GDTs (Gas Discharge Tubes) provide high surge current handling capabilities ideal for protecting power lines, while TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) diodes offer fast response times suitable for sensitive electronic circuits. Your choice depends on the specific application's voltage level and response speed requirements.
Table of Comparison
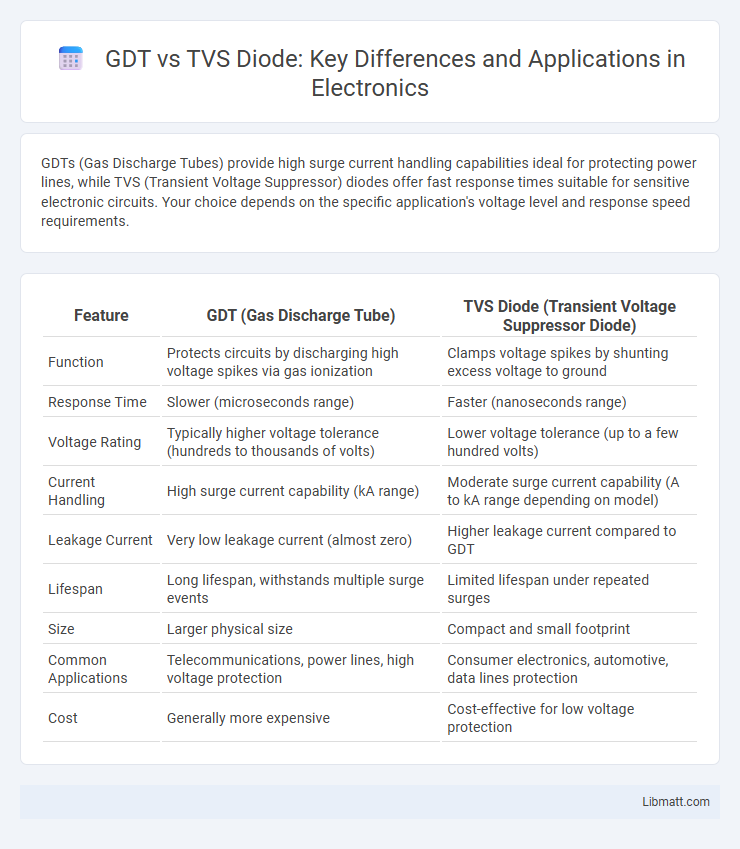
| Feature | GDT (Gas Discharge Tube) | TVS Diode (Transient Voltage Suppressor Diode) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Protects circuits by discharging high voltage spikes via gas ionization | Clamps voltage spikes by shunting excess voltage to ground |
| Response Time | Slower (microseconds range) | Faster (nanoseconds range) |
| Voltage Rating | Typically higher voltage tolerance (hundreds to thousands of volts) | Lower voltage tolerance (up to a few hundred volts) |
| Current Handling | High surge current capability (kA range) | Moderate surge current capability (A to kA range depending on model) |
| Leakage Current | Very low leakage current (almost zero) | Higher leakage current compared to GDT |
| Lifespan | Long lifespan, withstands multiple surge events | Limited lifespan under repeated surges |
| Size | Larger physical size | Compact and small footprint |
| Common Applications | Telecommunications, power lines, high voltage protection | Consumer electronics, automotive, data lines protection |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | Cost-effective for low voltage protection |
Introduction to GDT and TVS Diode
Gas Discharge Tubes (GDT) and Transient Voltage Suppressor (TVS) diodes are essential components for protecting electronic circuits from voltage spikes. GDTs rely on ionized gas to create a low-resistance path during high-voltage surges, effectively diverting excess current, while TVS diodes use semiconductor materials to clamp voltage by rapidly changing resistance. Your choice between GDT and TVS diode depends on the specific application requirements, such as response time, clamping voltage, and durability under repetitive surges.
Basic Working Principle of GDT
Gas Discharge Tubes (GDTs) operate by ionizing gas within a sealed chamber when voltage exceeds a certain threshold, creating a low-resistance path to divert surge currents safely to ground. Unlike TVS diodes, which respond instantly by clamping voltage spikes electronically, GDTs require a breakdown voltage to trigger their protective response. Your choice between GDTs and TVS diodes depends on the specific surge protection needs, with GDTs excelling in handling high-energy transients.
Basic Working Principle of TVS Diode
TVS diodes operate by clamping voltage spikes, instantly diverting excess transient energy away from sensitive electronics during surge events. Unlike GDTs (Gas Discharge Tubes), which ionize gas to create a low-resistance path at high voltage thresholds, TVS diodes respond within nanoseconds to transient overvoltages, providing rapid protection. Your circuit benefits from the TVS diode's precise voltage clamping capability, ensuring minimal disturbance during electrostatic or lightning-induced surges.
Key Differences Between GDT and TVS Diode
Gas Discharge Tubes (GDT) and Transient Voltage Suppression (TVS) diodes both protect electronic circuits from voltage spikes, but they differ significantly in operation and application. GDTs rely on ionized gas to conduct high-energy surges, providing effective protection against lightning and high-voltage transients, while TVS diodes use semiconductor junctions to clamp voltage rapidly, offering faster response times for low-energy spikes. GDTs have higher breakdown voltages and slower response, making them suitable for industrial environments, whereas TVS diodes excel in sensitive electronics due to their precise voltage clamping and quick reaction speed.
Applications of GDT in Lightning and Surge Protection
Gas Discharge Tubes (GDTs) are widely used in lightning and surge protection systems due to their high-voltage handling capability and fast response to transient overvoltages. Their ability to safely divert large surge currents makes them ideal for protecting telecommunications equipment, power distribution networks, and sensitive electronic devices from lightning strikes and electrical surges. Unlike TVS diodes, GDTs excel in scenarios requiring robust, long-duration surge suppression with minimal leakage current under normal operating conditions.
Applications of TVS Diode in Circuit Protection
TVS diodes are widely used in circuit protection to safeguard sensitive electronic components from transient voltage spikes caused by electrostatic discharge (ESD), lightning surges, and inductive load switching. Common applications include protecting power supply lines, data communication interfaces, automotive electronics, and consumer devices such as smartphones and laptops. Their fast response time and high surge current handling capabilities make TVS diodes essential in preventing permanent damage and ensuring system reliability.
Advantages and Limitations of GDT
Gas Discharge Tubes (GDT) offer high surge current handling capabilities and excellent robustness against repeated transients, making them ideal for protecting sensitive electronics from large voltage spikes. However, GDTs have slower response times and higher voltage clamping levels compared to TVS diodes, which can limit their effectiveness in protecting low-voltage circuits. You should consider GDTs for applications requiring high energy absorption and long-term reliability but be mindful of their limitations in fast-response scenarios.
Advantages and Limitations of TVS Diode
TVS diodes offer fast response times and precise voltage clamping, making them ideal for protecting sensitive electronic circuits from transient voltage spikes. They have advantages such as low leakage current, stable operation, and small size, enabling easy integration into compact designs. However, TVS diodes are limited by their relatively lower energy absorption capacity compared to GDTs and can suffer from heat dissipation issues under high surge currents.
Factors to Consider When Choosing GDT vs TVS Diode
When choosing between a Gas Discharge Tube (GDT) and a Transient Voltage Suppressor (TVS) diode, consider factors such as response time, voltage rating, and energy absorption capacity. GDTs are ideal for high-voltage, high-energy surges but have slower response times, whereas TVS diodes provide fast clamping for low to medium-energy transients. Your specific application requirements, including the environment and protection level needed, will determine the best choice for surge protection.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Surge Protection Device
Selecting the right surge protection device depends on your specific application requirements and circuit characteristics. GDTs (Gas Discharge Tubes) offer high current handling and robustness for industrial or high-voltage systems, while TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) diodes provide fast response time and precise voltage clamping ideal for sensitive electronics. Understanding your system's surge energy levels and response speed ensures your protection strategy maximizes device longevity and circuit safety.
GDT vs TVS Diode Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com