Conformal coating provides a thin, protective layer that shields PCB components from moisture, dust, and chemicals without significantly altering their size or weight. Potting encapsulates the entire assembly in a solid or gel-like compound, offering more robust mechanical protection and environmental resistance but adding bulk and making repairs more difficult.
Table of Comparison
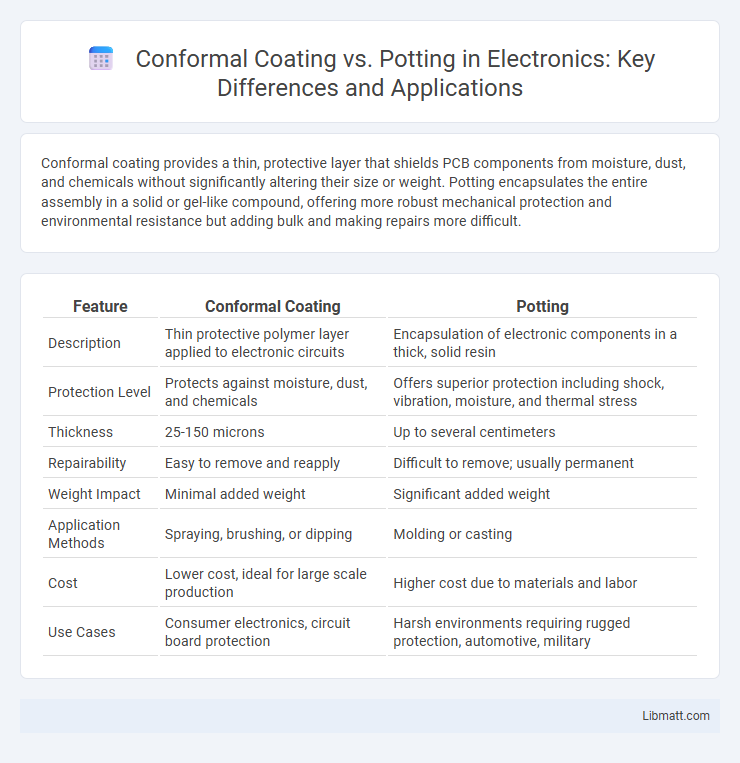
| Feature | Conformal Coating | Potting |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Thin protective polymer layer applied to electronic circuits | Encapsulation of electronic components in a thick, solid resin |
| Protection Level | Protects against moisture, dust, and chemicals | Offers superior protection including shock, vibration, moisture, and thermal stress |
| Thickness | 25-150 microns | Up to several centimeters |
| Repairability | Easy to remove and reapply | Difficult to remove; usually permanent |
| Weight Impact | Minimal added weight | Significant added weight |
| Application Methods | Spraying, brushing, or dipping | Molding or casting |
| Cost | Lower cost, ideal for large scale production | Higher cost due to materials and labor |
| Use Cases | Consumer electronics, circuit board protection | Harsh environments requiring rugged protection, automotive, military |
Introduction to Electronic Protection Methods
Electronic protection methods such as conformal coating and potting safeguard circuit boards from environmental factors like moisture, dust, chemicals, and mechanical stress. Conformal coating provides a thin protective film that maintains board accessibility and heat dissipation, while potting involves encapsulating components in a solid or gel-like compound for robust mechanical and environmental protection. Choosing between conformal coating and potting depends on application requirements, including protection level, thermal management, repairability, and cost.
What is Conformal Coating?
Conformal coating is a thin, protective polymer layer applied to electronic circuit boards to shield them from moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature extremes. This lightweight coating maintains the board's functionality and performance without significantly increasing its size or weight. Your electronic devices benefit from improved reliability and extended lifespan when conformal coating is properly applied.
What is Potting in Electronics?
Potting in electronics involves encapsulating electronic components with a solid or gel-like insulating material to provide protection against moisture, vibration, dust, and chemical exposure. This process enhances durability by filling the entire enclosure, ensuring resistance to mechanical shock and environmental hazards. Potting materials commonly include epoxies, silicones, and polyurethanes, chosen for their thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties.
Key Differences Between Conformal Coating and Potting
Conformal coating provides a thin protective layer that shields electronic components from moisture, dust, and chemicals without significantly adding bulk, making it ideal for space-constrained applications. Potting involves encapsulating entire assemblies in resin, offering superior mechanical support and enhanced protection against vibration and shock but increasing weight and size. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right method for your device's environmental resilience and performance requirements.
Advantages of Conformal Coating
Conformal coating offers excellent protection against moisture, dust, and chemical contaminants while maintaining the circuit board's visibility for inspection and testing. It provides a lightweight, thin barrier that minimizes added bulk and preserves thermal management, improving overall device reliability. Your electronics benefit from enhanced flexibility in design and easier rework compared to potting, making conformal coating a cost-effective solution for protecting sensitive components.
Advantages of Potting
Potting offers superior protection by fully encapsulating electronic components, providing enhanced resistance against moisture, dust, vibration, and mechanical shock. Its robust barrier prevents corrosion and extends the lifespan of sensitive circuitry in harsh environments, making it ideal for industrial, automotive, and outdoor applications. You benefit from improved reliability and durability, especially when devices are exposed to extreme conditions that conformal coatings alone cannot withstand.
Application Methods: Conformal Coating vs Potting
Conformal coating is applied using methods such as brushing, spraying, or dipping, offering a thin and uniform protective layer ideal for delicate electronics. Potting involves encasing components in a thicker resin using mold or manual pouring techniques, providing robust protection against moisture, vibration, and mechanical stress. Both methods vary significantly in thickness and durability, with conformal coating suited for lightweight protection and potting for heavy-duty encapsulation.
Cost Considerations and Material Choices
Conformal coating offers a cost-effective solution for protecting electronic components with thin, lightweight materials like acrylic, silicone, or polyurethane, making it ideal for applications where budget constraints and flexibility are important. Potting involves encapsulating components in robust materials such as epoxy or silicone, providing superior protection against moisture, vibration, and chemical exposure but at a higher cost due to increased material use and labor. When evaluating cost considerations and material choices, your decision should weigh the trade-offs between the level of protection required and budget limitations to ensure optimal performance and durability.
Typical Use Cases and Industry Applications
Conformal coating offers a thin protective layer ideal for electronic assemblies in aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics to prevent moisture, dust, and chemical corrosion. Potting provides a thick encapsulation suited for harsh environments like industrial controls, automotive power modules, and medical devices, ensuring robust mechanical protection and electrical insulation. Your choice depends on the level of protection required and the specific industry standards applicable to the electronic components.
How to Choose: Conformal Coating or Potting?
Choosing between conformal coating and potting depends on your product's environmental exposure and protection requirements. Conformal coating offers a thin, protective layer ideal for moisture, dust, and chemical resistance while maintaining component accessibility and heat dissipation. Potting provides a thick, robust encapsulation that excels in shock, vibration, and extreme environmental protection but limits repairability and heat transfer.
Conformal Coating vs Potting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com