MCUs (Microcontroller Units) are optimized for general-purpose control tasks, offering integrated peripherals and low power consumption, ideal for embedded applications. DSPs (Digital Signal Processors) specialize in high-speed numerical processing of signals like audio and video, providing enhanced performance for complex mathematical operations in your real-time systems.
Table of Comparison
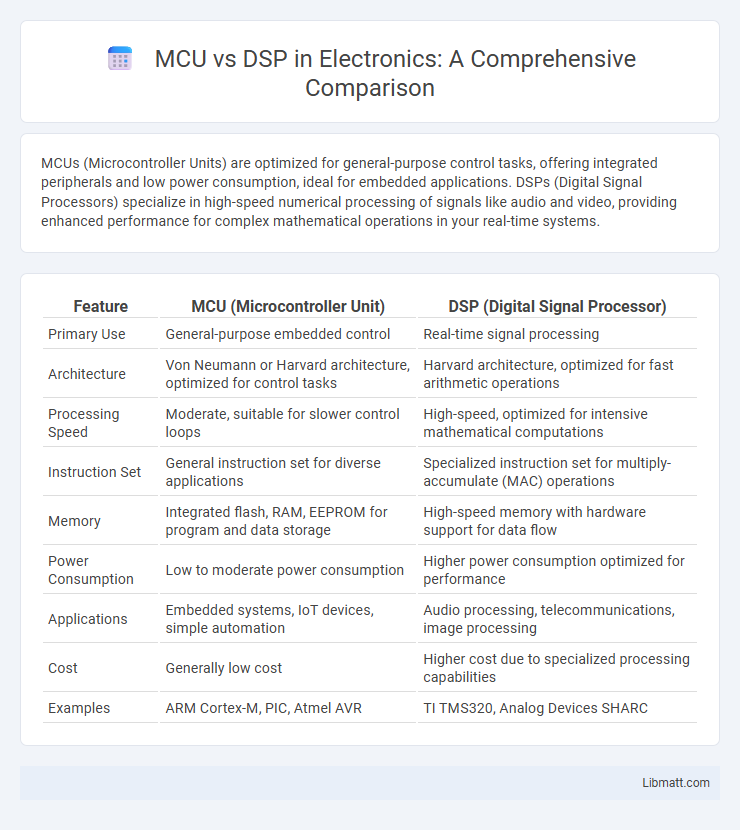
| Feature | MCU (Microcontroller Unit) | DSP (Digital Signal Processor) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | General-purpose embedded control | Real-time signal processing |
| Architecture | Von Neumann or Harvard architecture, optimized for control tasks | Harvard architecture, optimized for fast arithmetic operations |
| Processing Speed | Moderate, suitable for slower control loops | High-speed, optimized for intensive mathematical computations |
| Instruction Set | General instruction set for diverse applications | Specialized instruction set for multiply-accumulate (MAC) operations |
| Memory | Integrated flash, RAM, EEPROM for program and data storage | High-speed memory with hardware support for data flow |
| Power Consumption | Low to moderate power consumption | Higher power consumption optimized for performance |
| Applications | Embedded systems, IoT devices, simple automation | Audio processing, telecommunications, image processing |
| Cost | Generally low cost | Higher cost due to specialized processing capabilities |
| Examples | ARM Cortex-M, PIC, Atmel AVR | TI TMS320, Analog Devices SHARC |
Introduction to MCU and DSP
Microcontroller Units (MCUs) are compact integrated circuits designed for specific control applications, combining a processor, memory, and peripherals in a single chip. Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) specialize in high-speed numeric calculations, optimizing operations like filtering, audio processing, and real-time data analysis. Understanding the unique architectures of MCU and DSP helps you select the right solution for embedded systems requiring precise control or intensive signal processing.
Core Architectural Differences
Microcontroller Units (MCUs) feature a simplified, fixed instruction pipeline optimized for control-oriented tasks with lower clock frequencies, emphasizing low power consumption and real-time responsiveness. Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) incorporate specialized hardware such as multiple execution units, single-cycle multiply-accumulate (MAC) operations, and specialized addressing modes, enabling high-throughput data processing and efficient handling of complex numerical algorithms. The core architectural difference lies in MCUs' general-purpose design versus DSPs' tailored architecture for intensive signal processing workloads.
Processing Capabilities and Performance
MCUs offer efficient control-oriented processing with lower clock speeds and limited parallelism, ideal for real-time embedded applications. DSPs excel in high-speed mathematical computations, featuring specialized hardware like MAC units and SIMD instructions, delivering superior performance in signal processing tasks. Your choice depends on whether your application demands versatile general-purpose control or intensive numeric data processing.
Typical Applications of MCUs
MCUs are widely used in embedded systems for applications such as home automation, automotive control systems, and consumer electronics due to their ability to handle multiple peripheral interfaces and low power consumption. Typical MCU applications include sensor control, user interface management, and simple real-time control tasks, making them ideal for IoT devices and smart appliances. Your choice of MCU enables efficient processing for tasks requiring moderate computational power and real-time responsiveness.
Typical Applications of DSPs
Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) excel in applications requiring real-time data processing such as audio and speech recognition, image processing, and telecommunications. You will find DSPs embedded in devices like mobile phones, hearing aids, and radar systems where fast mathematical computations on signals are critical. These processors are optimized for algorithms involving Fourier transforms, filtering, and adaptive signal processing, making them indispensable for signal analysis and enhancement tasks.
Power Efficiency Comparison
MCUs typically offer lower power consumption for general control tasks due to their simplified architecture and integrated peripherals, making them ideal for battery-powered applications. DSPs consume more power as they perform complex, high-speed numerical computations essential for advanced signal processing tasks. Your choice depends on balancing power efficiency with processing requirements, where MCUs excel in low-power operation and DSPs deliver optimized performance at a higher energy cost.
Development Tools and Ecosystem
MCUs offer extensive development tools with integrated IDEs, extensive libraries, and community support for rapid prototyping and embedded applications. DSPs provide specialized toolchains optimized for real-time signal processing with advanced debugging and profiling features tailored to algorithm development. The MCU ecosystem emphasizes versatility and ease of use, while the DSP environment targets performance-critical applications with specialized hardware acceleration.
Cost Considerations
MCUs generally offer lower upfront costs and are more cost-effective for simple control tasks due to integrated peripherals and reduced component count. DSPs tend to have higher prices driven by specialized architecture designed for complex mathematical operations and high-performance signal processing. Cost considerations also include development time and software tools, where MCUs often benefit from broader ecosystem support and lower maintenance expenses.
Scalability and Integration
MCUs offer high scalability with flexible core options and integrated peripherals, enabling seamless integration into diverse embedded systems. DSPs excel in computational scalability for signal processing tasks but often require external components for broader system integration. Combining MCU and DSP capabilities can optimize both scalability and integration in complex real-time applications.
Selecting the Right Solution for Your Project
Choosing between an MCU (Microcontroller Unit) and a DSP (Digital Signal Processor) depends on your project's processing needs and real-time performance requirements. MCUs excel in control-oriented applications with low power consumption and integrated peripherals, while DSPs offer superior performance for complex mathematical computations, signal filtering, and audio processing tasks. Evaluate factors like computational intensity, power budget, latency tolerance, and real-time signal processing demands to select the optimal architecture for embedded system design.
MCU vs DSP Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com