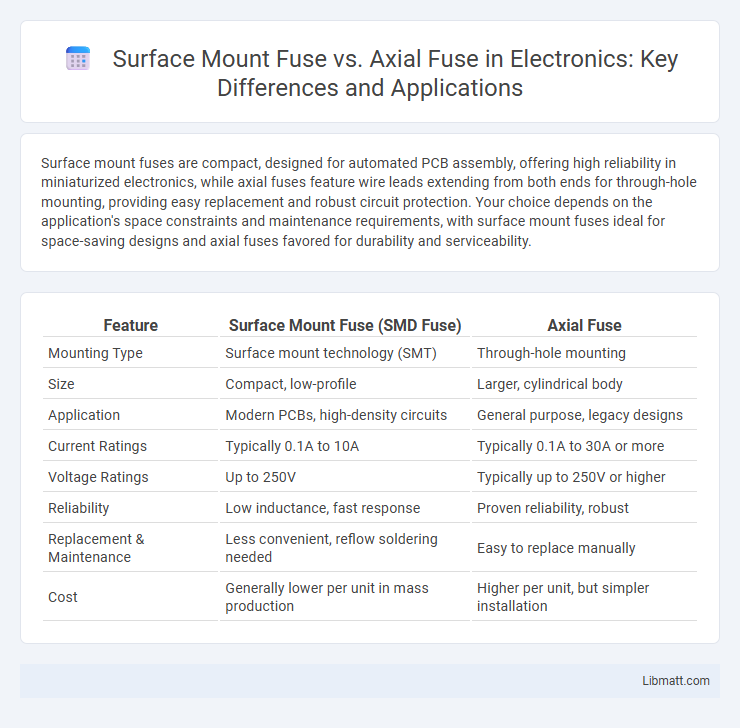
Surface mount fuses are compact, designed for automated PCB assembly, offering high reliability in miniaturized electronics, while axial fuses feature wire leads extending from both ends for through-hole mounting, providing easy replacement and robust circuit protection. Your choice depends on the application's space constraints and maintenance requirements, with surface mount fuses ideal for space-saving designs and axial fuses favored for durability and serviceability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Surface Mount Fuse (SMD Fuse) | Axial Fuse |
|---|---|---|
| Mounting Type | Surface mount technology (SMT) | Through-hole mounting |
| Size | Compact, low-profile | Larger, cylindrical body |
| Application | Modern PCBs, high-density circuits | General purpose, legacy designs |
| Current Ratings | Typically 0.1A to 10A | Typically 0.1A to 30A or more |
| Voltage Ratings | Up to 250V | Typically up to 250V or higher |
| Reliability | Low inductance, fast response | Proven reliability, robust |
| Replacement & Maintenance | Less convenient, reflow soldering needed | Easy to replace manually |
| Cost | Generally lower per unit in mass production | Higher per unit, but simpler installation |
Introduction to Surface Mount and Axial Fuses
Surface mount fuses are compact and designed for automated placement on printed circuit boards, enabling high-density electronic assemblies with low-profile packaging. Axial fuses feature wire leads extending from each end, suited for through-hole mounting and providing robustness for higher current and voltage applications. Understanding your circuit requirements helps determine whether a surface mount fuse or an axial fuse optimally enhances protection and performance.
Construction and Design Differences
Surface mount fuses feature compact, rectangular packages designed for automated PCB assembly, making them ideal for high-density electronics, while axial fuses have cylindrical bodies with wire leads extending from either end, suitable for through-hole mounting. The construction of surface mount fuses involves a flat ceramic or glass body with metal end caps, enhancing thermal performance and reliability in tight spaces. Your choice depends on device layout and space constraints, as axial fuses are easier to replace manually, whereas surface mount fuses support miniaturization and automated production.
Installation Methods: SMT vs Through-Hole
Surface Mount Fuses (SMF) utilize Surface Mount Technology (SMT), enabling automated placement directly onto the PCB surface, leading to faster assembly and smaller board space requirements. Axial Fuses rely on through-hole installation, where leads pass through PCB holes and are soldered on the opposite side, offering stronger mechanical support but requiring more manual labor or wave soldering processes. Your choice between SMT and through-hole fuses impacts manufacturing efficiency, assembly costs, and design compactness.
Space and Layout Considerations
Surface mount fuses require significantly less PCB space than axial fuses, enabling higher component density and more compact device designs. The flat profile of surface mount fuses allows for streamlined layout and easier automated assembly, reducing manufacturing costs and improving reliability. Axial fuses, with their leaded design, demand more clearance on the board, often limiting flexibility in tight layouts and increasing overall device footprint.
Current and Voltage Ratings Comparison
Surface mount fuses typically support lower current ratings, ranging from 0.1A to 10A, and voltage ratings up to 32V, suited for compact, low-power circuit protection in modern electronics. Axial fuses generally handle higher current capacities, from 0.5A to 30A, with voltage ratings that can exceed 250V, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring robust overload protection. Selecting between surface mount and axial fuses depends largely on the current and voltage demands of the specific electrical circuit.
Response Time and Performance
Surface mount fuses offer faster response times due to their lower inductance and smaller size, making them ideal for high-speed circuit protection. Axial fuses typically have longer response times but provide robust performance in high-current applications and easier replacement. Your choice depends on balancing the need for rapid protection with the fuse's current rating and physical requirements.
Reliability and Durability
Surface mount fuses offer enhanced reliability and durability due to their compact design and efficient heat dissipation, making them ideal for high-density electronic circuits. Axial fuses, while robust and easy to replace, are generally more susceptible to mechanical stress and vibration, potentially reducing their lifespan in demanding environments. You can rely on surface mount fuses for longer-lasting protection in modern electronics where space and performance are critical.
Applications: Where Each Fuse Excels
Surface mount fuses excel in compact electronic devices, including smartphones, laptops, and medical equipment, due to their small size and ease of automated assembly on printed circuit boards (PCBs). Axial fuses are ideal for higher current applications in automotive, industrial machinery, and power supplies where robust physical durability and quick replacement are essential. Each fuse type serves distinct roles based on space constraints and electrical load requirements in consumer electronics versus heavy-duty environments.
Cost and Availability
Surface mount fuses generally offer lower costs due to automated manufacturing processes and widespread use in compact electronic devices. Axial fuses tend to be more expensive and less readily available, often favored for applications requiring higher current ratings and durability. Your choice depends on balancing budget constraints with the specific availability and performance needs of the fuse type.
Choosing the Right Fuse for Your Circuit
Selecting the right fuse for your circuit depends on factors such as space constraints, current rating, and ease of replacement. Surface mount fuses (SMD fuses) are ideal for compact, high-density PCBs requiring automated assembly, offering low profile and fast response time. Axial fuses suit applications needing easy manual replacement and higher voltage tolerance, often found in through-hole designs with visible fuse elements for inspection.
Surface Mount Fuse vs Axial Fuse Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com