AC motors offer efficient operation and simple design for applications requiring consistent speed, while DC motors provide precise speed control and high starting torque ideal for variable-speed applications. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize energy efficiency and low maintenance (AC) or controllability and torque performance (DC).
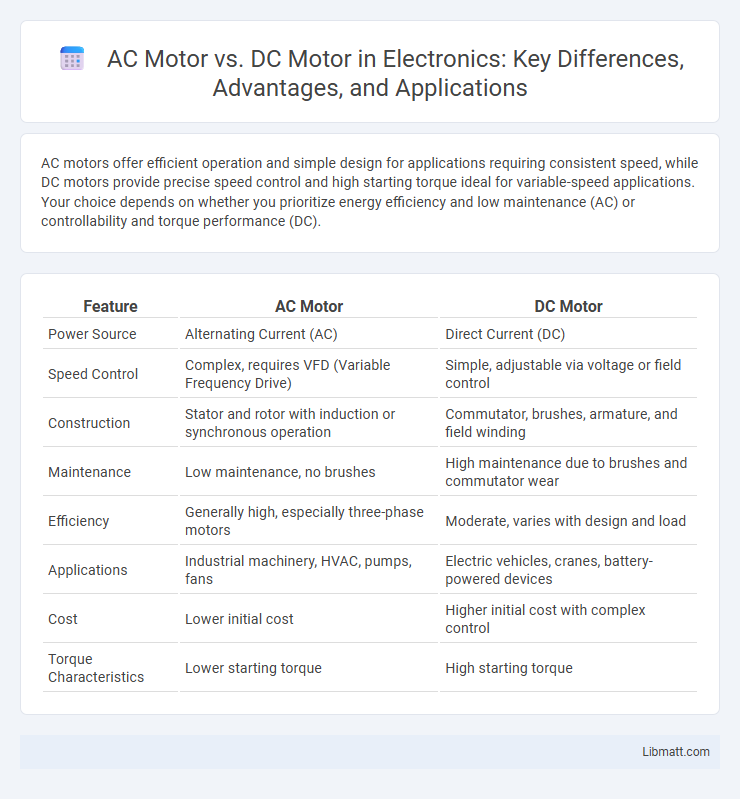
Table of Comparison
| Feature | AC Motor | DC Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) |
| Speed Control | Complex, requires VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) | Simple, adjustable via voltage or field control |
| Construction | Stator and rotor with induction or synchronous operation | Commutator, brushes, armature, and field winding |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, no brushes | High maintenance due to brushes and commutator wear |
| Efficiency | Generally high, especially three-phase motors | Moderate, varies with design and load |
| Applications | Industrial machinery, HVAC, pumps, fans | Electric vehicles, cranes, battery-powered devices |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost with complex control |
| Torque Characteristics | Lower starting torque | High starting torque |
Introduction to AC and DC Motors
AC motors operate using alternating current, which periodically reverses direction, making them ideal for household appliances and industrial machinery requiring consistent power supply. DC motors run on direct current, providing precise speed control and high starting torque, often used in battery-powered devices and electric vehicles. Understanding the fundamental differences between these motors helps you select the right type for your specific application.
Basic Working Principles
AC motors operate by converting alternating current into mechanical energy using a rotating magnetic field generated by the stator, which induces current in the rotor to produce torque. DC motors function by applying direct current through brushes and a commutator to the rotor windings, creating a consistent magnetic field interaction that drives rotation. Understanding these fundamental principles helps you choose the appropriate motor type based on your application's speed control and efficiency requirements.
Key Structural Differences
AC motors feature a stator with windings connected to an alternating current power source, creating a rotating magnetic field, while DC motors have a stator with either permanent magnets or windings supplied by direct current. The rotor in AC motors is typically a squirrel cage or wound type, whereas DC motors use a commutator and brushes to facilitate current flow and torque generation. Understanding these key structural differences helps you select the appropriate motor type based on application requirements like speed control and power efficiency.
Types of AC and DC Motors
AC motors include induction, synchronous, and universal types, each optimized for different industrial applications and speeds. DC motors primarily consist of brushed and brushless variants, offering precise speed control and high starting torque suitable for your specialized machinery. Selection depends on your operational requirements, power source, and efficiency needs.
Efficiency and Performance Comparison
AC motors generally offer higher efficiency and lower maintenance costs due to their simple design and lack of brushes, making them suitable for continuous operation in industrial settings. DC motors provide superior performance in applications requiring precise speed control and high starting torque, benefiting your systems with responsiveness and flexibility. Choosing the right motor depends on balancing efficiency needs with performance demands specific to your application.
Applications in Industry
AC motors dominate industrial applications requiring high power and efficiency, such as conveyor systems, pumps, and HVAC equipment, due to their durability and low maintenance. DC motors are preferred in applications demanding precise speed control and high starting torque, including robotics, electric vehicles, and cranes. Your choice between AC and DC motors depends on the specific performance and control needs of your industrial operation.
Maintenance and Durability
AC motors generally require less maintenance compared to DC motors because they have fewer brushes and commutators prone to wear and tear. DC motors tend to demand more frequent servicing due to brush replacements and commutator cleaning, impacting their overall durability. Understanding these differences helps you select a motor that balances low maintenance needs with long-lasting performance for your specific application.
Cost Analysis and Energy Consumption
AC motors generally have lower initial costs and simpler maintenance due to their robust construction and widespread availability, making them cost-effective for long-term usage. DC motors, while typically more expensive upfront, offer higher efficiency and precise speed control, which can lead to energy savings in applications requiring variable speed operation. Evaluating your specific operational needs and load profiles will help determine whether the lower energy consumption of a DC motor justifies its higher investment compared to the more economical AC motor.
Advantages and Disadvantages
AC motors offer advantages such as simpler construction, lower cost, and higher durability with less maintenance, making them ideal for continuous industrial applications. DC motors provide superior speed control and high starting torque, which benefits applications requiring variable speed and precise control but involve more complex and costly maintenance due to brushes and commutators. The trade-off between AC and DC motors largely depends on application requirements, including control precision, cost constraints, and operational environment.
Future Trends in Motor Technology
Future trends in motor technology emphasize the integration of smart sensors and IoT connectivity to enhance the efficiency and predictive maintenance of AC and DC motors. Advances in materials, such as rare-earth magnets for DC motors and silicon carbide semiconductors for AC motor drives, are driving increases in power density and energy efficiency. The rising demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy systems is accelerating the development of brushless DC motors and high-efficiency AC induction motors with improved control algorithms and reduced carbon footprints.
AC Motor vs DC Motor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com