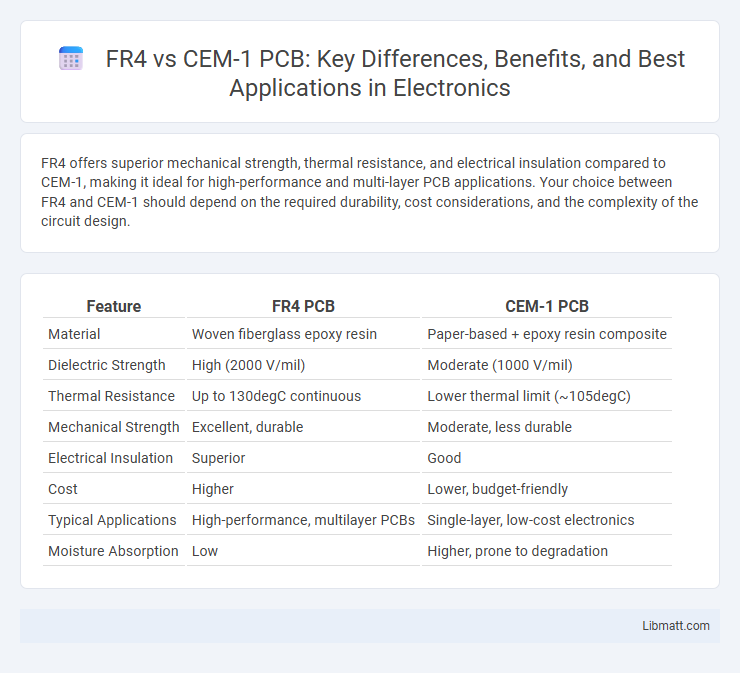
FR4 offers superior mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and electrical insulation compared to CEM-1, making it ideal for high-performance and multi-layer PCB applications. Your choice between FR4 and CEM-1 should depend on the required durability, cost considerations, and the complexity of the circuit design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | FR4 PCB | CEM-1 PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Woven fiberglass epoxy resin | Paper-based + epoxy resin composite |
| Dielectric Strength | High (2000 V/mil) | Moderate (1000 V/mil) |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 130degC continuous | Lower thermal limit (~105degC) |
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent, durable | Moderate, less durable |
| Electrical Insulation | Superior | Good |
| Cost | Higher | Lower, budget-friendly |
| Typical Applications | High-performance, multilayer PCBs | Single-layer, low-cost electronics |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | Higher, prone to degradation |
Introduction to FR4 and CEM-1 PCB Materials
FR4 is a high-quality epoxy resin-based laminate material known for its excellent mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and thermal resistance, making it the industry standard for multilayer PCB fabrication. CEM-1, composed of woven glass fabric and paper-based phenolic resin, offers a cost-effective alternative primarily used in single-layer or simple double-layer PCBs. The choice between FR4 and CEM-1 depends on factors such as application complexity, electrical performance requirements, and budget constraints.
Key Differences Between FR4 and CEM-1
FR4 PCBs are made from woven fiberglass cloth with epoxy resin, providing superior mechanical strength, heat resistance, and electrical insulation compared to CEM-1, which uses paper with epoxy resin as the base material. The thermal stability of FR4 exceeds 130degC, making it suitable for high-performance applications, whereas CEM-1 typically withstands lower temperatures around 105degC. FR4's layered glass fiber structure offers better durability and flame retardancy, while CEM-1 is cost-effective and primarily used for simple, single-sided circuits.
Material Composition of FR4 and CEM-1
FR4 PCB material consists of woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with epoxy resin, providing high mechanical strength, excellent electrical insulation, and superior moisture resistance. CEM-1 PCB, on the other hand, is made from a paper-based phenolic resin composite with woven glass fabric layers, offering lower cost but reduced durability and electrical properties compared to FR4. The fiberglass content in FR4 significantly enhances thermal stability and structural integrity, making it ideal for complex and high-performance electronic applications.
Electrical Performance Comparison
FR4 PCBs offer superior electrical performance due to their high dielectric strength and low moisture absorption, ensuring stable signal integrity and minimal signal loss in high-frequency applications. CEM-1 PCBs, made from paper-based substrates, exhibit higher dielectric constant and increased moisture sensitivity, which can lead to degraded electrical performance and reduced reliability in complex circuits. Your choice between FR4 and CEM-1 will significantly impact signal quality and overall circuit efficiency, especially in high-frequency or high-performance electronic designs.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
FR4 PCBs exhibit superior mechanical strength and durability due to their fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin composition, allowing them to withstand higher stress and environmental factors compared to CEM-1. CEM-1 PCBs, made from paper-phenolic material with a single layer of woven glass fabric, offer lower mechanical robustness and are more prone to damage under mechanical strain and thermal cycling. For applications requiring long-term reliability and resistance to physical wear, FR4 is the preferred choice over CEM-1.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
FR4 PCBs exhibit superior thermal stability and heat resistance compared to CEM-1, with a glass transition temperature (Tg) typically around 130-140degC, enabling better performance under high-temperature conditions. CEM-1 boards have a lower Tg, approximately 105degC, which limits their ability to withstand prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures without deformation or degradation. Your choice between FR4 and CEM-1 should consider the operating environment where thermal stability is critical for PCB reliability and longevity.
Cost Analysis: FR4 vs CEM-1
FR4 PCBs typically have a higher cost compared to CEM-1 due to superior material properties like better thermal resistance and mechanical strength, making them ideal for complex, high-performance applications. CEM-1 PCBs are more budget-friendly and suited for simpler, low-cost electronic devices where high durability and heat tolerance are less critical. Your choice between FR4 and CEM-1 should balance cost constraints with performance requirements to optimize overall project value.
Common Applications for FR4 and CEM-1 PCBs
FR4 PCBs are widely used in complex electronic devices such as computer motherboards, industrial control systems, and consumer electronics due to their superior mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and electrical insulation properties. CEM-1 PCBs are typically found in simple, low-cost applications like calculators, power tools, and basic household electronics where moderate performance and cost-efficiency are priorities. The choice between FR4 and CEM-1 depends on the application's complexity, thermal requirements, and budget constraints, with FR4 favored for high-reliability circuits and CEM-1 for less demanding, cost-sensitive products.
Pros and Cons of FR4 and CEM-1
FR4 PCB offers superior mechanical strength, excellent thermal resistance up to 130degC, and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for high-performance electronic applications; however, it comes with a higher cost compared to CEM-1. CEM-1 PCB features cost-effectiveness and good electrical insulation for simple, single-sided circuits but lacks the durability and heat resistance of FR4, limiting its use in more demanding environments. FR4's flame retardant properties and dimensional stability outclass CEM-1's basic resin-paper composite, which is prone to delamination and lower mechanical reliability under stress.
Choosing the Right PCB Material for Your Project
FR4 offers superior mechanical strength, higher temperature resistance, and better electrical insulation compared to CEM-1, making it ideal for complex, high-performance electronic projects. CEM-1 is more cost-effective and suitable for simple, low-frequency applications or prototypes where budget is a priority. Evaluating your project's durability requirements, thermal conditions, and electrical performance needs helps you choose the right PCB material.
FR4 vs CEM-1 PCB Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com