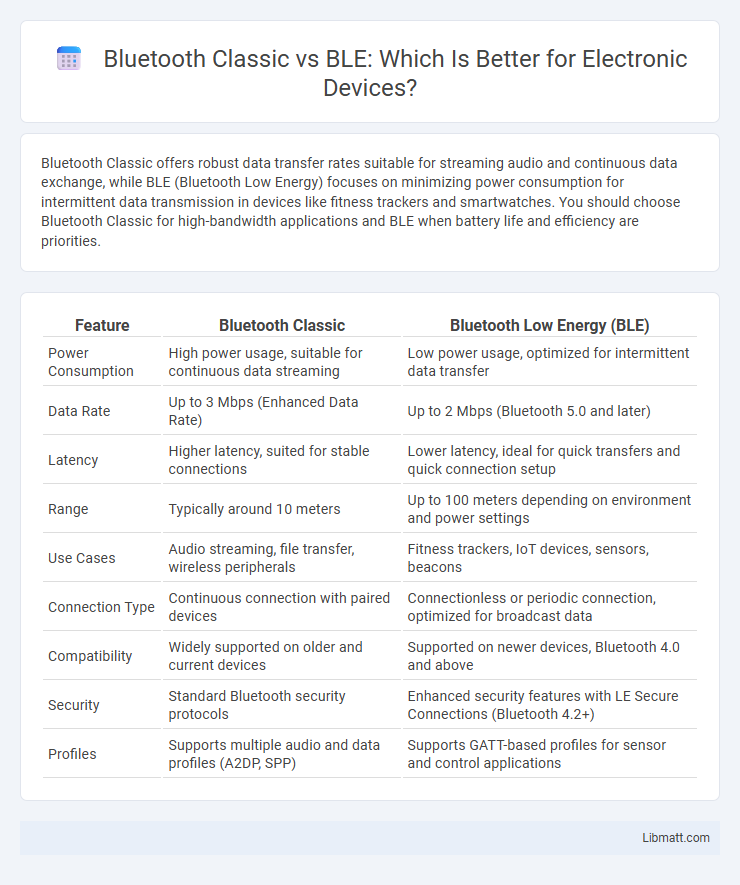
Bluetooth Classic offers robust data transfer rates suitable for streaming audio and continuous data exchange, while BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) focuses on minimizing power consumption for intermittent data transmission in devices like fitness trackers and smartwatches. You should choose Bluetooth Classic for high-bandwidth applications and BLE when battery life and efficiency are priorities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bluetooth Classic | Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) |
|---|---|---|
| Power Consumption | High power usage, suitable for continuous data streaming | Low power usage, optimized for intermittent data transfer |
| Data Rate | Up to 3 Mbps (Enhanced Data Rate) | Up to 2 Mbps (Bluetooth 5.0 and later) |
| Latency | Higher latency, suited for stable connections | Lower latency, ideal for quick transfers and quick connection setup |
| Range | Typically around 10 meters | Up to 100 meters depending on environment and power settings |
| Use Cases | Audio streaming, file transfer, wireless peripherals | Fitness trackers, IoT devices, sensors, beacons |
| Connection Type | Continuous connection with paired devices | Connectionless or periodic connection, optimized for broadcast data |
| Compatibility | Widely supported on older and current devices | Supported on newer devices, Bluetooth 4.0 and above |
| Security | Standard Bluetooth security protocols | Enhanced security features with LE Secure Connections (Bluetooth 4.2+) |
| Profiles | Supports multiple audio and data profiles (A2DP, SPP) | Supports GATT-based profiles for sensor and control applications |
Introduction to Bluetooth Classic and BLE
Bluetooth Classic, also known as Bluetooth BR/EDR (Basic Rate/Enhanced Data Rate), delivers continuous, high-speed wireless communication ideal for audio streaming and file transfer with data rates up to 3 Mbps. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), introduced in Bluetooth 4.0, prioritizes ultra-low power consumption for applications like fitness trackers and smart home devices, enabling long battery life with intermittent data transmission rates up to 1 Mbps. Both technologies coexist within the Bluetooth 5.x standard, allowing devices to optimize connectivity based on power and data requirements.
Core Differences Between Bluetooth Classic and BLE
Bluetooth Classic and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) differ primarily in power consumption and data transfer rates, with Bluetooth Classic supporting continuous streaming and higher bandwidth suitable for audio devices, while BLE is designed for low power consumption and intermittent data transmission ideal for sensors and IoT applications. Bluetooth Classic operates using traditional Bluetooth protocols for connecting devices in a paired and sustained manner, whereas BLE uses a different set of protocols optimized for quick device discovery and short bursts of data exchange. The frequency bands remain the same at 2.4 GHz, but the modulation techniques and connection intervals vary significantly between Bluetooth Classic and BLE to meet their distinct application requirements.
Use Cases for Bluetooth Classic
Bluetooth Classic excels in high-bandwidth applications such as wireless audio streaming, including headphones and car infotainment systems, where continuous data transmission is critical. It is well-suited for data-intensive device connections like file transfers, gaming controllers, and hands-free calling due to its reliable and established communication protocols. The technology supports a wide range of peripherals needing sustained power and steady data rates, making it ideal for legacy devices and complex device-to-device interactions.
Use Cases for Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is ideal for applications requiring low power consumption and intermittent data transmission, such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and medical devices. Its energy-efficient protocol supports complex sensor data and real-time updates, making it suitable for home automation, asset tracking, and proximity marketing. BLE's optimized design extends battery life while maintaining reliable connectivity in Internet of Things (IoT) environments.
Data Transfer Speed Comparison
Bluetooth Classic offers data transfer speeds up to 3 Mbps, making it suitable for continuous, high-bandwidth applications such as audio streaming and file transfers. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), designed for low power consumption, typically supports data rates up to 2 Mbps with Bluetooth 5.0 and later versions, optimized for intermittent bursts of data rather than sustained high-speed transfers. The speed advantage of Bluetooth Classic favors scenarios requiring stable, high-throughput connections, while BLE prioritizes energy efficiency in devices like fitness trackers and smart home sensors.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) significantly outperforms Bluetooth Classic in power consumption and efficiency, consuming up to 90% less energy by utilizing short bursts of data transmission and extended sleep modes. BLE's optimized protocol is designed for intermittent data exchange, making it ideal for battery-operated devices requiring long operational life. Choosing BLE for your application enhances energy efficiency, prolongs battery life, and supports the growing demand for sustainable wireless communication.
Device Compatibility and Ecosystem
Bluetooth Classic supports a broader range of devices, including audio equipment, computers, and automotive systems, making it ideal for high-bandwidth applications within expansive ecosystems. BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) excels in compatibility with wearable devices, smart home gadgets, and IoT sensors, offering extended battery life and efficient data transfer within specialized ecosystems. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize widespread device availability or optimized low-power connectivity for specific, modern applications.
Security Features in Bluetooth Classic vs BLE
Bluetooth Classic employs robust security features such as Secure Simple Pairing (SSP) and encryption standards like E0 stream cipher, which provide strong protection for audio and data transmissions. BLE enhances security with advanced encryption using AES-128 CCM and employs Privacy features like address randomization to prevent tracking, making it ideal for IoT devices requiring efficient and secure communication. Your choice between Bluetooth Classic and BLE should consider these security protocols based on the sensitivity and power requirements of your application.
Application Scenarios: Choosing the Right Technology
Bluetooth Classic suits applications requiring continuous data streaming and higher bandwidth, such as wireless audio devices and hands-free calling systems. BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) excels in scenarios demanding low power consumption and intermittent data transfer, ideal for fitness trackers, smartwatches, and IoT sensors. Your choice depends on whether the priority is sustained connectivity or long battery life for periodic data communication.
Future Trends and Developments in Bluetooth Connectivity
Bluetooth Classic and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) are evolving with advancements like enhanced data rates and improved energy efficiency to meet growing IoT demands. Future developments emphasize seamless integration with 5G networks and ultra-low-latency communication for real-time applications in smart homes and healthcare. Innovations in mesh networking and AI-driven adaptive connectivity are set to optimize performance and expand Bluetooth's role in connected ecosystems.
Bluetooth Classic vs BLE Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com