Schottky diodes offer low forward voltage drop and fast switching speeds, making them ideal for power rectification and high-frequency applications. Zener diodes provide voltage regulation by maintaining a stable reference voltage in reverse bias, protecting your circuits from overvoltage conditions.
Table of Comparison
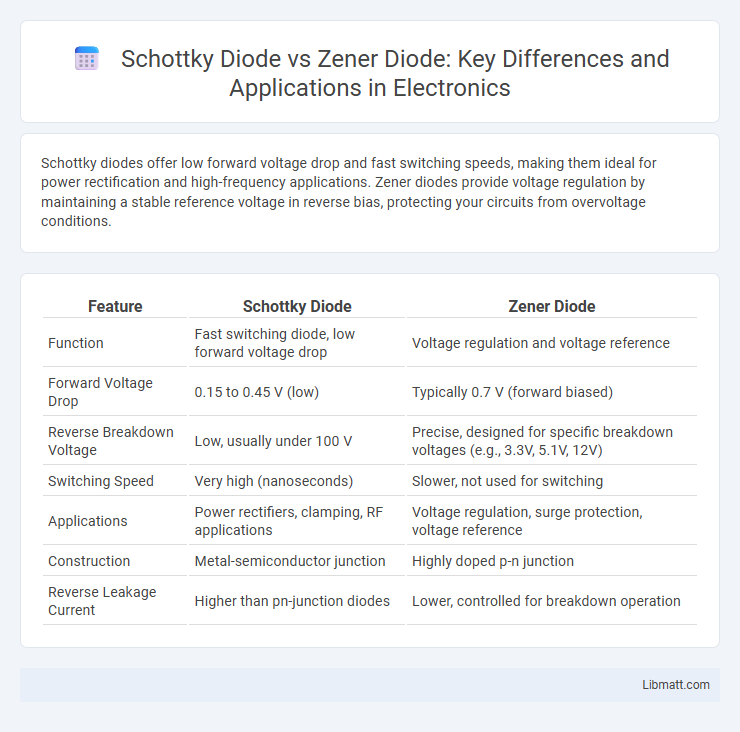
| Feature | Schottky Diode | Zener Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Fast switching diode, low forward voltage drop | Voltage regulation and voltage reference |
| Forward Voltage Drop | 0.15 to 0.45 V (low) | Typically 0.7 V (forward biased) |
| Reverse Breakdown Voltage | Low, usually under 100 V | Precise, designed for specific breakdown voltages (e.g., 3.3V, 5.1V, 12V) |
| Switching Speed | Very high (nanoseconds) | Slower, not used for switching |
| Applications | Power rectifiers, clamping, RF applications | Voltage regulation, surge protection, voltage reference |
| Construction | Metal-semiconductor junction | Highly doped p-n junction |
| Reverse Leakage Current | Higher than pn-junction diodes | Lower, controlled for breakdown operation |
Introduction to Schottky and Zener Diodes
Schottky diodes are semiconductor devices known for their low forward voltage drop and fast switching speeds, making them ideal for power rectification and RF applications. Zener diodes are designed to operate in the reverse breakdown region, providing voltage regulation and overvoltage protection by maintaining a stable reference voltage. Both diodes serve distinct roles in electronic circuits, with Schottky diodes emphasizing efficiency in high-frequency contexts and Zener diodes ensuring voltage stability.
Structural Differences
Schottky diodes feature a metal-semiconductor junction formed by placing a metal layer in direct contact with an n-type semiconductor, resulting in low forward voltage drop and fast switching speeds. Zener diodes have a heavily doped p-n junction designed to operate in reverse breakdown mode, allowing precise voltage regulation by maintaining a stable reference voltage. Understanding these structural differences helps optimize your circuit design for efficiency and reliability based on the specific diode function required.
Principle of Operation
Schottky diodes operate based on the metal-semiconductor junction, enabling rapid switching with low forward voltage drop and minimal charge storage. Zener diodes function by exploiting the Zener breakdown effect in a heavily doped p-n junction, maintaining a constant voltage across the diode when reverse biased. These distinct principles make Schottky diodes ideal for high-speed switching, while Zener diodes are primarily used for voltage regulation and protection.
Forward and Reverse Voltage Characteristics
Schottky diodes exhibit low forward voltage drop, typically between 0.2 to 0.3 volts, enabling faster switching and higher efficiency in low-voltage applications. Zener diodes operate primarily in reverse bias with a precise breakdown voltage, used for voltage regulation by maintaining a constant reverse voltage. Understanding these forward and reverse voltage characteristics is essential when selecting the appropriate diode to ensure optimal performance in your electronic circuits.
Switching Speed Comparison
Schottky diodes exhibit significantly faster switching speeds than Zener diodes due to their metal-semiconductor junction, which results in minimal charge storage and lower forward voltage drop. Zener diodes, designed primarily for voltage regulation through breakdown voltage operation, have slower switching characteristics because of their p-n junction structure and higher junction capacitance. In high-frequency or fast-switching applications, Schottky diodes are preferred for their rapid response, while Zener diodes are mainly utilized for voltage stabilization where switching speed is less critical.
Power Dissipation and Efficiency
Schottky diodes exhibit lower forward voltage drops, typically around 0.2 to 0.3 volts, resulting in reduced power dissipation and higher efficiency in switching and low-voltage applications. Zener diodes, characterized by their voltage regulation functionality, often experience higher power dissipation due to continuous reverse current flow during voltage stabilization, which can limit overall efficiency in power supply circuits. The choice between Schottky and Zener diodes impacts thermal management and energy conservation, with Schottky diodes favored in low-loss rectification and Zener diodes in voltage clamping where stable reference voltages are critical.
Applications of Schottky Diodes
Schottky diodes are widely used in high-speed switching applications and power rectification due to their low forward voltage drop and fast recovery time. They are ideal for power supplies, radio frequency (RF) applications, and clamping circuits where efficiency and minimal signal loss are crucial. Your electronic devices benefit from Schottky diodes' ability to reduce power consumption and improve overall performance in circuits requiring rapid response times.
Applications of Zener Diodes
Zener diodes are primarily used for voltage regulation in power supplies, providing stable reference voltages in circuits. They are essential in protecting sensitive electronic components by acting as voltage clamps or surge protectors. Common applications include voltage limiter circuits, wave shaping, and voltage reference in measurement devices.
Key Advantages and Disadvantages
Schottky diodes offer low forward voltage drop (typically 0.2 to 0.3 volts) resulting in higher efficiency and faster switching speeds, making them ideal for high-frequency applications, but they have lower reverse voltage ratings and higher leakage currents compared to Zener diodes. Zener diodes excel in voltage regulation and voltage reference roles due to their precise breakdown voltage and ability to operate in reverse breakdown mode, though they exhibit higher forward voltage drops (around 0.7 volts) and slower switching speeds. The choice between Schottky and Zener diodes depends on the application's requirements for speed, voltage regulation, efficiency, and tolerance to leakage current.
How to Choose Between Schottky and Zener Diodes
When choosing between Schottky and Zener diodes, consider the application's voltage and switching requirements; Schottky diodes offer low forward voltage drop and fast switching suited for high-frequency circuits and power rectification. Zener diodes are ideal for voltage regulation and voltage reference tasks, maintaining a stable output voltage despite fluctuations in input voltage or load conditions. Your selection should depend on whether you prioritize efficient signal rectification or precise voltage clamping for protecting sensitive components.
Schottky diode vs Zener diode Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com