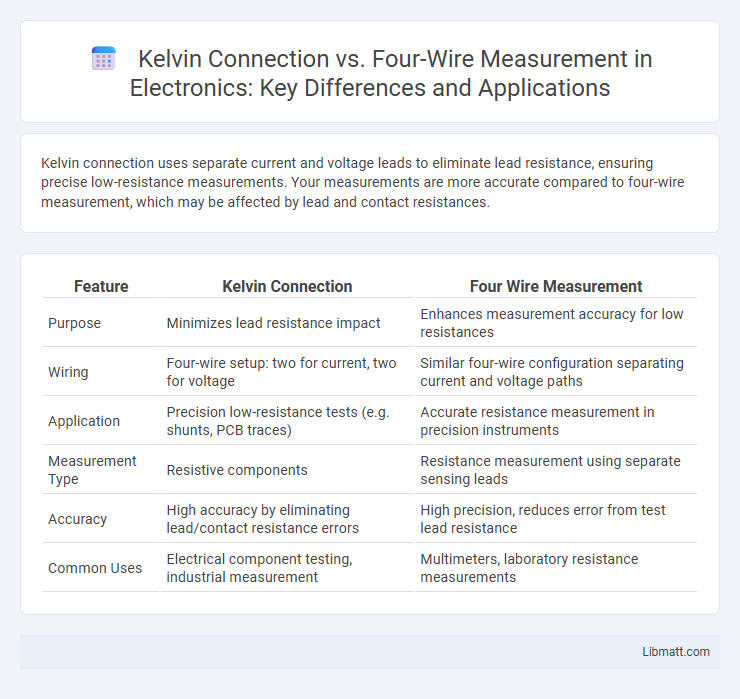
Kelvin connection uses separate current and voltage leads to eliminate lead resistance, ensuring precise low-resistance measurements. Your measurements are more accurate compared to four-wire measurement, which may be affected by lead and contact resistances.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Kelvin Connection | Four Wire Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Minimizes lead resistance impact | Enhances measurement accuracy for low resistances |
| Wiring | Four-wire setup: two for current, two for voltage | Similar four-wire configuration separating current and voltage paths |
| Application | Precision low-resistance tests (e.g. shunts, PCB traces) | Accurate resistance measurement in precision instruments |
| Measurement Type | Resistive components | Resistance measurement using separate sensing leads |
| Accuracy | High accuracy by eliminating lead/contact resistance errors | High precision, reduces error from test lead resistance |
| Common Uses | Electrical component testing, industrial measurement | Multimeters, laboratory resistance measurements |
Introduction to Precision Electrical Measurements
Kelvin Connection and Four Wire Measurement are essential techniques used to achieve high-precision electrical measurements by minimizing the effects of lead and contact resistance. In a Kelvin Connection, separate pairs of wires are employed for current supply and voltage sensing, ensuring that the voltage drop across the test leads does not affect the measurement. Your accurate readings in sensitive applications depend on implementing these methods to reduce errors and improve measurement reliability.
Understanding the Kelvin Connection
Kelvin Connection, also known as four-wire measurement, uses separate pairs of current-carrying and voltage-sensing leads to eliminate the impact of lead resistance on measurement accuracy. This technique is essential for precise low-resistance measurements in applications like electrical component testing or PCB trace resistance evaluation. Your measurements become more reliable by minimizing voltage drops caused by connecting wires, ensuring accurate readings even with very low resistance values.
Overview of Four Wire Measurement Technique
Four wire measurement, also known as Kelvin connection, eliminates the effects of lead and contact resistance by using separate pairs of current-carrying and voltage-sensing electrodes. This technique enhances measurement accuracy in low-resistance components by ensuring that voltage is measured directly across the test sample without interference from wire resistances. Commonly applied in precision resistance meters and sensor calibration, four wire measurement is essential for obtaining reliable and repeatable electrical readings.
Key Differences Between Kelvin Connection and Four Wire Measurement
Kelvin Connection employs separate pairs of current-carrying and voltage-sensing leads to eliminate lead and contact resistance effects, enhancing measurement accuracy in low-resistance applications. Four Wire Measurement also uses four leads to measure voltage and current independently but is primarily designed for precision resistance measurements by minimizing lead resistance impact. The key difference lies in Kelvin Connection's emphasis on high-current, low-voltage scenarios with specialized terminal design, whereas Four Wire Measurement focuses on general precision resistance measurement techniques.
Importance of Accurate Low-Resistance Measurements
Accurate low-resistance measurements are critical for ensuring reliable performance in electrical and electronic systems, as even minor resistance inaccuracies can lead to significant energy losses and thermal issues. Kelvin connection, also known as four-wire measurement, eliminates the influence of lead and contact resistance by using separate pairs of current-carrying and voltage-sensing electrodes, enhancing measurement precision. This method is essential for applications such as battery testing, superconductors, and precision resistors, where exact resistance values directly impact efficiency and safety.
Applications of Kelvin Connection
Kelvin Connection is widely used in precision measurement applications such as low-resistance testing, battery testing, and sensing electrical contacts where accurate voltage drops need to be measured without influence from lead or contact resistance. This method eliminates errors caused by test lead resistance, making it ideal for high-accuracy current and voltage measurements in electrical components and assemblies. You can rely on Kelvin Connection in scenarios requiring meticulous resistance measurement for quality control and detailed electrical analysis.
Use Cases for Four Wire Measurement
Four wire measurement is predominantly used in precision low-resistance measurements where accuracy is critical, such as in sensing and calibration applications. It is essential in environments with significant lead or contact resistance, like measuring resistance of thin-film resistors, PCB traces, or wiring harnesses. This method effectively eliminates errors caused by lead resistance, ensuring highly reliable results in laboratory and industrial testing scenarios.
Advantages and Limitations of Both Methods
Kelvin connection provides precise resistance measurements by eliminating lead and contact resistance effects, making it ideal for low-resistance components but requires specialized four-terminal test fixtures and is more complex to set up. Four-wire measurement offers high accuracy through separate current and voltage paths, minimizing measurement errors in low-resistance circuits but can be more costly due to additional wiring and instrumentation. Both methods improve measurement reliability, yet Kelvin connection excels in ultra-low resistance scenarios while traditional four-wire setups balance accuracy with practical application in broader contexts.
Common Errors and How to Avoid Them
Common errors in Kelvin Connection arise from incorrect placement of current and voltage probes, leading to inaccurate resistance measurements due to lead and contact resistance. In Four Wire Measurement, errors often stem from loose connections or using inappropriate test equipment, causing voltage drop distortions. You can avoid these issues by ensuring proper probe configuration, maintaining tight connections, and using calibrated instruments designed for precise low-resistance measurements.
Selecting the Best Method for Your Measurement Needs
Kelvin Connection offers superior accuracy in low-resistance measurements by eliminating lead and contact resistance, making it ideal for precise applications such as measuring small resistors or PCB traces. Four Wire Measurement, while also providing accuracy benefits over two-wire methods, is better suited for general resistance measurements where extreme precision is less critical. Selecting the best method depends on factors like the required measurement accuracy, the resistance range, and the impact of lead resistance on the results.
Kelvin Connection vs Four Wire Measurement Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com