Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance in smaller sizes and better stability under temperature changes compared to ceramic capacitors, which excel in high-frequency applications due to their low equivalent series resistance (ESR). Your choice depends on the specific requirements of your circuit, such as size constraints, frequency response, and reliability needs.
Table of Comparison
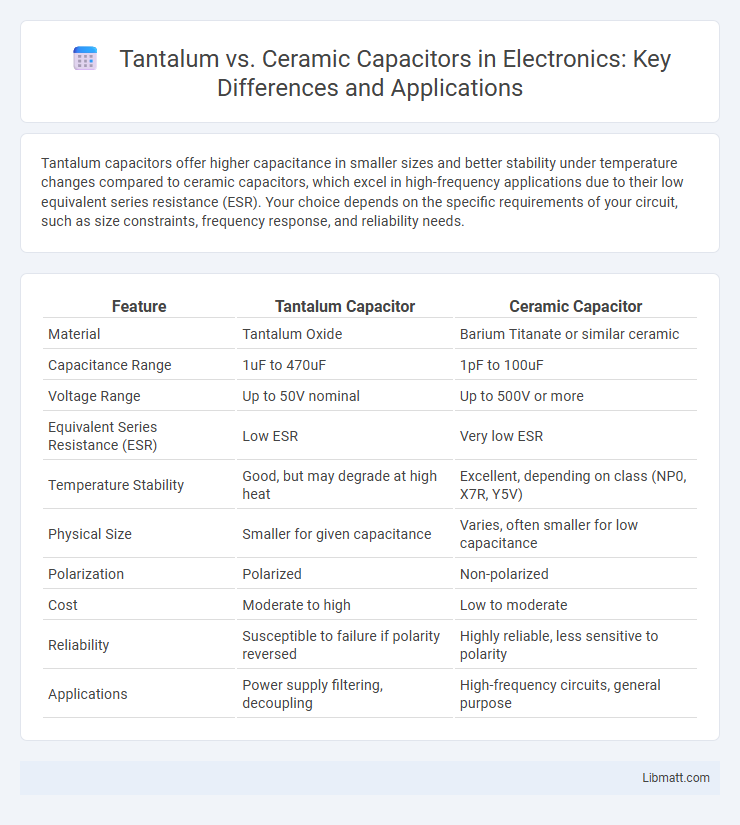
| Feature | Tantalum Capacitor | Ceramic Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Tantalum Oxide | Barium Titanate or similar ceramic |
| Capacitance Range | 1uF to 470uF | 1pF to 100uF |
| Voltage Range | Up to 50V nominal | Up to 500V or more |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | Low ESR | Very low ESR |
| Temperature Stability | Good, but may degrade at high heat | Excellent, depending on class (NP0, X7R, Y5V) |
| Physical Size | Smaller for given capacitance | Varies, often smaller for low capacitance |
| Polarization | Polarized | Non-polarized |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Reliability | Susceptible to failure if polarity reversed | Highly reliable, less sensitive to polarity |
| Applications | Power supply filtering, decoupling | High-frequency circuits, general purpose |
Introduction to Tantalum and Ceramic Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance in a small size with excellent stability and reliability, making them ideal for space-sensitive electronic circuits. Ceramic capacitors provide a broad range of values, low equivalent series resistance (ESR), and strong performance at high frequencies, suitable for general-purpose filtering and decoupling applications. Understanding the characteristics of both types helps optimize Your electronic designs for performance, size, and cost.
Construction and Materials Explained
Tantalum capacitors consist of a tantalum metal anode, coated with a thin oxide layer that acts as the dielectric, and are typically encased in a solid epoxy resin. Ceramic capacitors utilize ceramic materials such as barium titanate as the dielectric, with metal electrodes layered within the ceramic structure, resulting in a multilayer design. Your choice between tantalum and ceramic capacitors depends on specific performance requirements like voltage stability, capacitance density, and temperature characteristics tied directly to their distinct construction and materials.
Electrical Characteristics Comparison
Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance per volume and stable electrical characteristics with low Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR), making them ideal for applications requiring reliable performance under steady voltage conditions. Ceramic capacitors provide excellent high-frequency response, low losses, and superior stability over temperature, but they may exhibit capacitance variation due to applied voltage or temperature changes. Your choice depends on the circuit demands for capacitance density, frequency response, and stability requirements.
Capacitance Range and Stability
Tantalum capacitors offer a capacitance range typically between 0.1 uF to 470 uF with high volumetric efficiency, making them ideal for stable, long-term applications. Ceramic capacitors provide a broader capacitance range from picofarads to several microfarads, but their stability varies significantly with temperature and voltage, especially in Class II and III dielectrics. Your choice depends on whether you need wide capacitance options with moderate stability or a compact, stable capacitor for precision circuits.
Voltage Ratings and Tolerance
Tantalum capacitors typically offer voltage ratings ranging from 4V to 50V with tolerances around +-10%, making them suitable for low-voltage, high-capacitance applications. Ceramic capacitors provide a wider voltage rating spectrum, from as low as 6.3V up to several hundred volts, with tighter tolerances often at +-5% or better, ideal for high-frequency and precision circuits. The voltage rating and tolerance differences significantly influence capacitor selection based on application requirements such as voltage stability and circuit sensitivity.
ESR and Performance Differences
Tantalum capacitors typically have lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) compared to ceramic capacitors, resulting in better performance at higher frequencies and improved stability in filtering applications. Ceramic capacitors, especially multi-layer types, excel with high capacitance values and low inductance but often exhibit higher ESR, which can cause increased heat and reduced efficiency under heavy ripple currents. Understanding these ESR and performance differences helps you choose the ideal capacitor type for power management and signal integrity in your electronic circuits.
Applications in Electronics
Tantalum capacitors are widely used in applications requiring high capacitance in a small size, such as in power supply filtering, audio equipment, and medical devices. Ceramic capacitors excel in high-frequency circuits, decoupling, and timing applications due to their low equivalent series resistance (ESR) and stability. Your choice depends on the specific electronic requirements, including voltage range, capacitance value, and operating environment.
Reliability and Lifespan
Tantalum capacitors offer high reliability with stable electrical characteristics under steady voltage conditions, but they can be prone to catastrophic failure if exposed to voltage spikes or improper polarity. Ceramic capacitors generally provide longer lifespan and superior reliability in high-frequency and high-temperature applications due to their robust dielectric materials and resistance to cracking. The choice between tantalum and ceramic capacitors depends on the specific application requirements, prioritizing either energy density and stability (tantalum) or durability and thermal performance (ceramic).
Cost and Availability Considerations
Tantalum capacitors generally exhibit higher costs due to their specialized materials and manufacturing processes, making them less readily available in standard inventory compared to ceramic capacitors. Ceramic capacitors benefit from mass production, which lowers their price and ensures wider availability across various capacitance values and voltage ratings. Engineers often select ceramic capacitors for budget-sensitive projects or high-volume applications where cost efficiency and component accessibility are critical factors.
Choosing the Right Capacitor for Your Project
Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance in a small size with excellent stability and low ESR, making them ideal for compact, high-performance electronics. Ceramic capacitors provide superior frequency response and a wide temperature range, suited for filtering and decoupling applications in demanding environments. Selecting the right capacitor depends on your project's voltage requirements, size constraints, and performance needs to ensure reliability and efficiency.
Tantalum vs Ceramic Capacitor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com