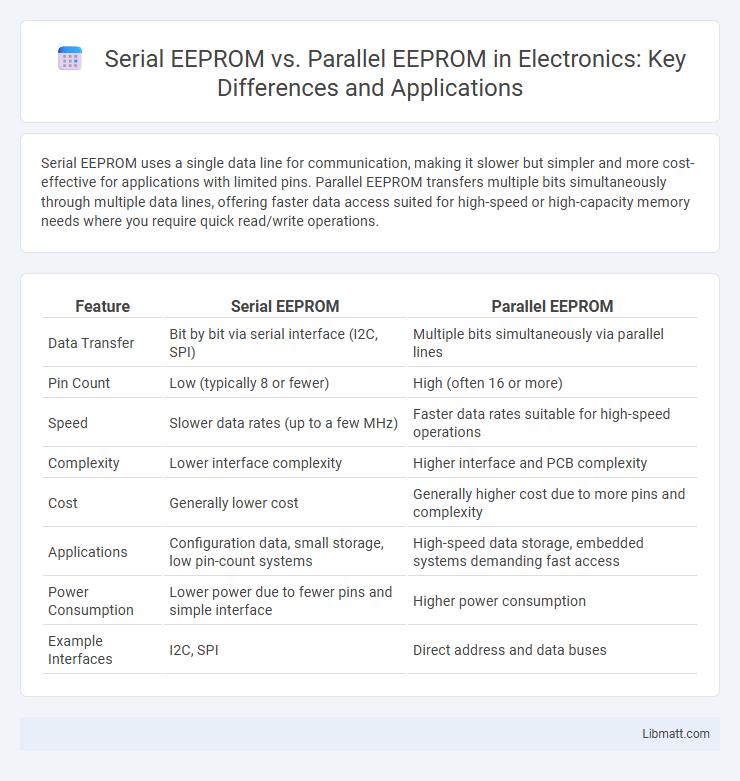
Serial EEPROM uses a single data line for communication, making it slower but simpler and more cost-effective for applications with limited pins. Parallel EEPROM transfers multiple bits simultaneously through multiple data lines, offering faster data access suited for high-speed or high-capacity memory needs where you require quick read/write operations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Serial EEPROM | Parallel EEPROM |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transfer | Bit by bit via serial interface (I2C, SPI) | Multiple bits simultaneously via parallel lines |
| Pin Count | Low (typically 8 or fewer) | High (often 16 or more) |
| Speed | Slower data rates (up to a few MHz) | Faster data rates suitable for high-speed operations |
| Complexity | Lower interface complexity | Higher interface and PCB complexity |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Generally higher cost due to more pins and complexity |
| Applications | Configuration data, small storage, low pin-count systems | High-speed data storage, embedded systems demanding fast access |
| Power Consumption | Lower power due to fewer pins and simple interface | Higher power consumption |
| Example Interfaces | I2C, SPI | Direct address and data buses |
Introduction to EEPROM Technology
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory) technology enables non-volatile data storage that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. Serial EEPROM interfaces utilize a single data line for communication, offering compact design and simplicity ideal for low-pin-count applications, while Parallel EEPROMs employ multiple data lines to transfer bytes simultaneously, providing faster access speeds suitable for high-performance systems. Both types leverage floating-gate transistors to retain data without power, with their interface choice impacting system architecture, speed, and complexity.
What is Serial EEPROM?
Serial EEPROM is a non-volatile memory device that stores data using a serial communication interface, typically I2C or SPI, allowing data to be read or written one bit or byte at a time. It offers a compact pin configuration and lower power consumption compared to parallel EEPROM, making it ideal for applications with limited I/O pins and space constraints. Serial EEPROM is commonly used in embedded systems, microcontrollers, and consumer electronics for storing configuration settings and calibration data.
What is Parallel EEPROM?
Parallel EEPROM is a type of Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory that allows simultaneous access to multiple data bits via several data lines, enhancing read and write speeds compared to Serial EEPROM. It is commonly used in applications requiring fast data transfer and high throughput, such as embedded systems and industrial controls. Your choice between parallel and serial EEPROM will depend on the speed requirements and hardware interface complexity of your project.
Key Differences Between Serial and Parallel EEPROM
Serial EEPROM transfers data bit by bit using a single data line, which results in slower access speeds but requires fewer pins and simpler circuit design compared to Parallel EEPROM. Parallel EEPROM utilizes multiple data lines simultaneously, allowing faster read and write operations suited for applications needing high-speed data access but demands more pins and complex hardware integration. Key differences include interface complexity, access speed, pin count, and power consumption, making Serial EEPROM ideal for space-constrained, low-speed tasks while Parallel EEPROM fits high-speed, high-throughput requirements.
Advantages of Serial EEPROM
Serial EEPROM offers significant advantages such as reduced pin count, which simplifies circuit design and lowers manufacturing costs. Its serial interface allows for smaller package sizes and easier integration with microcontrollers, enhancing system compactness. Additionally, Serial EEPROM typically consumes less power, making it ideal for battery-operated and portable devices.
Advantages of Parallel EEPROM
Parallel EEPROM offers faster data access and higher transfer rates compared to Serial EEPROM, making it ideal for applications requiring rapid read and write operations. It allows simultaneous data transfer on multiple lines, reducing latency and improving overall system performance. Your choice of Parallel EEPROM can enhance efficiency in embedded systems demanding low-latency memory access.
Applications and Use Cases
Serial EEPROM is widely used in applications requiring compact, low-pin-count memory solutions such as configuration storage in embedded systems, consumer electronics, and IoT devices. Parallel EEPROM serves well in high-speed data access scenarios like microprocessor memory systems, industrial control, and legacy hardware where rapid byte-wide access is critical. Selection depends on trade-offs between interface complexity, speed, and board space requirements in specific use cases.
Speed and Performance Comparison
Serial EEPROM offers slower data transfer rates compared to Parallel EEPROM due to its bit-by-bit communication through a single data line, typically operating at speeds up to a few MHz. Parallel EEPROM provides significantly faster read and write performance by transferring multiple bits simultaneously across multiple data lines, making it suitable for applications requiring high-speed data access. Your choice depends on the specific speed and performance requirements of your embedded system or device.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Serial EEPROM generally offers lower cost and higher availability due to simpler design and widespread adoption in consumer electronics, making it ideal for cost-sensitive applications. Parallel EEPROM, while typically more expensive, provides faster data access speeds but is less common in modern markets, resulting in limited availability. Your choice between the two should weigh budget constraints against performance requirements and component accessibility.
Choosing the Right EEPROM for Your Project
Serial EEPROM offers simpler wiring and reduced pin count, making it ideal for space-constrained projects requiring moderate data transfer speeds. Parallel EEPROM delivers faster data access and higher throughput, suitable for applications demanding rapid memory operations and greater bandwidth. Your choice depends on balancing complexity, speed requirements, and available hardware interface options.
Serial EEPROM vs Parallel EEPROM Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com