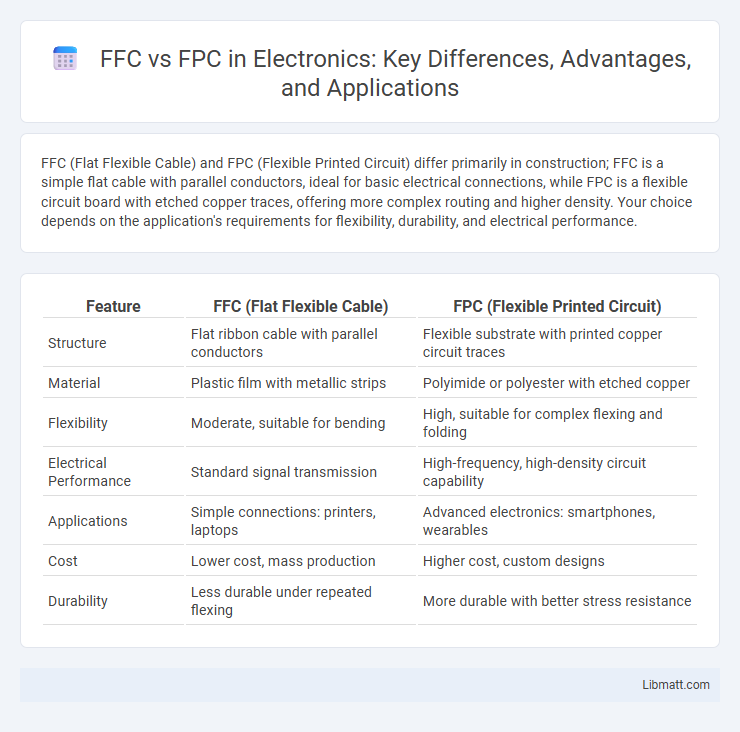
FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) and FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) differ primarily in construction; FFC is a simple flat cable with parallel conductors, ideal for basic electrical connections, while FPC is a flexible circuit board with etched copper traces, offering more complex routing and higher density. Your choice depends on the application's requirements for flexibility, durability, and electrical performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) | FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Flat ribbon cable with parallel conductors | Flexible substrate with printed copper circuit traces |
| Material | Plastic film with metallic strips | Polyimide or polyester with etched copper |
| Flexibility | Moderate, suitable for bending | High, suitable for complex flexing and folding |
| Electrical Performance | Standard signal transmission | High-frequency, high-density circuit capability |
| Applications | Simple connections: printers, laptops | Advanced electronics: smartphones, wearables |
| Cost | Lower cost, mass production | Higher cost, custom designs |
| Durability | Less durable under repeated flexing | More durable with better stress resistance |
Introduction to FFC and FPC
Flat Flexible Cable (FFC) consists of thin, flexible flat conductors laminated between insulating plastic films, widely used for compact electronic connections due to their lightweight and space-saving design. Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) is a printed circuit board made of flexible polymer substrates that supports both conductive pathways and electronic components, enabling complex circuit designs in curved or tight spaces. Both FFC and FPC are essential in modern electronics for enhancing flexibility and reducing assembly size, yet FPC offers greater durability and design versatility compared to the simpler FFC structure.
What is FFC (Flexible Flat Cable)?
FFC (Flexible Flat Cable) is a type of electrical cable characterized by a flat and flexible plastic film base with multiple flat conductors bonded inside. Commonly used in compact electronic devices, FFCs provide reliable, space-saving cable solutions for internal connections in laptops, printers, and cameras. Their lightweight and flexible nature allows easy bending without damaging the conductors, enhancing durability in dynamic applications.
What is FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit)?
FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) is a type of electronic circuit that uses flexible plastic substrates such as polyimide or polyester, enabling the circuit to bend and flex without damage. It is commonly used in compact electronic devices like smartphones, laptops, and wearable technology due to its lightweight and space-saving properties. Unlike FFC (Flat Flexible Cable), which consists of parallel flat conductors, FPC integrates both the conductive traces and the insulating layers, providing enhanced durability and design versatility.
Key Differences Between FFC and FPC
FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) consists of flat, ribbon-like conductors primarily used for simple, low-profile connections, featuring a solid plastic insulation. FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) integrates printed circuitry on a flexible substrate, allowing for complex, multi-layered circuits with enhanced durability and higher density interconnections. Understanding these key differences helps you select the right cable type for applications requiring either straightforward connectivity or advanced flexibility with intricate circuit designs.
Design and Structure Comparison
FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) features a simple, flat design with parallel conductors laminated between thin plastic layers, making it ideal for compact electronic devices with limited space. FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) offers a more complex and customizable structure that includes flexible substrates like polyimide, allowing for intricate circuit patterns and multiple layers, enhancing flexibility and durability. This structural versatility enables FPCs to accommodate varying electrical and mechanical requirements beyond the basic connectivity provided by FFCs.
Application Areas of FFC
FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) excels in compact electronic applications such as laptops, cameras, and smartphones due to its thin profile and flexibility. You can find FFC widely used in printers, LCD displays, and other consumer electronics where lightweight and space-saving connections are essential. Its adaptability to high-density and confined spaces makes it ideal for precision devices requiring reliable electrical connections.
Application Areas of FPC
Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC) is extensively used in compact electronic devices like smartphones, laptops, and wearable technology due to its lightweight and high-density interconnection capabilities. FPC's adaptability allows integration into automotive systems, medical devices, and aerospace applications where complex circuitry and space-saving solutions are critical. The superior flexibility and reliability of FPCs make them essential in consumer electronics, industrial equipment, and advanced communication devices.
Advantages and Limitations of FFC
Flexible Flat Cables (FFC) offer significant advantages such as high flexibility, compact design, and ease of mass termination, making them ideal for space-constrained applications like laptops and smartphones. Their thin profile reduces weight and improves durability against repeated bending, but they have limitations including lower current capacity and reduced shielding compared to Flexible Printed Circuits (FPC). FFCs also face challenges with signal integrity in high-frequency applications and generally lack the ability to incorporate complex circuitry or multiple layers found in FPCs.
Advantages and Limitations of FPC
FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) offers significant advantages such as high flexibility, lightweight design, and the ability to fit into compact or irregular spaces, making it ideal for modern electronics like smartphones and wearable devices. Limitations of FPC include its higher cost compared to FFC (Flat Flexible Cable), sensitivity to mechanical stress, and potential difficulties in repair or replacement due to delicate materials. Your choice of FPC should consider these factors to maximize performance and durability in your electronic applications.
How to Choose Between FFC and FPC
Choosing between FFC (Flat Flexible Cable) and FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) depends on specific application requirements such as space constraints, flexibility, and signal integrity. FFCs are more suitable for straightforward, low-cost connections with limited bending, while FPCs offer greater design versatility, higher density, and better durability for complex, compact electronic devices. Evaluating factors like electrical performance, mechanical robustness, and manufacturing costs helps determine the optimal choice for interconnect solutions.
FFC vs FPC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com