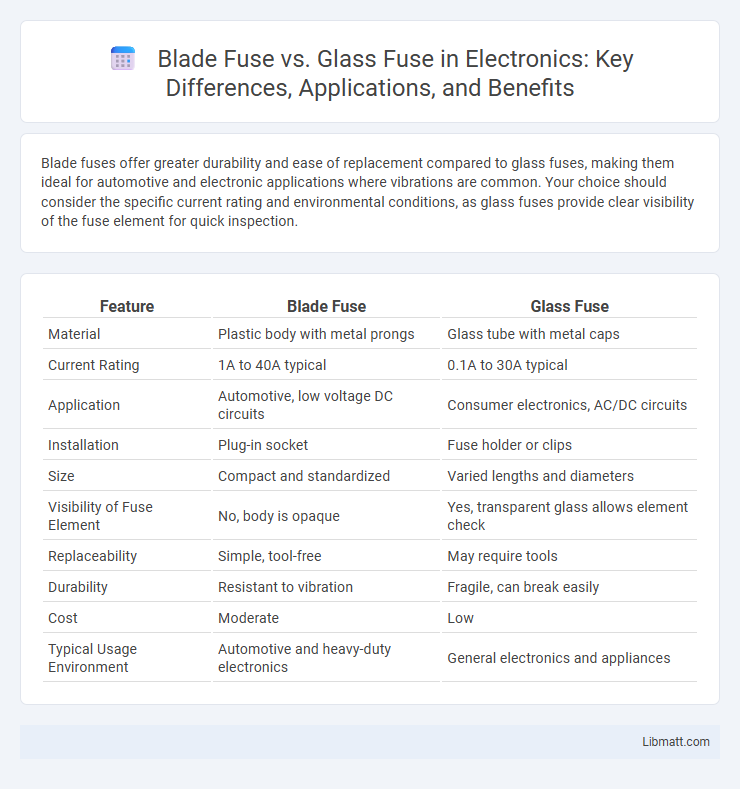
Blade fuses offer greater durability and ease of replacement compared to glass fuses, making them ideal for automotive and electronic applications where vibrations are common. Your choice should consider the specific current rating and environmental conditions, as glass fuses provide clear visibility of the fuse element for quick inspection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Blade Fuse | Glass Fuse |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Plastic body with metal prongs | Glass tube with metal caps |
| Current Rating | 1A to 40A typical | 0.1A to 30A typical |
| Application | Automotive, low voltage DC circuits | Consumer electronics, AC/DC circuits |
| Installation | Plug-in socket | Fuse holder or clips |
| Size | Compact and standardized | Varied lengths and diameters |
| Visibility of Fuse Element | No, body is opaque | Yes, transparent glass allows element check |
| Replaceability | Simple, tool-free | May require tools |
| Durability | Resistant to vibration | Fragile, can break easily |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
| Typical Usage Environment | Automotive and heavy-duty electronics | General electronics and appliances |
Overview of Blade and Glass Fuses
Blade fuses are compact, standardized automotive fuses featuring a plastic body with two metal prongs designed for easy insertion into fuse holders, commonly rated between 1 to 40 amps for vehicle electrical protection. Glass fuses consist of a cylindrical glass tube with metal end caps, offering visual inspection of the filament condition, typically ranging from 0.1 to 30 amps and used in various electronic and electrical devices. Blade fuses provide quicker replacement and better vibration resistance, while glass fuses allow for precise amperage ratings and visibility for fuse status.
Key Differences in Fuse Design
Blade fuses feature a flat, plastic body with two metal prongs designed for easy insertion into fuse boxes, while glass fuses use a cylindrical glass tube encasing a thin metal wire. Blade fuses provide visual identification of fuse ratings through colored plastic housings, enhancing quick replacement, whereas glass fuses allow inspection of the molten wire to determine if the fuse has blown. Your choice between these designs depends on the application requirements, ease of replacement, and space constraints within the electrical system.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Blade fuses offer superior electrical performance with faster response times and better current interruption capabilities, reducing the risk of electrical damage. Glass fuses provide reliable overcurrent protection but generally have slower reaction speeds and limited capacity for high current applications. The robust design of blade fuses ensures enhanced durability and consistent electrical conductivity, making them preferable for modern automotive and electronic systems.
Typical Applications for Each Fuse Type
Blade fuses are commonly used in automotive and marine applications due to their compact size and ease of replacement, making them ideal for protecting low-voltage circuits in cars, trucks, and boats. Glass fuses, often found in older electronics and household appliances, provide reliable protection for small electronic devices and control circuits where precise current ratings and visual inspection of the fuse element are essential. Each fuse type suits specific environments: blade fuses excel in modern, space-constrained settings, while glass fuses are preferred for vintage equipment and applications requiring straightforward fuse status verification.
Installation and Replacement Considerations
Blade fuses feature a plug-in design that allows for quick and tool-free installation, making replacement straightforward and convenient, especially in automotive applications. Glass fuses typically require fuse holders and may necessitate tools for removal and replacement, which can be less convenient in tight spaces or on-the-go repairs. The durability of blade fuses often translates to fewer replacements, while glass fuses provide clear visual inspection of the filament to easily identify blown fuses.
Safety Features and Reliability
Blade fuses offer enhanced safety features with their plastic body design that reduces the risk of accidental electric shock and provides clear visual indication when blown, improving reliability in automotive and electronic applications. Glass fuses, while providing precise protection, lack the insulation properties of blade fuses and are more fragile, making them less reliable in environments subject to vibration and impact. The robust construction and ease of replacement make blade fuses preferable for applications demanding higher safety and dependable circuit protection.
Cost and Availability
Blade fuses generally offer lower cost and wider availability due to their standardized design used in most modern vehicles, making replacements easy and affordable. Glass fuses tend to be slightly more expensive and less common, primarily found in older or specialized electronic devices, limiting their accessibility in mainstream retail outlets. The broad distribution and mass production of blade fuses contribute to their cost-effectiveness and convenient sourcing.
Lifespan and Durability
Blade fuses offer superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to glass fuses due to their robust plastic housing and solid metal strips, which resist vibration and corrosion more effectively. Glass fuses, while providing clear visibility of the fuse element for easy inspection, are more prone to breakage and wear over time, especially in high-vibration environments. The enhanced resilience of blade fuses makes them ideal for automotive and heavy-duty applications where reliability and longevity are critical.
Common Misconceptions and Myths
Blade fuses and glass fuses often get confused, but they serve different purposes and have unique characteristics. Many mistakenly believe that blade fuses are less reliable than glass fuses; however, blade fuses provide quicker replacement and better circuit protection in automotive applications. Your choice between the two should depend on the specific electrical system requirements rather than common myths surrounding their performance or durability.
Choosing the Right Fuse for Your Needs
Blade fuses offer compact size and easy replacement, making them ideal for automotive and electronic applications requiring reliable overcurrent protection. Glass fuses provide precise visual inspection of the filament, suited for high-quality audio equipment and sensitive circuits where clear fuse status is essential. Selecting the right fuse depends on application requirements, space constraints, and the need for visual verification to ensure optimal circuit protection.
Blade fuse vs Glass fuse Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com