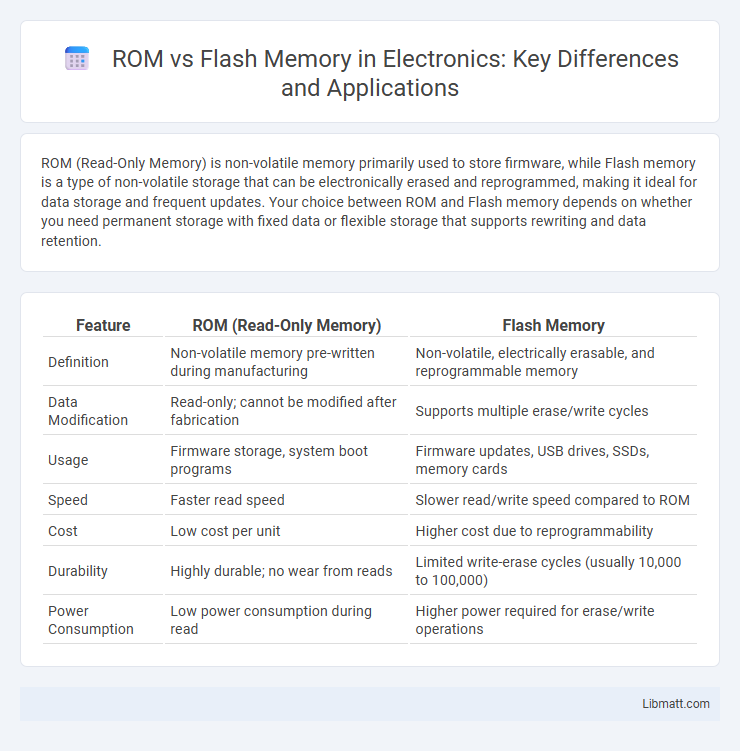
ROM (Read-Only Memory) is non-volatile memory primarily used to store firmware, while Flash memory is a type of non-volatile storage that can be electronically erased and reprogrammed, making it ideal for data storage and frequent updates. Your choice between ROM and Flash memory depends on whether you need permanent storage with fixed data or flexible storage that supports rewriting and data retention.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | ROM (Read-Only Memory) | Flash Memory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-volatile memory pre-written during manufacturing | Non-volatile, electrically erasable, and reprogrammable memory |
| Data Modification | Read-only; cannot be modified after fabrication | Supports multiple erase/write cycles |
| Usage | Firmware storage, system boot programs | Firmware updates, USB drives, SSDs, memory cards |
| Speed | Faster read speed | Slower read/write speed compared to ROM |
| Cost | Low cost per unit | Higher cost due to reprogrammability |
| Durability | Highly durable; no wear from reads | Limited write-erase cycles (usually 10,000 to 100,000) |
| Power Consumption | Low power consumption during read | Higher power required for erase/write operations |
Introduction to ROM and Flash Memory
ROM (Read-Only Memory) is a type of non-volatile memory that permanently stores firmware and system software essential for booting your device. Flash memory, a modern variant of ROM, enables electrical erasure and reprogramming, offering flexible storage solutions for devices like USB drives and smartphones. Understanding the differences between these memory types helps optimize data retention and device performance according to your needs.
Definition and Purpose of ROM
Read-Only Memory (ROM) is a type of non-volatile storage that permanently holds data essential for booting and hardware initialization in computers and electronic devices. Unlike Flash memory, which can be electrically erased and reprogrammed for data storage and frequent updates, ROM stores firmware and system instructions that remain unchanged during regular operation. ROM ensures stable and secure access to critical code, enabling devices to start correctly and perform foundational tasks without loss of information when powered off.
Definition and Purpose of Flash Memory
Flash memory is a non-volatile storage technology used for storing and retrieving digital data in devices such as USB drives, SSDs, and memory cards. Unlike ROM, which is primarily read-only and used to store firmware, flash memory allows data to be electronically erased and reprogrammed multiple times. Its purpose is to provide fast, reliable, and rewritable storage that retains information without power.
Key Differences Between ROM and Flash Memory
ROM (Read-Only Memory) is non-volatile storage used primarily to store firmware permanently, with data that cannot be easily modified or erased, while Flash memory is a type of non-volatile memory that allows for electrical erasing and reprogramming, making it ideal for storage devices like USB drives and SSDs. ROM typically contains fixed data essential for booting up hardware, whereas Flash memory enables repeated write and erase cycles, providing flexibility for data updates. Your choice between ROM and Flash memory depends on the need for permanent storage versus rewritable, high-density memory solutions.
Types of ROM
ROM includes several types such as Mask ROM, which is programmed during manufacturing and cannot be altered; Programmable ROM (PROM), allowing one-time programming by users; Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM), which can be erased with UV light and reprogrammed; and Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM (EEPROM), enabling multiple rewrites electrically without removal from the device. Flash memory, often considered a type of EEPROM, offers block-level erasing and faster rewriting, making it suitable for high-capacity storage. Each ROM type serves distinct purposes based on permanence, reprogrammability, and application needs.
Types of Flash Memory
Flash memory primarily comes in two types: NAND and NOR, each offering distinct advantages for different applications. NAND flash is widely used for data storage in smartphones, USB drives, and SSDs due to its high density and fast write speeds, while NOR flash provides faster read speeds and is often employed in embedded systems for code storage. Understanding these types helps you choose the right memory for your device's performance and reliability requirements.
Data Storage and Retention Capabilities
ROM (Read-Only Memory) stores data permanently, retaining information even when the power is off, making it ideal for firmware and system boot instructions. Flash memory, a type of non-volatile storage, combines fast read/write access with long-term data retention, suitable for applications requiring frequent updates like USB drives and SSDs. Your choice depends on whether data permanence or rewritability is the priority for your device's storage needs.
Applications of ROM in Modern Devices
Read-Only Memory (ROM) plays a critical role in embedded systems by storing firmware essential for booting and hardware initialization in devices such as smartphones, gaming consoles, and printers. It ensures data permanence and security, making it ideal for firmware storage in medical devices and automotive control systems. Unlike Flash memory, which allows for frequent rewriting, ROM retains its contents without power, providing stability for crucial low-level software applications.
Applications of Flash Memory in Modern Devices
Flash memory is extensively used in smartphones, tablets, and USB drives due to its non-volatile storage capabilities and fast read/write speeds. It also powers solid-state drives (SSDs), enhancing data access speed and durability in laptops and desktop computers. Embedded systems like digital cameras and gaming consoles rely on flash memory for efficient storage and quick firmware updates.
Choosing Between ROM and Flash Memory
Choosing between ROM and Flash memory depends on the specific application requirements such as write frequency, cost, and speed. ROM offers permanent data storage with fast read access and is ideal for firmware that does not require updates, while Flash memory provides rewritable, non-volatile storage suitable for frequent updates like in mobile devices and SSDs. Consider the trade-offs between durability, power consumption, and data retention when selecting the appropriate memory type.
ROM vs Flash memory Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com