Synchronous communication requires participants to interact in real-time, which enhances immediate feedback and collaboration, while asynchronous communication allows you to respond at your convenience, promoting flexibility and thoughtful responses. Choosing between synchronous and asynchronous methods depends on your specific needs for urgency, engagement, and communication clarity.
Table of Comparison
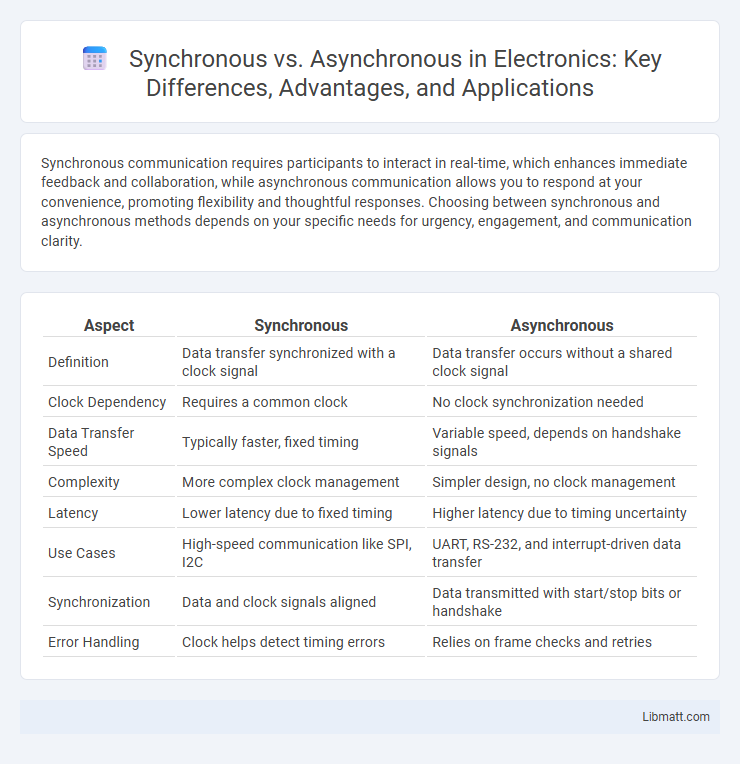
| Aspect | Synchronous | Asynchronous |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data transfer synchronized with a clock signal | Data transfer occurs without a shared clock signal |
| Clock Dependency | Requires a common clock | No clock synchronization needed |
| Data Transfer Speed | Typically faster, fixed timing | Variable speed, depends on handshake signals |
| Complexity | More complex clock management | Simpler design, no clock management |
| Latency | Lower latency due to fixed timing | Higher latency due to timing uncertainty |
| Use Cases | High-speed communication like SPI, I2C | UART, RS-232, and interrupt-driven data transfer |
| Synchronization | Data and clock signals aligned | Data transmitted with start/stop bits or handshake |
| Error Handling | Clock helps detect timing errors | Relies on frame checks and retries |
Introduction to Synchronous and Asynchronous Communication
Synchronous communication occurs in real-time, requiring participants to be engaged simultaneously, such as in phone calls or live video chats, enabling immediate feedback and collaborative interaction. Asynchronous communication allows messages to be sent and received at different times, exemplified by emails and online forums, providing flexibility and time for thoughtful responses. Understanding these communication methods helps you choose the best approach for efficiency and clarity in various personal or professional contexts.
Key Definitions: Synchronous vs Asynchronous
Synchronous communication requires participants to interact in real-time, with immediate responses and simultaneous engagement. Asynchronous communication allows participants to respond at their own pace, providing flexibility and time for thoughtful replies. Understanding these key definitions helps you choose the most effective communication method for your specific context or project needs.
Core Differences Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Methods
Synchronous methods involve tasks executed sequentially, where each operation waits for the previous one to complete, ensuring strict order and immediate response. Asynchronous methods allow tasks to run independently of the main program flow, enabling concurrent execution and improving resource utilization by not blocking waiting for responses. The core difference lies in synchronization: synchronous requires blocking until completion, while asynchronous promotes non-blocking, enhancing efficiency in I/O-bound and high-latency operations.
Pros and Cons of Synchronous Communication
Synchronous communication offers real-time interaction, enhancing immediate feedback, clearer understanding, and faster decision-making, which can improve team collaboration and productivity. However, it can also lead to interruptions, decreased flexibility, and challenges in coordinating schedules across different time zones. Your team may benefit from synchronous communication when quick responses and active engagement are crucial, but it may hinder workflow if constant availability is required.
Pros and Cons of Asynchronous Communication
Asynchronous communication allows you to send and receive messages without needing both parties to be available simultaneously, improving flexibility and enabling better time management across different time zones. However, it can lead to delays in responses, potential misunderstandings, and lack of immediate feedback, which may hinder quick decision-making and reduce the effectiveness of urgent collaborations. This communication method is ideal for tasks requiring thoughtful responses but may challenge projects needing real-time interaction.
Common Use Cases for Synchronous Communication
Synchronous communication is commonly used in real-time collaboration environments such as video conferencing, live chats, and phone calls where immediate feedback is critical. It allows teams to quickly clarify misunderstandings, make decisions, and coordinate tasks efficiently during meetings or brainstorming sessions. Industries like customer support, healthcare, and software development rely heavily on synchronous communication for time-sensitive interactions and rapid problem-solving.
Common Use Cases for Asynchronous Communication
Asynchronous communication is widely used in remote work environments, where team members collaborate across different time zones without the need for immediate responses. Platforms like email, project management tools, and messaging apps facilitate asynchronous exchanges, allowing for thoughtful, flexible communication that accommodates varying schedules. Your productivity can improve significantly by leveraging asynchronous communication for tasks that require reflection, documentation, and non-urgent discussions.
Choosing the Right Method: Factors to Consider
Choosing between synchronous and asynchronous communication depends on factors such as urgency, context, and participant availability. Synchronous methods like video calls enable real-time interaction, ideal for urgent decisions and collaborative tasks. Asynchronous options such as email or messaging offer flexibility, better suited for complex discussions or when participants operate across different time zones.
Impact on Productivity and Collaboration
Synchronous communication, such as video calls and chat, enables real-time interaction that boosts immediate feedback and faster decision-making, enhancing team collaboration and productivity in dynamic environments. Asynchronous communication, including emails and project management tools, allows team members to work on tasks independently at their own pace, reducing interruptions and accommodating different time zones, which improves deep work and overall efficiency. Balancing synchronous and asynchronous methods optimizes productivity by ensuring timely collaboration while supporting focused, uninterrupted work.
Future Trends in Synchronous and Asynchronous Communication
Future trends in synchronous communication emphasize enhanced real-time collaboration through AI-powered video conferencing and augmented reality integration, improving immediacy and engagement. Asynchronous communication is evolving with advanced AI-driven messaging platforms that enable context-aware responses and seamless information retrieval, optimizing flexibility and productivity. The convergence of synchronous and asynchronous tools will likely create hybrid models that adapt dynamically to user preferences and work environments.
Synchronous vs Asynchronous Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com