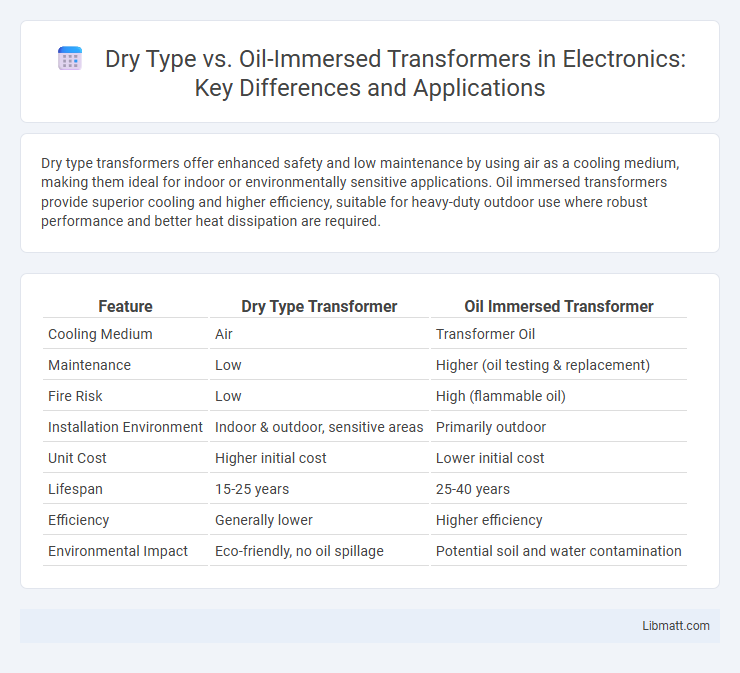
Dry type transformers offer enhanced safety and low maintenance by using air as a cooling medium, making them ideal for indoor or environmentally sensitive applications. Oil immersed transformers provide superior cooling and higher efficiency, suitable for heavy-duty outdoor use where robust performance and better heat dissipation are required.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dry Type Transformer | Oil Immersed Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Medium | Air | Transformer Oil |
| Maintenance | Low | Higher (oil testing & replacement) |
| Fire Risk | Low | High (flammable oil) |
| Installation Environment | Indoor & outdoor, sensitive areas | Primarily outdoor |
| Unit Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Lifespan | 15-25 years | 25-40 years |
| Efficiency | Generally lower | Higher efficiency |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, no oil spillage | Potential soil and water contamination |
Introduction to Transformer Cooling Methods
Dry type transformers use air as the primary cooling medium, relying on natural or forced ventilation to dissipate heat, making them ideal for indoor and environmentally sensitive applications. Oil immersed transformers utilize mineral or synthetic oil to absorb and transfer heat away from the core and windings, providing superior cooling efficiency and enabling higher load capacities. Your choice between these cooling methods impacts maintenance needs, operational safety, and installation flexibility.
Overview of Dry Type Transformers
Dry type transformers use air instead of liquid for cooling, making them safer and environmentally friendly for indoor applications. They consist of resin-encapsulated coils, which provide excellent electrical insulation and reduce fire hazards compared to oil immersed transformers. These transformers require less maintenance and offer high performance in ventilation-challenged or moisture-prone environments.
Overview of Oil Immersed Transformers
Oil immersed transformers use insulating oil to dissipate heat and enhance electrical insulation, making them ideal for high voltage and heavy-duty applications. The oil acts as both a coolant and insulator, improving efficiency and extending the lifespan of the transformer. Your choice of transformer depends on factors like maintenance requirements, environmental conditions, and installation costs.
Key Differences Between Dry Type and Oil Immersed Transformers
Dry type transformers use air for cooling and are commonly found indoors due to their reduced fire risk, while oil immersed transformers rely on mineral oil or synthetic fluids for efficient heat dissipation and are typically used outdoors. Dry type transformers offer safer operation in sensitive environments with lower maintenance needs, whereas oil immersed transformers generally provide higher capacity and better insulation properties. Your choice depends on application requirements such as safety, cooling efficiency, maintenance, and installation location.
Advantages of Dry Type Transformers
Dry type transformers offer superior safety benefits due to the absence of flammable insulating oil, reducing fire hazards in enclosed or indoor environments. These transformers require lower maintenance since there is no risk of oil leaks or contamination, resulting in increased reliability and longer service life. They also provide better environmental compatibility, making them ideal for sensitive locations such as hospitals and commercial buildings where environmental regulations are stringent.
Advantages of Oil Immersed Transformers
Oil immersed transformers offer superior cooling efficiency due to the natural circulation of oil, which helps in maintaining lower operating temperatures and extending the transformer's lifespan. They exhibit higher power ratings and better voltage regulation compared to dry type transformers, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. Enhanced insulation properties of the oil reduce the risk of electrical faults, resulting in improved reliability and performance in demanding environments.
Applications and Suitability for Each Transformer Type
Dry type transformers are ideal for indoor applications such as commercial buildings, hospitals, and schools due to their enhanced safety and low maintenance requirements. Oil-immersed transformers are better suited for outdoor or industrial environments where higher power capacity and efficient cooling are critical. Your choice depends on factors like environmental conditions, maintenance preferences, and installation location.
Maintenance Requirements and Safety Comparison
Dry type transformers require less frequent maintenance due to the absence of insulating oil, reducing risks associated with leaks and fire hazards, enhancing overall safety for Your facility. Oil immersed transformers necessitate regular oil testing and replacement to prevent contamination, ensuring effective insulation and cooling but posing greater fire and environmental risks. Choosing between these types hinges on balancing Your maintenance capacity and the safety standards required for the operating environment.
Environmental Impact and Energy Efficiency
Dry type transformers have a lower environmental impact due to the absence of oil, eliminating risks of leaks and soil contamination while offering better fire safety. Oil immersed transformers typically have higher energy efficiency thanks to superior cooling properties of the oil, which reduces core and winding losses during operation. Your choice should balance the ecological benefits of dry type transformers with the energy efficiency advantages of oil immersed models based on specific application needs.
How to Choose the Right Transformer for Your Needs
Choosing the right transformer depends on factors such as installation environment, cooling requirements, and maintenance preferences. Dry type transformers are ideal for indoor use with better safety and lower fire risk, while oil immersed transformers offer higher efficiency and cooling capacity suited for outdoor or heavy-load applications. Evaluating load demand, space constraints, and environmental regulations ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Dry Type vs Oil Immersed Transformer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com