PCB refers to the bare printed circuit board that provides the physical platform for electronic components, while PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) involves the process of soldering and assembling these components onto the PCB, turning it into a functional electronic device. Understanding the difference helps you choose the right option for manufacturing or repairing electronic products.
Table of Comparison
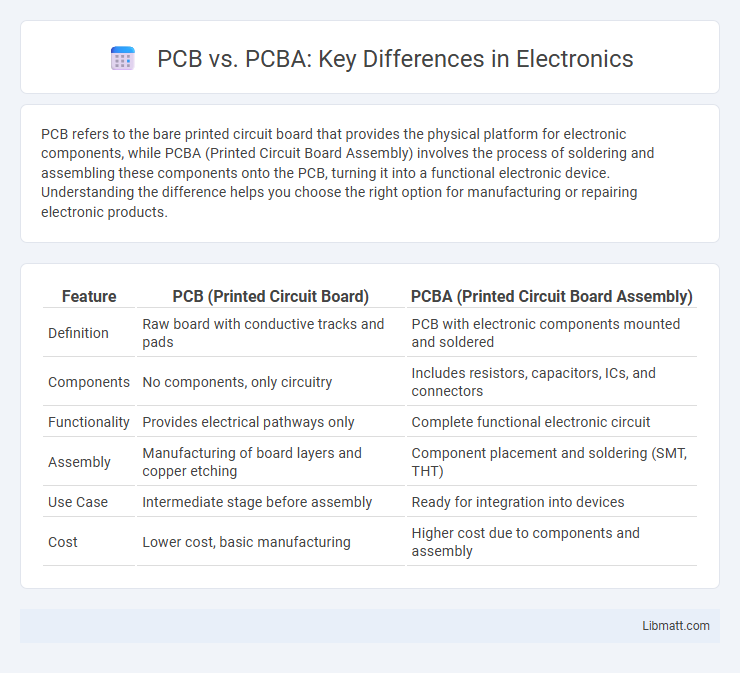
| Feature | PCB (Printed Circuit Board) | PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Raw board with conductive tracks and pads | PCB with electronic components mounted and soldered |
| Components | No components, only circuitry | Includes resistors, capacitors, ICs, and connectors |
| Functionality | Provides electrical pathways only | Complete functional electronic circuit |
| Assembly | Manufacturing of board layers and copper etching | Component placement and soldering (SMT, THT) |
| Use Case | Intermediate stage before assembly | Ready for integration into devices |
| Cost | Lower cost, basic manufacturing | Higher cost due to components and assembly |
Introduction to PCB and PCBA
Printed Circuit Boards (PCB) serve as the foundational platform for electronic components, providing mechanical support and electrical connections through conductive pathways. Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) refers to the process of mounting and soldering electronic components onto the PCB, transforming it into a functional electronic module. Understanding the distinction between PCB and PCBA is essential for your electronic design and manufacturing processes.
Definitions: What is a PCB?
A PCB, or Printed Circuit Board, is a flat board made of non-conductive material that mechanically supports and electrically connects electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks, or signal traces etched from copper sheets. It serves as the foundational platform in electronic devices, providing the physical structure and electrical connections necessary for component integration. PCBs come in various layers, including single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer configurations, tailored for different complexity levels in electronic circuits.
Definitions: What is a PCBA?
A PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) is a fully assembled board where electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits are mounted and soldered onto a bare PCB (Printed Circuit Board). Unlike a PCB, which is just the physical substrate with conductive pathways, a PCBA is ready for integration into electronic devices, functioning as a complete electronic module. PCBAs enable the execution of complex electronic operations by combining the physical board with active and passive components.
Key Differences Between PCB and PCBA
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) serves as the foundational board providing the physical structure and electrical pathways for electronic components, while PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) refers to the fully assembled PCB with all components soldered in place. The key difference lies in PCB being just the bare board, whereas PCBA includes various electronic parts such as resistors, capacitors, ICs, and connectors mounted on the board. PCB manufacturing involves processes like substrate fabrication and copper layering, whereas PCBA encompasses soldering techniques, component placement, and testing to create functional electronic devices.
PCB Manufacturing Process
The PCB manufacturing process involves multiple precise steps including substrate preparation, layering, etching, drilling, and plating to create the physical circuit board. Advanced techniques such as photolithography and solder mask application ensure accurate circuit patterns and protection against environmental damage. Quality control measures like electrical testing and inspection verify the integrity and functionality of the finished printed circuit board before assembly.
PCBA Assembly Process
The PCBA assembly process involves mounting electronic components onto a bare PCB (Printed Circuit Board) through soldering techniques such as Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT). Automated machines like pick-and-place devices ensure precision placement, while reflow ovens or wave soldering solidify connections, resulting in a fully functional Printed Circuit Board Assembly. Efficient PCBA assembly streamlines your product manufacturing by enhancing circuit reliability and performance.
Applications of PCB vs. PCBA
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) serve as foundational platforms in electronics, providing mechanical support and electrical connections in devices like computers, smartphones, and industrial machinery. Printed Circuit Board Assemblies (PCBAs), which incorporate mounted components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits, enable fully functional electronic systems used in complex applications like aerospace, medical devices, and automotive control systems. Understanding the distinction helps you choose the right solution for prototyping or production based on whether passive or fully assembled electronic functionality is required.
Cost Comparison: PCB vs. PCBA
Cost comparison between PCB (Printed Circuit Board) and PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) hinges on the scope of production; PCBs are generally less expensive as they only involve the bare board fabrication without components. PCBA includes the cost of soldering and assembling electronic components onto the PCB, increasing the overall expense due to labor, parts, and testing processes. Your choice should consider the total cost of ownership, where PCBA offers a ready-to-use product, potentially reducing downstream assembly and integration costs.
Quality and Reliability Considerations
PCB quality hinges on precise material selection, accurate multilayer construction, and stringent manufacturing tolerances to ensure optimal electrical performance. PCBA quality integrates these factors with meticulous component placement, soldering processes, and rigorous testing protocols to guarantee reliability under operational stress. Ensuring your assembly adheres to IPC standards and undergoes thorough inspections reduces failure rates and enhances long-term device dependability.
Conclusion: Choosing Between PCB and PCBA
Choosing between PCB and PCBA depends on the project's complexity and readiness for assembly; PCBs are bare boards requiring further component mounting, while PCBA refers to fully assembled and tested circuit boards ready for integration. For rapid prototyping or design validation, PCBs offer flexibility, whereas PCBA suits mass production and functional deployment. Understanding the distinctions ensures optimal decision-making based on budget, timeline, and application requirements.
PCB vs PCBA Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com