ESD diodes provide fast, low-capacitance clamping to protect sensitive electronics from electrostatic discharge events, making them ideal for high-speed data lines. TVS arrays offer robust protection against higher-energy transient voltage spikes with multiple channels in a single package, enhancing Your circuit's resilience against both ESD and lightning-induced surges.
Table of Comparison
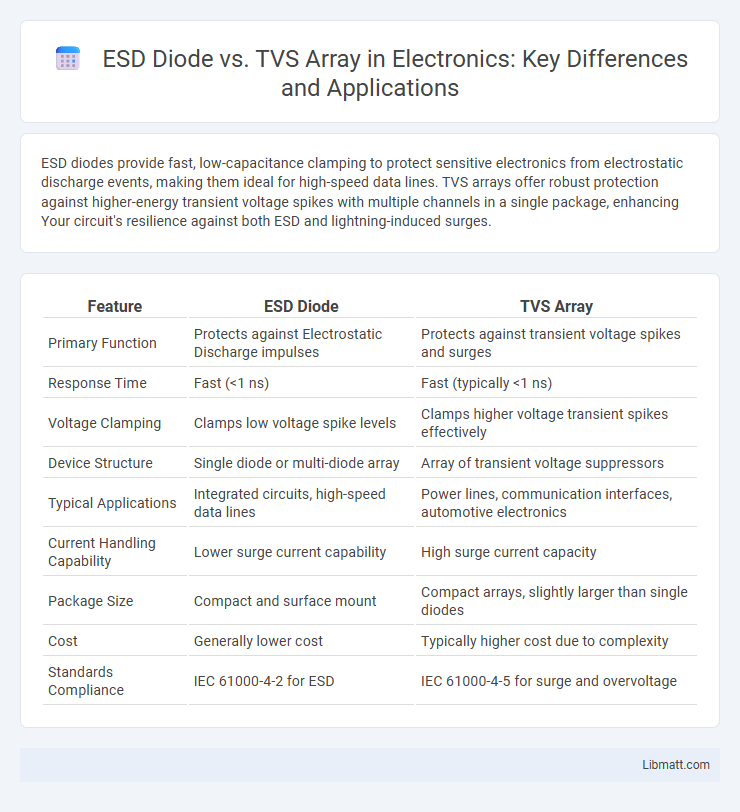
| Feature | ESD Diode | TVS Array |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Protects against Electrostatic Discharge impulses | Protects against transient voltage spikes and surges |
| Response Time | Fast (<1 ns) | Fast (typically <1 ns) |
| Voltage Clamping | Clamps low voltage spike levels | Clamps higher voltage transient spikes effectively |
| Device Structure | Single diode or multi-diode array | Array of transient voltage suppressors |
| Typical Applications | Integrated circuits, high-speed data lines | Power lines, communication interfaces, automotive electronics |
| Current Handling Capability | Lower surge current capability | High surge current capacity |
| Package Size | Compact and surface mount | Compact arrays, slightly larger than single diodes |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost due to complexity |
| Standards Compliance | IEC 61000-4-2 for ESD | IEC 61000-4-5 for surge and overvoltage |
Overview of ESD Diodes and TVS Arrays
ESD diodes and TVS arrays protect sensitive electronic components from voltage spikes, but they differ in design and application. ESD diodes are compact, fast-response devices ideal for clamping electrostatic discharge events in low-voltage circuits. TVS arrays offer multi-line protection with higher energy absorption, making them suitable for complex systems requiring robust transient voltage suppression.
Working Principle of ESD Diodes
ESD diodes operate by clamping voltage spikes to safe levels through a fast-responding semiconductor junction that diverts excessive electrostatic discharge current away from sensitive components. These diodes remain non-conductive during normal operation and instantly become conductive when the voltage exceeds a predefined threshold, providing effective protection against transient ESD events. The rapid response time and low clamping voltage make ESD diodes ideal for safeguarding integrated circuits in static discharge scenarios.
Working Principle of TVS Arrays
TVS arrays protect circuits by clamping voltage spikes during transient events, rapidly diverting excess current away from sensitive components. Unlike simple ESD diodes that discharge electrostatic charges in a single path, TVS arrays consist of multiple diodes arranged to safeguard multiple lines simultaneously. Your circuit benefits from TVS arrays through enhanced multi-channel protection and fast response times during electrostatic discharge or surge events.
Key Differences Between ESD Diodes and TVS Arrays
ESD diodes primarily protect sensitive electronic components from electrostatic discharge by clamping voltage spikes quickly at low energy levels, while TVS arrays safeguard circuits against higher-energy transient voltage surges, such as those caused by lightning or switching events. ESD diodes typically have faster response times and lower capacitance, making them ideal for protecting data lines and low-voltage interfaces, whereas TVS arrays offer broader, multi-channel protection with higher power handling capabilities. The choice between ESD diodes and TVS arrays depends on the specific application requirements including voltage thresholds, response speed, energy absorption, and the nature of the transient threats.
Application Scenarios for ESD Diodes
ESD diodes are crucial in protecting sensitive electronic circuits from electrostatic discharge in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and portable devices where fast response times are essential. These diodes are typically integrated at the input/output ports to clamp voltage spikes and prevent damage to semiconductors during static discharge events. Your device benefits from ESD diodes when reliability is paramount in low-voltage, high-frequency applications requiring precise transient voltage suppression.
Application Scenarios for TVS Arrays
TVS arrays are extensively used in high-speed data lines and multi-channel interfaces, providing robust transient voltage suppression to protect sensitive electronic components from voltage spikes and electrostatic discharge events. Ideal application scenarios include USB ports, Ethernet lines, and HDMI interfaces where simultaneous protection of multiple lines is essential. These arrays offer superior clamping performance and rapid response times, ensuring reliable safeguarding in complex, multi-line circuit configurations.
Performance Comparison: Speed, Clamping, and Capacitance
ESD diodes offer fast response times and low capacitance, making them ideal for protecting sensitive high-speed data lines, while TVS arrays typically provide higher clamping voltages and greater energy absorption capacity for robust surge protection. The clamping performance of TVS arrays is superior under high transient conditions, but ESD diodes excel in minimizing signal distortion due to their lower capacitance values. Choosing the right device depends on your circuit's sensitivity to speed and voltage spikes, with ESD diodes favored for low-capacitance, rapid response protection and TVS arrays suited for heavy-duty voltage clamping.
Selection Criteria: When to Use ESD Diode vs TVS Array
Choosing between an ESD diode and a TVS array depends on the voltage transient protection requirements and circuit sensitivity. ESD diodes offer fast response times and low capacitance, making them ideal for protecting high-speed data lines from electrostatic discharge events. TVS arrays provide robust protection against higher energy surges and are suitable when multiple lines need simultaneous safeguarding or when transient voltage spikes are more severe.
Design Considerations and Integration Tips
When choosing between an ESD diode and a TVS array, consider the specific voltage clamping levels and response times critical to your circuit's protection requirements. ESD diodes offer low capacitance and fast response, making them ideal for high-speed signal lines, while TVS arrays provide multi-line protection with higher energy absorption suited for power circuits. For seamless integration, carefully evaluate your PCB layout to minimize parasitic inductance and ensure proper grounding, as these factors significantly impact the effectiveness of both protection devices in your design.
Future Trends in ESD and TVS Protection Technologies
Future trends in ESD diode and TVS array technologies emphasize enhanced integration with semiconductor processes to support smaller, more sensitive devices while maintaining robust surge protection. Advances in material science and device architecture enable faster response times and lower capacitance, critical for high-speed digital circuits and RF applications. Your choice of protection technology will increasingly depend on the balance between space constraints, energy absorption requirements, and the need for minimal signal distortion in next-generation electronics.
ESD diode vs TVS array Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com