Power MOSFETs are designed for high current and voltage switching applications, offering low on-resistance and high efficiency in power management circuits. Logic level MOSFETs are optimized to fully switch on at lower gate voltages compatible with standard microcontroller logic levels, making Your circuit design more efficient without requiring additional gate drive components.
Table of Comparison
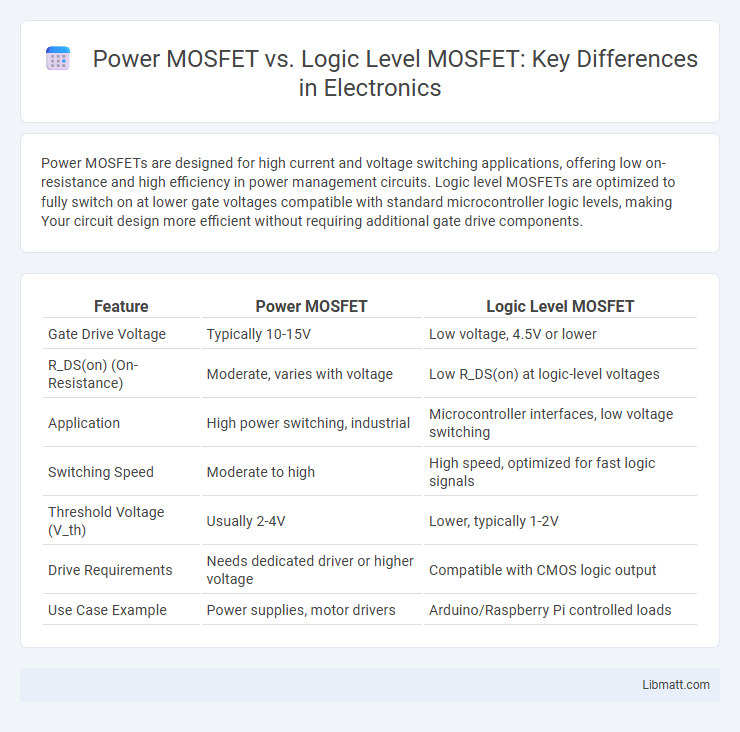
| Feature | Power MOSFET | Logic Level MOSFET |
|---|---|---|
| Gate Drive Voltage | Typically 10-15V | Low voltage, 4.5V or lower |
| R_DS(on) (On-Resistance) | Moderate, varies with voltage | Low R_DS(on) at logic-level voltages |
| Application | High power switching, industrial | Microcontroller interfaces, low voltage switching |
| Switching Speed | Moderate to high | High speed, optimized for fast logic signals |
| Threshold Voltage (V_th) | Usually 2-4V | Lower, typically 1-2V |
| Drive Requirements | Needs dedicated driver or higher voltage | Compatible with CMOS logic output |
| Use Case Example | Power supplies, motor drivers | Arduino/Raspberry Pi controlled loads |
Introduction to Power MOSFETs and Logic Level MOSFETs
Power MOSFETs are high-voltage transistors designed for efficient switching and power management in applications like motor drives and power supplies, offering low on-resistance and fast switching times. Logic Level MOSFETs are specially engineered to fully switch on at lower gate voltages compatible with microcontrollers and logic circuits, enabling direct drive from low-voltage logic signals. Choosing between a Power MOSFET and a Logic Level MOSFET depends on your circuit's voltage requirements and switching characteristics.
Key Differences Between Power and Logic Level MOSFETs
Power MOSFETs offer high voltage and current handling capabilities ideal for power management, while Logic Level MOSFETs are designed to switch efficiently at lower gate drive voltages compatible with microcontrollers. You benefit from using Logic Level MOSFETs in low-voltage digital circuits where reduced gate threshold voltage enhances performance and energy efficiency. The key difference lies in the gate drive voltage requirement and switching characteristics, with Power MOSFETs prioritizing robustness and Logic Level MOSFETs optimizing signal-level compatibility.
Gate Drive Voltage Requirements
Power MOSFETs typically require higher gate drive voltages, often around 10 to 15 volts, to achieve low on-resistance and efficient conduction. Logic Level MOSFETs are designed to fully turn on at lower gate voltages, usually between 4.5 to 5 volts, enabling compatibility with standard logic circuits and microcontrollers. Choosing the correct MOSFET depends on the available gate drive voltage to ensure optimal switching performance and minimal power loss.
Applications of Power MOSFETs
Power MOSFETs are widely used in high-current and high-voltage applications such as power supplies, motor controllers, and RF amplifiers, where efficient switching and low conduction loss are critical. Unlike logic level MOSFETs designed for direct interfacing with microcontrollers, Power MOSFETs handle substantial power loads in industrial and automotive environments. Your projects demanding robust power management benefit from the superior thermal performance and switching speed of Power MOSFETs.
Applications of Logic Level MOSFETs
Logic level MOSFETs are specifically designed to operate efficiently with low gate voltages commonly found in microcontroller and digital logic circuits, making them ideal for switching applications in battery-powered devices and portable electronics. Their ability to fully turn on at gate voltages as low as 4.5V ensures reliable performance in circuits where power efficiency and fast switching are critical. You can leverage logic level MOSFETs for precise control in motor drivers, power management modules, and voltage regulators within embedded systems.
Performance Characteristics and Efficiency
Power MOSFETs offer high voltage and current handling capabilities with low on-resistance (R_DS(on)), making them suitable for high-power applications, but they require higher gate drive voltages, typically around 10-15V, to fully switch on. Logic Level MOSFETs are optimized for low gate voltages, usually around 4.5V, ensuring efficient switching in low-voltage logic circuits while maintaining moderate R_DS(on) for lower power losses. The efficiency of Power MOSFETs excels in heavy-duty power management, whereas Logic Level MOSFETs deliver optimized performance in low-voltage systems by reducing gate drive power consumption and enabling faster switching speeds.
Selection Criteria for Your Project
When selecting between a Power MOSFET and a Logic Level MOSFET for your project, consider the gate drive voltage requirements and switching speed to ensure optimal performance. Logic Level MOSFETs are designed to fully turn on with lower gate voltages, typically around 4.5V or lower, making them ideal for microcontroller interfaces. Power MOSFETs offer higher current handling and lower conduction losses but may require higher gate voltages, so matching the MOSFET specifications to your power source and control circuitry is crucial.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Type
Power MOSFETs offer high voltage and current handling capabilities with low on-resistance, making them ideal for high-power applications, but they often require higher gate drive voltages and can have slower switching speeds. Logic Level MOSFETs operate efficiently at lower gate voltages, enabling direct control from microcontrollers and logic circuits, yet they typically have higher on-resistance and lower maximum voltage ratings compared to standard Power MOSFETs. Choosing the right MOSFET depends on Your application's voltage, current, and control signal requirements for optimal performance and efficiency.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Power MOSFETs and Logic Level MOSFETs are often confused due to overlapping applications, but a key misconception is that Logic Level MOSFETs can always replace standard Power MOSFETs in high-current circuits; in reality, Logic Level MOSFETs are optimized for low gate voltage operation rather than maximum current handling. Many believe that all Power MOSFETs require high gate voltages to turn on effectively, while Logic Level MOSFETs are specifically designed to fully switch at lower voltages (typically 4.5V or less), making them ideal for direct drive from microcontrollers. It is also incorrectly assumed that both types have identical RDS(on) values under any conditions, but RDS(on) varies significantly with gate voltage and device design, impacting efficiency and thermal performance in electronic circuits.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right MOSFET for Your Needs
Power MOSFETs offer robust current handling and low on-resistance, ideal for high-power applications requiring efficient switching and heat dissipation. Logic Level MOSFETs are optimized for low-voltage gate drive compatibility, making them perfect for microcontroller interfacing and low-power circuits. Selecting the right MOSFET depends on the voltage requirements, gate drive voltage, and power handling needs specific to your application.
Power MOSFET vs Logic Level MOSFET Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com