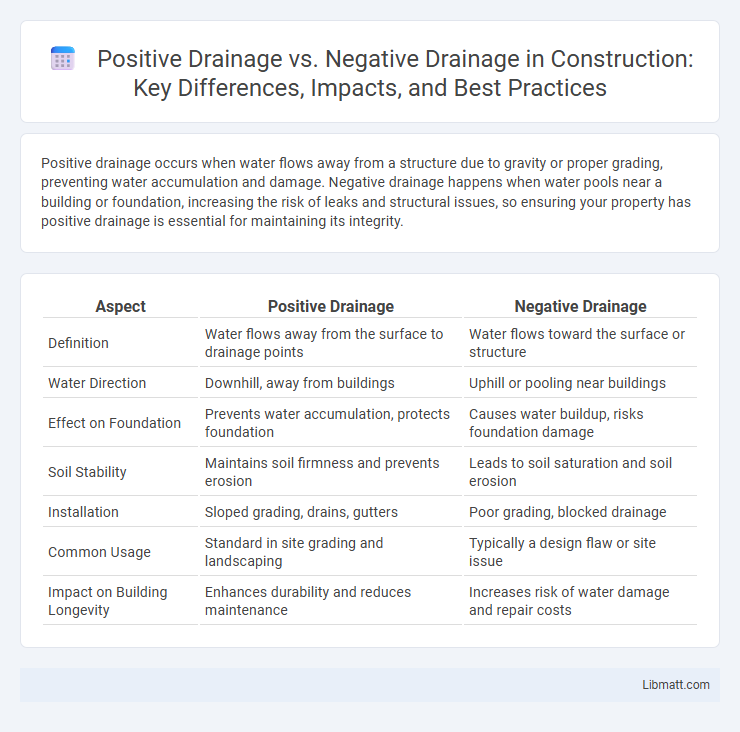
Positive drainage occurs when water flows away from a structure due to gravity or proper grading, preventing water accumulation and damage. Negative drainage happens when water pools near a building or foundation, increasing the risk of leaks and structural issues, so ensuring your property has positive drainage is essential for maintaining its integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Positive Drainage | Negative Drainage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Water flows away from the surface to drainage points | Water flows toward the surface or structure |
| Water Direction | Downhill, away from buildings | Uphill or pooling near buildings |
| Effect on Foundation | Prevents water accumulation, protects foundation | Causes water buildup, risks foundation damage |
| Soil Stability | Maintains soil firmness and prevents erosion | Leads to soil saturation and soil erosion |
| Installation | Sloped grading, drains, gutters | Poor grading, blocked drainage |
| Common Usage | Standard in site grading and landscaping | Typically a design flaw or site issue |
| Impact on Building Longevity | Enhances durability and reduces maintenance | Increases risk of water damage and repair costs |
Understanding Positive and Negative Drainage Systems
Positive drainage systems rely on gravity to direct water away from structures, preventing water accumulation and reducing the risk of foundation damage. Negative drainage occurs when water flows toward a structure, increasing the potential for water infiltration and structural issues. Understanding your property's drainage type helps implement effective solutions to maintain a dry and stable environment.
Key Differences Between Positive and Negative Drainage
Positive drainage actively directs water away from a structure using gravity or mechanical systems, preventing water accumulation and potential damage. Negative drainage occurs when the ground surface slopes toward the structure, causing water to pool near foundations, increasing the risk of seepage and structural issues. Effective landscape grading and drainage design are critical to ensuring positive drainage and avoiding the hazards associated with negative drainage.
Principles of Positive Drainage Design
Positive drainage design ensures water flows away from structures by utilizing gravity and carefully graded surfaces, preventing water accumulation and foundation damage. Techniques include creating slopes of at least 2% away from buildings, installing properly sized drainage pipes, and incorporating catch basins or channels to collect and redirect runoff efficiently. Your landscape or construction project benefits from enhanced longevity and reduced water-related issues by adhering to these core principles.
Applications of Negative Drainage in Construction
Negative drainage is commonly applied in basements and underground structures to prevent water infiltration by directing water away from the foundation using suction systems or vacuum drainage. It is essential in waterproofing applications where traditional gravity-based positive drainage is insufficient, ensuring the structural integrity of your building by managing hydrostatic pressure effectively. This method is especially vital in areas with high water tables or poor soil permeability, reducing potential water damage and maintenance costs.
Advantages of Positive Drainage Solutions
Positive drainage systems direct water away from structures, reducing the risk of foundation damage and soil erosion. These solutions enhance soil stability, prevent water accumulation, and minimize basement flooding by ensuring efficient runoff. Implementing positive drainage improves landscape longevity and protects property value through effective water management.
Limitations of Negative Drainage Systems
Negative drainage systems often face limitations such as increased risk of blockages due to debris accumulation and reliance on mechanical components prone to failure. These systems can be less efficient in preventing water backup during heavy rainfall, potentially causing property damage. Your choice should consider maintenance requirements and the environmental conditions to avoid costly repairs and system inefficiencies.
Impact of Drainage Type on Structural Integrity
Positive drainage effectively directs water away from structures, reducing soil saturation and preventing foundation weakening. Negative drainage causes water accumulation near the foundation, increasing hydrostatic pressure and risking structural damage such as cracks and settlement. Ensuring proper positive drainage around Your property is crucial for maintaining long-term structural integrity and preventing costly repairs.
Choosing the Right Drainage: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right drainage system depends on site topography, soil permeability, and water flow patterns to prevent flooding and structural damage. Positive drainage directs water away from buildings through slopes or drains, ideal for areas with high rainfall or poor soil absorption. Negative drainage, often used in flat or low-lying sites, manages water accumulation by controlled collection points but requires careful design to avoid waterlogging and foundation issues.
Maintenance Requirements for Drainage Systems
Positive drainage systems, designed to direct water away from structures, typically require less frequent maintenance due to efficient water flow that prevents pooling and erosion. Negative drainage systems, which allow water to collect near foundations, demand more intensive upkeep to address issues such as soil saturation, mold growth, and structural damage. Regular inspection and cleaning of gutters, downspouts, and surface grading are essential to maintain optimal functionality in both drainage types.
Future Trends in Drainage Technology
Future trends in drainage technology emphasize advanced materials and smart systems for both positive and negative drainage methods, improving durability and efficiency in water management. Positive drainage systems increasingly incorporate sensors and automated controls to optimize water flow and prevent flooding, while negative drainage innovations focus on enhanced sub-surface techniques to mitigate groundwater buildup. Your property benefits from these cutting-edge solutions, which promise sustainable and cost-effective drainage performance over time.
Positive drainage vs negative drainage Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com