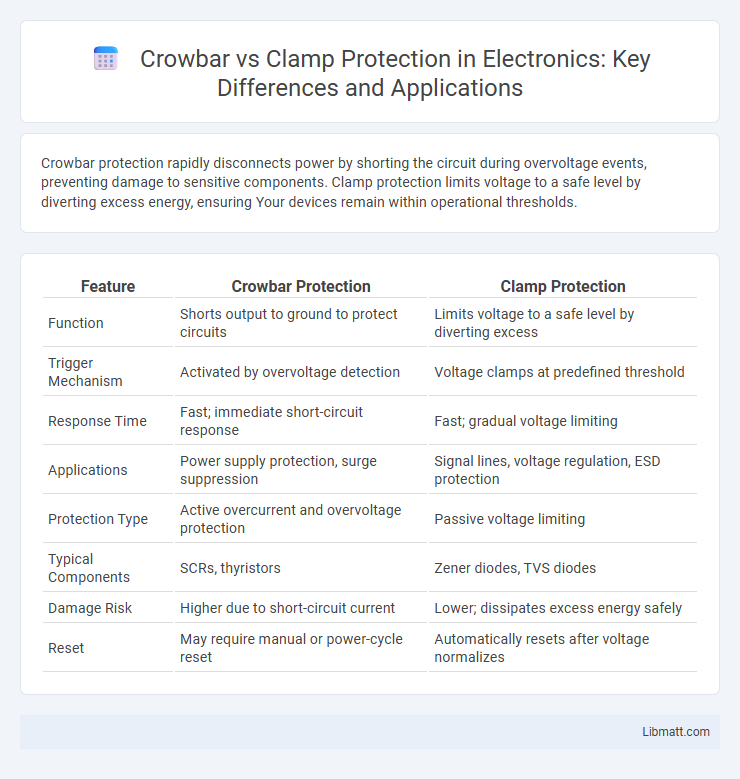
Crowbar protection rapidly disconnects power by shorting the circuit during overvoltage events, preventing damage to sensitive components. Clamp protection limits voltage to a safe level by diverting excess energy, ensuring Your devices remain within operational thresholds.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Crowbar Protection | Clamp Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Shorts output to ground to protect circuits | Limits voltage to a safe level by diverting excess |
| Trigger Mechanism | Activated by overvoltage detection | Voltage clamps at predefined threshold |
| Response Time | Fast; immediate short-circuit response | Fast; gradual voltage limiting |
| Applications | Power supply protection, surge suppression | Signal lines, voltage regulation, ESD protection |
| Protection Type | Active overcurrent and overvoltage protection | Passive voltage limiting |
| Typical Components | SCRs, thyristors | Zener diodes, TVS diodes |
| Damage Risk | Higher due to short-circuit current | Lower; dissipates excess energy safely |
| Reset | May require manual or power-cycle reset | Automatically resets after voltage normalizes |
Introduction to Overcurrent Protection
Overcurrent protection is essential in preventing damage to electrical circuits by interrupting excessive current flow. Crowbar protection rapidly triggers a short circuit to divert current away from sensitive components, ensuring immediate shutdown during fault conditions. Clamp protection, on the other hand, regulates voltage by limiting it to a safe threshold, maintaining circuit integrity and preventing component failure during transient overcurrent events.
What is Crowbar Protection?
Crowbar protection is a circuit safety mechanism designed to prevent overvoltage conditions by rapidly short-circuiting the power supply to ground, effectively clamping the voltage to a safe level. This method instantly protects sensitive electronic components from damage caused by excessive voltage spikes. You can rely on crowbar circuits in power supplies and battery chargers to enhance the durability and safety of your electronic systems.
How Clamp Protection Works
Clamp protection functions by limiting the voltage to a predefined threshold, preventing excessive voltage from reaching sensitive components. It uses components such as Zener diodes or transient voltage suppression (TVS) diodes that conduct current once the voltage exceeds the clamp level, thereby diverting the excess energy away from the protected circuit. This technique ensures voltage spikes are safely absorbed or redirected, minimizing potential damage to electronic devices.
Key Differences Between Crowbar and Clamp Protection
Crowbar protection rapidly shorts the power supply to ground during overvoltage conditions, effectively shutting down the circuit to prevent damage, whereas clamp protection limits voltage by shunting excess current through a voltage-dependent device such as a TVS diode without a complete circuit shutdown. Crowbar circuits provide a more aggressive and definitive response suitable for high-energy transients, while clamp protection offers continuous voltage regulation with minimal disruption, ideal for sensitive electronics. The choice between crowbar and clamp protection depends on factors like response time, energy dissipation, reset capability, and the potential impact on downstream circuitry.
Applications of Crowbar Protection Circuits
Crowbar protection circuits are widely applied in power supply systems to safeguard sensitive electronic components from overvoltage conditions by rapidly shorting the power source to ground. They are commonly used in high-voltage power converters, battery chargers, and voltage regulators to prevent damage caused by voltage spikes or transient surges. Industrial automation equipment and telecommunications hardware also rely on crowbar circuits for reliable overvoltage protection in critical operational environments.
Use Cases for Clamp Protection
Clamp protection is essential in safeguarding sensitive electronic devices from voltage spikes by limiting the voltage to a safe threshold, commonly used in telecommunications and consumer electronics. It is ideal for protecting power supplies, data lines, and circuits sensitive to transient overvoltages caused by lightning or switching surges. Clamp protection devices like transient voltage suppression diodes (TVS) are preferred in scenarios requiring rapid response and low clamping voltage to prevent equipment damage.
Advantages of Crowbar Protection
Crowbar protection offers rapid response and low clamping voltage, effectively safeguarding sensitive electronic components from overvoltage conditions. Its simplicity and robust design ensure reliable operation under high fault currents, minimizing damage during transient events. This method provides superior protection in power supply circuits by quickly diverting excess energy, preventing prolonged exposure to harmful voltages.
Benefits of Clamp Protection
Clamp protection offers precise voltage limiting by diverting excess current safely during transient events, minimizing damage to sensitive electronic components. This method enhances circuit reliability and extends device lifespan by preventing voltage spikes from causing irreversible harm. Its fast response time and consistent clamping voltage ensure effective safeguarding in power supply and signal line applications.
Selecting the Right Overcurrent Protection Method
Selecting the right overcurrent protection method involves evaluating the specific application requirements, where crowbar protection offers rapid response for short-circuit conditions by triggering a low-resistance path to ground, while clamp protection limits voltage spikes without creating a direct short. Crowbar devices are ideal for safeguarding sensitive electronics from catastrophic failure during severe faults, whereas clamp devices provide smoother voltage regulation and are better suited for transient suppression. Your choice depends on the desired balance between protection speed, circuit tolerance, and potential damage mitigation.
Crowbar vs Clamp Protection: Summary and Recommendations
Crowbar protection rapidly shorts the power supply output to ground during overvoltage events, providing fast and robust fault clearance, ideal for safeguarding sensitive electronics in high-voltage spikes. Clamp protection uses voltage clamps, such as Zener diodes or TVS diodes, to limit voltage to safe levels by dissipating excess energy, offering continuous overvoltage protection with less impact on circuit operation. For fast transient suppression in critical systems, crowbar protection is recommended, whereas clamp protection suits applications requiring continuous voltage regulation and energy absorption during moderate surges.
Crowbar vs Clamp protection Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com