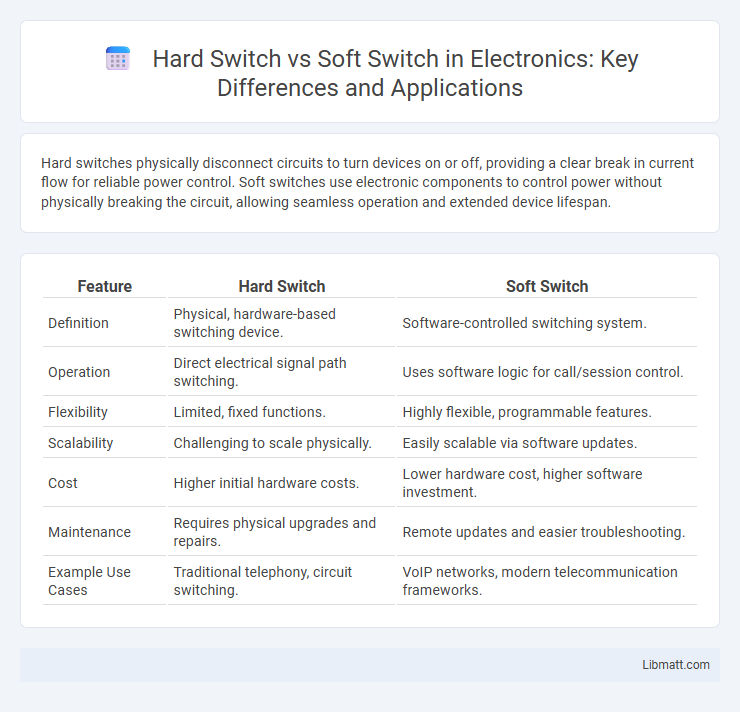
Hard switches physically disconnect circuits to turn devices on or off, providing a clear break in current flow for reliable power control. Soft switches use electronic components to control power without physically breaking the circuit, allowing seamless operation and extended device lifespan.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hard Switch | Soft Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical, hardware-based switching device. | Software-controlled switching system. |
| Operation | Direct electrical signal path switching. | Uses software logic for call/session control. |
| Flexibility | Limited, fixed functions. | Highly flexible, programmable features. |
| Scalability | Challenging to scale physically. | Easily scalable via software updates. |
| Cost | Higher initial hardware costs. | Lower hardware cost, higher software investment. |
| Maintenance | Requires physical upgrades and repairs. | Remote updates and easier troubleshooting. |
| Example Use Cases | Traditional telephony, circuit switching. | VoIP networks, modern telecommunication frameworks. |
Introduction to Hard Switch and Soft Switch
Hard switches are physical network devices that manage call routing by connecting circuits in traditional telephony systems, offering reliable, dedicated pathways for voice communication. Soft switches operate as software-based solutions within IP networks, controlling and directing voice, video, and data traffic through packet switching, enabling more flexible and scalable communication infrastructures. Understanding the differences between these switches allows you to optimize your telephony network for either legacy systems or modern VoIP implementations.
Defining Hard Switch: Key Characteristics
A hard switch refers to a physical network device that manages call routing and connection setup through dedicated hardware components, ensuring high reliability and low latency. Its key characteristics include fixed functionality, real-time processing, and robust performance under heavy telecommunications traffic. Understanding your network requirements will help determine if a hard switch, with its tangible infrastructure and predictable operation, suits your communication system's needs.
Understanding Soft Switch: Core Features
Soft switches utilize software-based technology to control telephony functions, enabling flexible call routing and management across IP networks. Core features include protocol interoperability, scalability for VoIP integration, and centralized control for multimedia communication services. These capabilities distinguish soft switches from traditional hard switches, which rely on hardware for circuit switching and offer limited adaptability.
How Hard Switches Work in Electrical Systems
Hard switches in electrical systems function by physically interrupting or connecting the circuit to control the flow of current, using mechanical components like toggle or push-button switches. When you operate a hard switch, it creates a direct and instantaneous change in the circuit's state, ensuring reliable on/off control without intermediate states. This mechanism is essential for high-power applications where precise and durable switching is required.
The Functionality of Soft Switches in Modern Applications
Soft switches enable seamless call control by managing signaling and media separately, enhancing flexibility in VoIP and cloud-based telephony systems. Their architecture supports rapid protocol integration, scalability, and efficient resource allocation, which improves overall network performance. Your communication infrastructure benefits from reduced hardware dependency and easier maintenance when utilizing soft switch technology.
Key Differences: Hard Switch vs Soft Switch
Hard switches physically disconnect and reconnect circuits, providing clear, immediate changes in network signal paths with minimal latency. Soft switches operate through software to manage call control and routing functions, enabling greater flexibility, scalability, and easier updates within IP-based networks. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize hardware reliability and simplicity or software-driven adaptability and advanced features.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hard Switching
Hard switching offers the advantage of simplicity and lower initial cost due to its straightforward on/off transistor operation, making it suitable for basic power electronics applications. However, it generates higher switching losses and electromagnetic interference (EMI) because the transistor operates under high voltage and current simultaneously during transitions. Your choice depends on balancing efficiency needs against cost and complexity, as hard switching typically leads to reduced energy efficiency and increased thermal stress on components.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Soft Switching Techniques
Soft switching techniques reduce switching losses and electromagnetic interference, enhancing energy efficiency and enabling higher switching frequencies in power converters. These benefits often lead to improved thermal management and increased system reliability in applications like renewable energy and electric vehicles. However, soft switching circuits can be more complex and costly to design and manufacture, potentially increasing the initial investment and requiring advanced control strategies.
Applications and Use Cases for Each Switch Type
Hard switches are commonly used in traditional telephony systems and industrial control applications where reliability and immediate physical disconnection are essential, such as emergency shutoff mechanisms and legacy PBX networks. Soft switches excel in modern VoIP networks, enabling scalable call routing, media gateway control, and integrated communication services in cloud-based telephony and unified communication platforms. Your choice between hard and soft switches should depend on the specific application requirements, including the need for physical hardware control versus the flexibility and programmability of software-based routing.
Choosing Between Hard Switch and Soft Switch
Choosing between a hard switch and a soft switch depends on factors such as network scalability, cost efficiency, and maintenance requirements. Hard switches provide dedicated hardware for high performance and low latency, ideal for large-scale, mission-critical networks, while soft switches offer flexibility through software-based control suitable for dynamic, cloud-based environments. Evaluating network size, traffic load, and integration complexity is essential for selecting the optimal switching technology.
Hard switch vs Soft switch Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com