Polyfuses provide resettable overcurrent protection by increasing resistance when heated, making them ideal for applications requiring automatic recovery, while glass fuses offer single-use protection by melting to break the circuit when current exceeds a specific limit. Your choice depends on whether you need a reusable safeguard or a one-time fail-safe solution for electrical circuits.
Table of Comparison
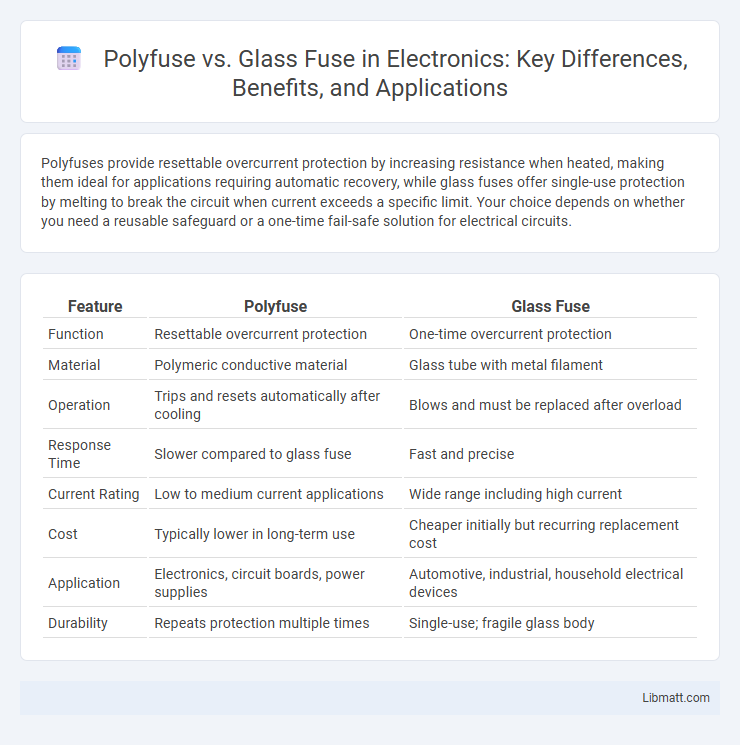
| Feature | Polyfuse | Glass Fuse |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Resettable overcurrent protection | One-time overcurrent protection |
| Material | Polymeric conductive material | Glass tube with metal filament |
| Operation | Trips and resets automatically after cooling | Blows and must be replaced after overload |
| Response Time | Slower compared to glass fuse | Fast and precise |
| Current Rating | Low to medium current applications | Wide range including high current |
| Cost | Typically lower in long-term use | Cheaper initially but recurring replacement cost |
| Application | Electronics, circuit boards, power supplies | Automotive, industrial, household electrical devices |
| Durability | Repeats protection multiple times | Single-use; fragile glass body |
Introduction to Fuses: Polyfuse vs Glass Fuse
Polyfuses and glass fuses serve as critical overcurrent protection devices in electronic circuits, each with distinct operational characteristics. Polyfuses, also known as resettable fuses or PTC fuses, automatically reset after tripping due to increased resistance when overheating, making them ideal for reusable protection. Glass fuses contain a metal wire inside a glass tube that melts and breaks the circuit under overload, requiring replacement after activation, which ensures a one-time, reliable fail-safe response.
How Polyfuses Work
Polyfuses, also known as resettable fuses, protect circuits by increasing their resistance significantly when excessive current flows, effectively limiting current without permanently breaking the circuit. Unlike glass fuses that melt and require replacement after a fault, polyfuses automatically reset once the temperature decreases and normal current levels resume. Your choice of polyfuse enhances circuit durability by providing continuous protection and reducing maintenance costs in electronic devices.
Glass Fuse: Principles and Applications
Glass fuses operate by encasing a thin metal wire within a transparent glass tube, allowing clear visual inspection of the filament's condition during circuit protection. They respond quickly to excessive current by melting the wire, effectively interrupting the electrical flow to prevent damage to electronic components. Commonly employed in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and industrial devices, glass fuses provide reliable overcurrent protection while facilitating easy replacement and troubleshooting.
Key Differences Between Polyfuse and Glass Fuse
Polyfuses, also known as resettable fuses, offer automatic recovery after overheating by resetting once the power normalizes, unlike glass fuses which must be replaced after blowing. Glass fuses provide fast and reliable protection with a clear indication of failure through their transparent casing, making fault diagnostics straightforward. Your choice between the two depends on whether you prioritize reusable protection or visual failure detection in your electrical circuit designs.
Applications Best Suited for Polyfuses
Polyfuses excel in applications requiring resettable overcurrent protection, such as portable electronics, computers, and telecommunication devices where automatic recovery is essential. They are ideal for protecting USB ports, battery packs, and power adapters due to their ability to self-reset after fault conditions without needing replacement. Your choice of polyfuse ensures reliable long-term protection in low-voltage DC circuits with frequent power cycling demands.
When to Choose Glass Fuses
Glass fuses are ideal for applications requiring clear visual inspection of fuse status, making it easier to identify when a fuse has blown. They are best suited for low-voltage circuits or electronic devices with steady current demands due to their reliable and precise interrupting capabilities. Your choice should favor glass fuses when you need quick fault diagnosis and moderate current protection in compact or sensitive electronic assemblies.
Performance and Reliability Comparison
Polyfuses offer superior resettable protection, automatically restoring functionality after overloads without replacement, enhancing device lifespan and reducing maintenance costs. Glass fuses provide reliable, one-time overcurrent protection with precise blowout characteristics, ensuring immediate circuit interruption during faults. Your choice between polyfuse and glass fuse depends on whether you prioritize reusable protection or precise, single-use reliability in your application.
Safety and Resettable Features
Polyfuses provide enhanced safety by automatically resetting after overcurrent conditions, preventing permanent damage and reducing downtime. Glass fuses offer reliable protection but require replacement after a single trip, which can delay repairs and increase maintenance costs. Your choice between polyfuse and glass fuse will impact the ease of resetting and overall safety in electronic applications.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Polyfuses are generally more cost-effective than glass fuses due to their resettable nature, reducing replacement expenses in the long term. Glass fuses tend to have a lower upfront cost but require frequent replacements, which can increase total costs over time. While glass fuses are widely available in various retail outlets, polyfuses may be less commonly stocked, often necessitating specialized suppliers for purchasing.
Polyfuse vs Glass Fuse: Which is Right for Your Project?
Polyfuses offer resettable overcurrent protection by increasing resistance when overloaded, making them ideal for reusable applications where automatic recovery is essential. Glass fuses provide one-time, precise overcurrent protection with clear visual indication of failure, best suited for permanent, high-current circuit safeguarding. Understanding your project's needs for reusability and current characteristics will help determine whether a polyfuse or glass fuse is the optimal choice.
Polyfuse vs Glass Fuse Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com