A soft switch uses software to manage call control and signaling functions, offering greater flexibility and scalability for modern communication networks, while a hard switch relies on dedicated hardware to perform these tasks, ensuring faster processing but less adaptability. Your choice between soft and hard switches depends on the need for customizable features versus the demand for high-speed and reliable performance.
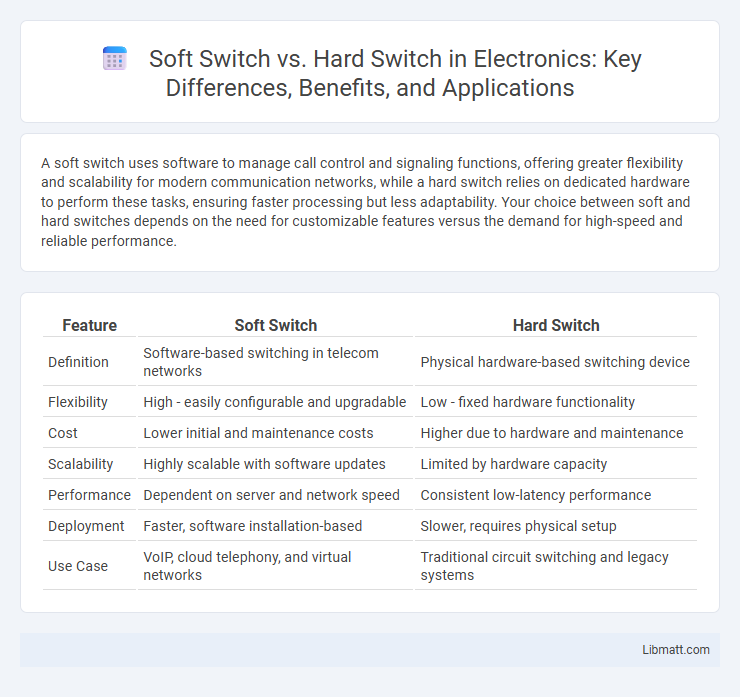
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Soft Switch | Hard Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software-based switching in telecom networks | Physical hardware-based switching device |
| Flexibility | High - easily configurable and upgradable | Low - fixed hardware functionality |
| Cost | Lower initial and maintenance costs | Higher due to hardware and maintenance |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with software updates | Limited by hardware capacity |
| Performance | Dependent on server and network speed | Consistent low-latency performance |
| Deployment | Faster, software installation-based | Slower, requires physical setup |
| Use Case | VoIP, cloud telephony, and virtual networks | Traditional circuit switching and legacy systems |
Introduction to Soft Switches and Hard Switches
Soft switches use software to manage voice and data traffic in IP networks, enabling flexible and scalable telecommunications services. Hard switches rely on dedicated hardware to route calls and data, providing robust performance with lower latency in traditional circuit-switched networks. Understanding the difference between soft switches and hard switches helps you choose the right technology for your communication infrastructure.
Key Definitions: What Are Soft Switches and Hard Switches?
Soft switches are software-based devices that manage voice and multimedia traffic in IP networks, enabling flexible call control and routing without dedicated hardware. Hard switches refer to physical hardware components that perform switching functions at the circuit level within traditional telephony systems. Your choice between soft switches and hard switches depends on the network environment, scalability needs, and desired operational flexibility.
Core Differences Between Soft Switches and Hard Switches
Soft switches operate through software to manage and control voice-over-IP (VoIP) calls by directing signals and managing call routing, while hard switches rely on physical hardware to establish and maintain circuit-switched connections. The core differences lie in flexibility and scalability, with soft switches offering easier updates and integration with IP networks, whereas hard switches provide more stable, dedicated pathways ideal for traditional telephony. Understanding your communication infrastructure needs helps determine whether a soft switch's programmability or a hard switch's robustness best suits your network requirements.
How Soft Switches Work: Technology and Architecture
Soft switches use software-based control mechanisms to manage voice traffic over IP networks, enabling the separation of call control from the underlying hardware. They rely on protocols like SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) and H.323 to establish, maintain, and terminate calls, facilitating seamless integration with various communication services. Your network benefits from the flexibility and scalability of soft switch architecture, which employs Media Gateways to handle media conversion while the software-based call agent manages signaling and call routing.
How Hard Switches Function: Design and Operations
Hard switches operate by directly interrupting and reconnecting electrical circuits through physical contact mechanisms, such as metal contacts that open or close a circuit path. Their design relies on mechanical parts that enable instantaneous disconnection or connection, ensuring reliable signal or power control without electronic mediation. Understanding how hard switches function can help you select the appropriate switch type for applications requiring robust, tactile control and immediate circuit response.
Advantages of Using Soft Switches
Soft switches offer superior flexibility by enabling centralized call control and management over IP networks, reducing the need for hardware-based routing. This results in lower operational costs and easier scalability compared to hard switches. You benefit from enhanced network efficiency and simplified integration with modern communication systems through software-driven configurations.
Benefits and Limitations of Hard Switches
Hard switches provide tactile feedback and precise control, making them ideal for users who prioritize durability and responsiveness in mechanical keyboards. Their limitations include higher noise levels and increased maintenance due to physical contact wear, which can reduce lifespan compared to softer alternatives. You may prefer hard switches if you value robust performance and clear typing feedback despite these constraints.
Use Cases: When to Choose Soft Switch or Hard Switch
Soft switches are ideal for large-scale VoIP networks requiring flexible call control, seamless protocol integration, and centralized management, commonly used in service providers and cloud-based telephony platforms. Hard switches suit scenarios demanding high-performance, low-latency packet switching with dedicated hardware, such as enterprise data centers and real-time communication systems. Choosing between soft and hard switches depends on factors like scalability, cost-efficiency, network complexity, and performance requirements.
Future Trends: Evolution in Switching Technologies
Future trends in switching technologies highlight a shift from traditional hard switches to advanced soft switches that utilize software-defined networking and virtualization for greater flexibility. Soft switches integrate cloud-based control and AI-driven traffic management, enabling efficient scalability and reduced hardware dependency. This evolution supports the development of 5G networks and IoT infrastructure by optimizing network performance and enabling seamless service provisioning.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice Between Soft and Hard Switches
Choosing between soft and hard switches depends on your specific needs for control and reliability in electronic devices. Soft switches offer smooth operation and programmable flexibility, ideal for modern, low-power applications, while hard switches provide robust mechanical feedback and durability suitable for high-demand environments. Understanding your device's requirements ensures you select the switch type that balances performance and user experience effectively.
Soft Switch vs Hard Switch Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com