Flash memory offers fast, block-level data storage ideal for large volumes, whereas EEPROM provides byte-level data access with higher endurance and precise rewrites. Your choice depends on whether you need speed and capacity or fine-grained control and durability in non-volatile storage.
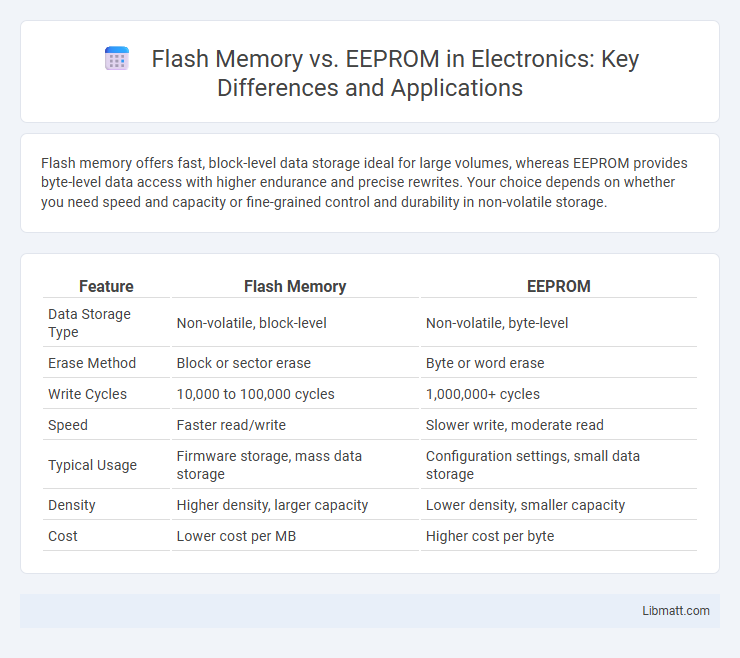
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Flash Memory | EEPROM |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage Type | Non-volatile, block-level | Non-volatile, byte-level |
| Erase Method | Block or sector erase | Byte or word erase |
| Write Cycles | 10,000 to 100,000 cycles | 1,000,000+ cycles |
| Speed | Faster read/write | Slower write, moderate read |
| Typical Usage | Firmware storage, mass data storage | Configuration settings, small data storage |
| Density | Higher density, larger capacity | Lower density, smaller capacity |
| Cost | Lower cost per MB | Higher cost per byte |
Introduction to Flash Memory and EEPROM
Flash memory and EEPROM are non-volatile storage technologies used to retain data without power. Flash memory offers higher density and faster write/erase cycles, making it ideal for applications like USB drives and SSDs. Your choice depends on the need for byte-level data updating, where EEPROM excels due to its precise erase/write capabilities.
Key Differences Between Flash Memory and EEPROM
Flash memory offers faster write and erase cycles compared to EEPROM, making it ideal for bulk data storage and firmware updates. EEPROM allows byte-level erasure and rewriting, providing finer granularity for small data changes in embedded systems. The higher endurance of Flash memory supports frequent write operations, whereas EEPROM's limited write cycles suit infrequent updates and more precise control.
Architecture and Design Overview
Flash memory features a block-based architecture that allows bulk erase and program operations, optimizing it for high-density data storage and rapid read/write cycles. EEPROM employs a byte-level architecture enabling individual byte erase and rewrite, suitable for frequent updates in embedded systems. The design differences impact endurance, speed, and application suitability, with Flash providing higher density and EEPROM offering finer granularity in data modification.
Data Storage and Retention Capabilities
Flash memory offers higher density storage suitable for large amounts of data and retains information for up to 10 years under optimal conditions, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent rewriting and bulk data retention. EEPROM provides slower write speeds but excels in data retention durability, often preserving data for over 20 years with reliable byte-level rewrites, perfect for storing configuration parameters and small datasets. Understanding your specific data storage needs and retention requirements will guide the choice between these non-volatile memory types.
Read and Write Operations: Speed and Efficiency
Flash memory offers faster read and write speeds compared to EEPROM, making it ideal for applications requiring rapid data access and higher storage capacities. EEPROM provides byte-level read and write capabilities, allowing more precise data manipulation but at slower speeds and higher power consumption for write operations. The trade-off between Flash's block-level efficiency and EEPROM's fine-grained control is crucial in selecting the appropriate non-volatile memory for specific embedded systems or microcontroller use cases.
Endurance and Lifespan Comparison
Flash memory typically offers lower endurance, supporting around 10,000 to 100,000 write-erase cycles, while EEPROM can endure approximately 1 million cycles before wearing out. The lifespan of flash memory is influenced by block erase operations, leading to potential degradation in performance over time, whereas EEPROM's byte-level erasure allows more precise and frequent writes, extending its usability for certain applications. Understanding these endurance differences helps optimize your choice for long-term data storage needs, especially in environments requiring frequent rewrites.
Power Consumption and Energy Efficiency
Flash memory typically consumes less power during read and write operations compared to EEPROM, making it more energy-efficient for large data storage applications. EEPROM's power consumption increases significantly with frequent byte-level write cycles, which often results in lower overall energy efficiency. Flash memory's ability to erase and write data in blocks rather than individual bytes reduces the power drain, making it suitable for battery-powered devices requiring extended operational life.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Flash memory is widely used in USB drives, solid-state drives (SSDs), and memory cards due to its high capacity and fast read/write speeds. EEPROM finds common applications in storing firmware, calibration data, and configuration settings in embedded systems where frequent but limited write cycles are required. Both memory types are crucial for non-volatile storage, with flash dominating consumer electronics and EEPROM preferred for precise control in industrial and automotive devices.
Security Features and Data Protection
Flash memory offers robust security features such as hardware-based encryption and secure boot capabilities, protecting data from unauthorized access and tampering. EEPROM provides byte-level data protection with built-in write-protect mechanisms and supports firmware-level encryption methods, enhancing data integrity in embedded systems. Both memory types incorporate error-correcting codes (ECC) and wear leveling to ensure data retention and reliability over time.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Needs
Flash memory offers faster write and erase cycles and higher density, making it ideal for applications requiring large storage and frequent data updates. EEPROM provides byte-level data erasure and rewriting, which suits use cases needing precise data modification and lower capacity requirements. Understanding the balance between speed, storage size, and data granularity helps you select the right non-volatile memory technology for your specific project.
Flash Memory vs EEPROM Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com