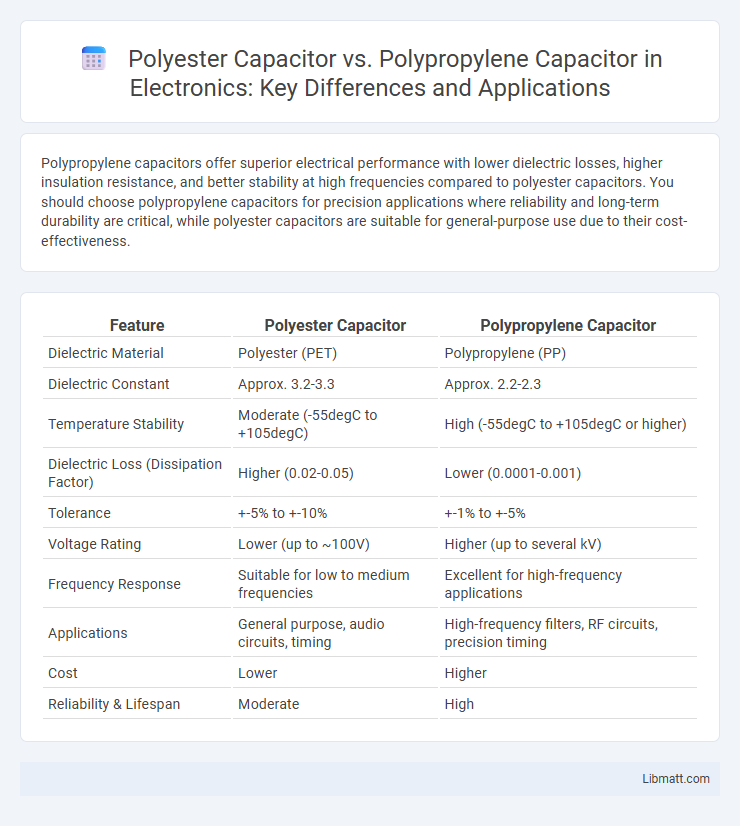
Polypropylene capacitors offer superior electrical performance with lower dielectric losses, higher insulation resistance, and better stability at high frequencies compared to polyester capacitors. You should choose polypropylene capacitors for precision applications where reliability and long-term durability are critical, while polyester capacitors are suitable for general-purpose use due to their cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyester Capacitor | Polypropylene Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Material | Polyester (PET) | Polypropylene (PP) |
| Dielectric Constant | Approx. 3.2-3.3 | Approx. 2.2-2.3 |
| Temperature Stability | Moderate (-55degC to +105degC) | High (-55degC to +105degC or higher) |
| Dielectric Loss (Dissipation Factor) | Higher (0.02-0.05) | Lower (0.0001-0.001) |
| Tolerance | +-5% to +-10% | +-1% to +-5% |
| Voltage Rating | Lower (up to ~100V) | Higher (up to several kV) |
| Frequency Response | Suitable for low to medium frequencies | Excellent for high-frequency applications |
| Applications | General purpose, audio circuits, timing | High-frequency filters, RF circuits, precision timing |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Reliability & Lifespan | Moderate | High |
Introduction to Polyester and Polypropylene Capacitors
Polyester capacitors feature a dielectric made from polyethylene terephthalate, offering moderate tolerance and stability ideal for general-purpose applications. Polypropylene capacitors use a polypropylene film dielectric, providing superior insulation resistance, lower dielectric loss, and high-frequency performance suited for precision circuits. Both capacitor types serve distinct roles based on their dielectric properties influencing capacitance stability, temperature coefficient, and frequency response.
Construction Differences
Polyester capacitors feature a dielectric made from biaxially oriented polyethylene terephthalate film, characterized by high dielectric constant and moderate dissipation factor, resulting in compact size but higher loss. Polypropylene capacitors use a dielectric of biaxially oriented polypropylene film, providing lower dielectric constant and minimal dissipation factor, which enhances stability and low loss at high frequencies. Construction-wise, polypropylene capacitors typically have thicker dielectric layers and superior insulation resistance compared to the thinner, more flexible layers of polyester capacitors, impacting performance and reliability in various applications.
Electrical Characteristics Comparison
Polypropylene capacitors exhibit superior electrical characteristics compared to polyester capacitors, including lower dielectric absorption, higher insulation resistance, and better stability over a wide temperature range. Polyester capacitors tend to have higher dissipation factors and lower voltage ratings, making them less suitable for precision filtering and high-frequency applications. Your choice depends on the required tolerance, temperature stability, and frequency response, with polypropylene capacitors preferred for demanding electrical environments.
Dielectric Properties
Polypropylene capacitors exhibit superior dielectric properties compared to polyester capacitors, including lower dielectric loss and a higher dielectric strength, making them ideal for high-frequency and precision applications. Polyester capacitors typically show higher dielectric absorption and increased dissipation factor, which can reduce efficiency in sensitive circuits. Understanding these dielectric characteristics helps you select the right capacitor for your project's performance and reliability needs.
Temperature Stability
Polypropylene capacitors offer superior temperature stability compared to polyester capacitors, maintaining consistent capacitance and low dielectric loss across a wide temperature range, typically from -55degC to 105degC. Polyester capacitors tend to exhibit higher dielectric absorption and capacitance variation when exposed to temperature fluctuations, making them less reliable in precision applications. The thermal endurance of polypropylene capacitors ensures better performance in demanding environments, enhancing their suitability for high-frequency and high-temperature circuits.
Frequency Response
Polypropylene capacitors offer superior frequency response compared to polyester capacitors due to their lower dielectric loss and higher insulation resistance, making them ideal for high-frequency applications such as RF circuits and precision filters. Polyester capacitors exhibit higher dielectric absorption and increased equivalent series resistance (ESR), which limits their performance in high-frequency environments. Selecting polypropylene capacitors enhances signal integrity and reduces distortion in circuits operating above 1 MHz.
Applications and Use Cases
Polyester capacitors excel in general-purpose electronic circuits, such as audio equipment, timing, and coupling applications, due to their affordable cost and moderate stability. Polypropylene capacitors are preferred in precision circuits requiring low dielectric loss and high insulation resistance, making them ideal for high-frequency filters, RF applications, and power factor correction. Their superior temperature stability and low dissipation factor extend usability to audio signal processing and high-voltage pulse circuits.
Cost and Availability
Polyester capacitors are generally more cost-effective and widely available due to their common use in various electronic applications. Polypropylene capacitors tend to be more expensive because of their superior electrical characteristics and durability, limiting their availability to specialized markets. The cost difference often influences the choice of capacitor based on budget constraints and performance requirements.
Pros and Cons of Each Type
Polyester capacitors offer excellent reliability and cost-effectiveness, making them suitable for general-purpose applications, but they have higher dielectric losses and lower voltage ratings compared to polypropylene capacitors. Polypropylene capacitors provide superior electrical performance with low dielectric absorption and high insulation resistance, ideal for precision circuits, yet they come at a higher price and larger physical size. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements, as polyester capacitors suit everyday use while polypropylene capacitors excel in high-frequency or sensitive electronic applications.
Choosing the Right Capacitor for Your Project
Polyester capacitors offer high capacitance values and good stability at a lower cost, making them ideal for applications requiring compact size and moderate performance. Polypropylene capacitors excel in low dielectric loss, high insulation resistance, and superior temperature stability, suited for precision filtering and high-frequency circuits. Your selection should balance cost, tolerance, and electrical characteristics to ensure optimal performance in your project.
Polyester Capacitor vs Polypropylene Capacitor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com