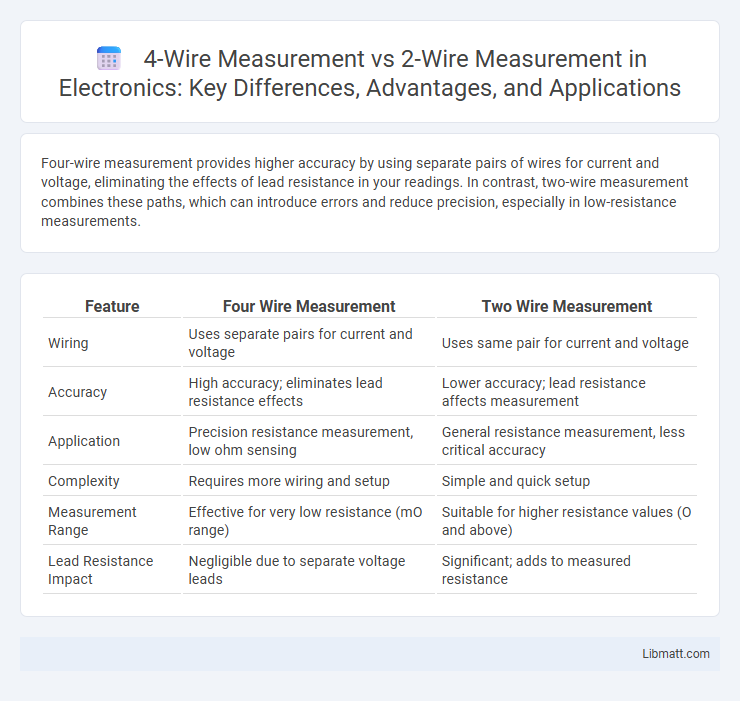
Four-wire measurement provides higher accuracy by using separate pairs of wires for current and voltage, eliminating the effects of lead resistance in your readings. In contrast, two-wire measurement combines these paths, which can introduce errors and reduce precision, especially in low-resistance measurements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Four Wire Measurement | Two Wire Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Wiring | Uses separate pairs for current and voltage | Uses same pair for current and voltage |
| Accuracy | High accuracy; eliminates lead resistance effects | Lower accuracy; lead resistance affects measurement |
| Application | Precision resistance measurement, low ohm sensing | General resistance measurement, less critical accuracy |
| Complexity | Requires more wiring and setup | Simple and quick setup |
| Measurement Range | Effective for very low resistance (mO range) | Suitable for higher resistance values (O and above) |
| Lead Resistance Impact | Negligible due to separate voltage leads | Significant; adds to measured resistance |
Introduction to Electrical Measurement Techniques
Four-wire measurement minimizes the effects of lead and contact resistance by using separate pairs of wires for current supply and voltage measurement, providing highly accurate voltage readings in low-resistance components. Two-wire measurement combines the current supply and voltage measurement in the same pair of wires, which can introduce errors due to lead resistance, making it less precise for low-resistance or high-accuracy applications. This distinction is crucial in precision electrical testing environments such as semiconductor device characterization and precision resistor calibration.
Understanding Two Wire Measurement
Two wire measurement uses the same pair of wires to supply current and measure voltage, which can introduce errors due to the resistance of the test leads. This method is simpler and cost-effective but is less accurate for low-resistance measurements since lead and contact resistances add to the reading. Commonly used in routine testing where high precision is not critical.
Exploring Four Wire Measurement
Four wire measurement, also known as Kelvin sensing, provides highly accurate resistance readings by separating the current-carrying and voltage-sensing pathways, eliminating lead and contact resistance errors common in two wire measurement. This technique is essential in applications requiring precision, such as low-resistance components and sensitive sensors, where traditional two wire methods can introduce significant measurement inaccuracies. You can achieve more reliable and repeatable results in critical testing environments by implementing four wire measurement.
Key Differences Between Two Wire and Four Wire Methods
The key differences between two wire and four wire measurement methods lie in accuracy and setup complexity. Two wire measurement uses the same pair of leads for current supply and voltage measurement, leading to potential errors from lead resistance, while four wire measurement employs separate pairs for current and voltage, significantly reducing measurement errors caused by lead and contact resistances. Your precision in low-resistance measurements improves dramatically with a four wire method due to its ability to eliminate the influence of lead resistance.
Accuracy and Precision: Comparing the Two Methods
Four wire measurement significantly improves accuracy and precision by eliminating the effect of lead and contact resistances, making it ideal for low-resistance measurements. Two wire measurement includes the resistance of the test leads, which can introduce errors and reduce measurement reliability, especially in sensitive applications. For critical measurements requiring high fidelity, four wire setups are preferred due to their ability to provide more consistent and exact resistance readings.
Applications Where Two Wire Measurement is Used
Two wire measurement is commonly used in simple resistance measurements, low-cost applications, and situations where high precision is not critical, such as checking continuity in electrical circuits or measuring battery voltage. This method is suitable for your typical household or industrial devices where the wiring length is short and lead resistance has minimal impact on accuracy. Its simplicity makes it ideal for quick diagnostics and troubleshooting but limits accuracy in precision instruments or long-distance measurements.
Advantages of Four Wire Measurement in Practice
Four wire measurement offers significant advantages in practice by eliminating the impact of lead and contact resistance, resulting in highly accurate resistance readings even for low-resistance components. This method uses separate pairs of current-carrying and voltage-sensing electrodes, which ensures that voltage measurements reflect only the device under test, unaffected by the resistance of test leads. Such precision is crucial in applications like precision resistor calibration, semiconductor testing, and sensitive electrical measurements where accuracy is paramount.
Limitations of Two Wire Measurement
Two Wire Measurement faces significant limitations due to the influence of lead and contact resistance, which can introduce errors in resistance readings, especially for low-resistance measurements. This method measures the combined resistance of the test specimen and the test leads, making it difficult to isolate the true resistance of your component. Four Wire Measurement overcomes these challenges by using separate pairs for current supply and voltage sensing, providing more accurate and reliable results.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Application
Four wire measurement provides superior accuracy by eliminating lead and contact resistance effects, making it ideal for precise low-resistance measurements in industrial and laboratory settings. Two wire measurement is simpler and cost-effective, suitable for less critical applications where slight measurement errors are acceptable. Selecting the right method depends on required measurement accuracy, system complexity, and budget constraints.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Measurement Technique
Four wire measurement offers superior accuracy by eliminating lead and contact resistance, making it ideal for precise low-resistance measurements in critical applications. Two wire measurement is simpler and suitable for less demanding scenarios where minor resistance errors do not impact results significantly. Your choice depends on the required measurement precision, with four wire preferred for high accuracy and two wire used when convenience and simplicity are prioritized.
Four Wire Measurement vs Two Wire Measurement Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com