Ancillary services support the reliable operation of the power grid by maintaining voltage, frequency, and reserve capacity, while balancing services specifically address real-time supply and demand fluctuations to keep the grid stable. Understanding the distinct roles of these services helps optimize Your energy management and ensures continuous power quality.
Table of Comparison
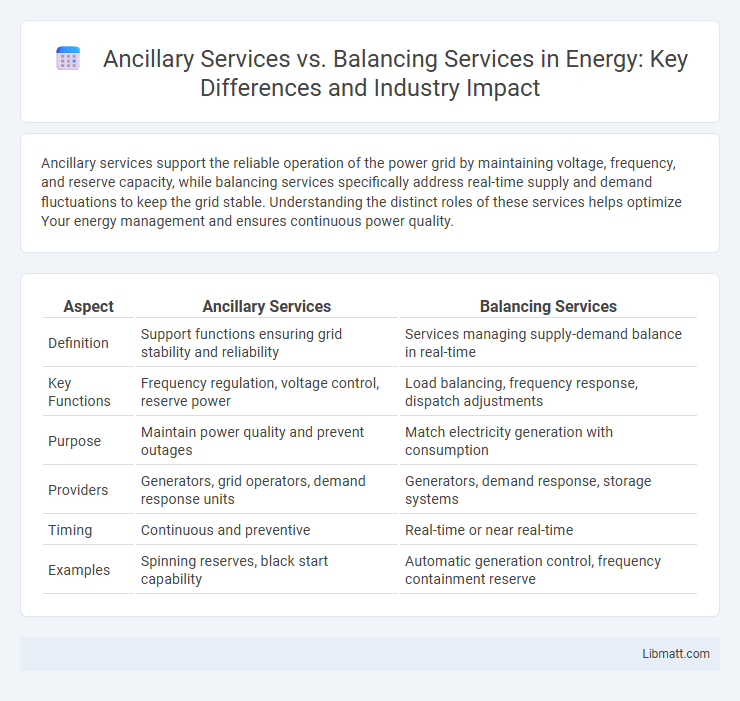
| Aspect | Ancillary Services | Balancing Services |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Support functions ensuring grid stability and reliability | Services managing supply-demand balance in real-time |
| Key Functions | Frequency regulation, voltage control, reserve power | Load balancing, frequency response, dispatch adjustments |
| Purpose | Maintain power quality and prevent outages | Match electricity generation with consumption |
| Providers | Generators, grid operators, demand response units | Generators, demand response, storage systems |
| Timing | Continuous and preventive | Real-time or near real-time |
| Examples | Spinning reserves, black start capability | Automatic generation control, frequency containment reserve |
Introduction to Ancillary and Balancing Services
Ancillary services support the reliable operation of the power grid by managing frequency, voltage, and reserves to maintain system stability. Balancing services specifically address real-time supply-demand mismatches, ensuring continuous equilibrium between electricity generation and consumption. Understanding these distinctions helps optimize Your energy management strategies and enhances grid reliability.
Defining Ancillary Services in Power Systems
Ancillary services in power systems encompass a range of support functions essential for maintaining grid reliability, such as frequency regulation, voltage control, and spinning reserves. These services enable stable power system operation by managing real-time imbalances between supply and demand. Balancing services, as a subset of ancillary services, specifically focus on correcting short-term discrepancies to ensure continuous synchronization between generation and consumption.
Understanding Balancing Services and Their Role
Balancing services ensure real-time equilibrium between electricity supply and demand, maintaining grid stability and preventing outages. These services include frequency regulation, reserve power activation, and load following, which adjust generation or consumption within seconds to minutes. Your energy system relies on balancing services to respond dynamically to fluctuations and sustain reliable power delivery.
Core Differences Between Ancillary and Balancing Services
Ancillary services support the reliable operation of the power grid by managing voltage, frequency, and reserve capacity, whereas balancing services specifically address real-time supply and demand fluctuations to maintain grid stability. The core difference lies in their scope: ancillary services provide a broad range of support functions, while balancing services focus solely on matching generation with consumption. Your energy management strategy must differentiate these roles to optimize grid performance and compliance.
Key Functions of Ancillary Services
Ancillary services play a crucial role in maintaining grid reliability by supporting essential functions such as frequency regulation, voltage control, and reserve capacity. These services ensure the continuous balance between electricity supply and demand, preventing outages and maintaining stable power quality. Unlike balancing services, which primarily address real-time supply-demand matching, ancillary services provide the necessary support infrastructure to sustain overall grid stability and operational security.
Main Responsibilities of Balancing Services
Balancing services are primarily responsible for maintaining the stability and reliability of the power grid by managing real-time supply and demand fluctuations to prevent frequency deviations and voltage instability. These services ensure that generation and consumption remain in equilibrium, mitigating risks of blackouts and ensuring continuous electricity delivery. You rely on balancing services to provide rapid response corrections that support grid resilience and operational efficiency.
Importance in Grid Stability and Reliability
Ancillary services, including frequency regulation and voltage support, play a critical role in maintaining grid stability by managing real-time power quality and preventing outages. Balancing services specifically address the continuous matching of electricity supply and demand, ensuring instantaneous system equilibrium and preventing frequency deviations. Both services are essential for reliable grid operation, with ancillary services providing broader system support and balancing services maintaining the fundamental energy balance.
Market Structures and Regulatory Perspectives
Ancillary services and balancing services operate within distinct market structures shaped by regulatory frameworks aimed at maintaining grid stability. Ancillary services typically function in competitive markets with defined product categories such as frequency regulation, voltage control, and spinning reserves, subject to market-based procurement and performance standards. Balancing services are often governed by system operators under regulatory oversight, involving real-time adjustments and reserve balancing mechanisms to manage supply-demand discrepancies and ensure continuous grid reliability.
Technological Evolution in Ancillary and Balancing Services
Technological evolution in ancillary and balancing services has significantly enhanced grid stability and reliability through advanced automation, real-time data analytics, and faster response capabilities. Innovations such as battery storage, demand response technologies, and AI-driven forecasting optimize both ancillary services like frequency regulation and balancing services that manage supply-demand fluctuations. Your energy management can benefit from these technologies, ensuring more efficient integration of renewable resources and improved system resilience.
Future Trends and Challenges in Grid Support Services
Future trends in ancillary services and balancing services emphasize integration of advanced grid technologies like AI-driven demand response and energy storage systems to enhance real-time grid stability. Challenges include managing increased variability from renewable energy sources and addressing regulatory complexities across regions to ensure seamless market participation. Enhanced grid digitalization and interoperability standards are critical for optimizing resource allocation and maintaining system reliability amid growing decentralized energy resources.
Ancillary services vs Balancing services Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com