Cold milling removes asphalt layers by grinding at ambient temperatures, preserving the material's integrity for recycling, while hot milling heats the pavement surface to soften it, allowing for deeper cuts and smoother finishes. Choosing between cold and hot milling depends on your project's requirements for precision, depth, and material reuse.
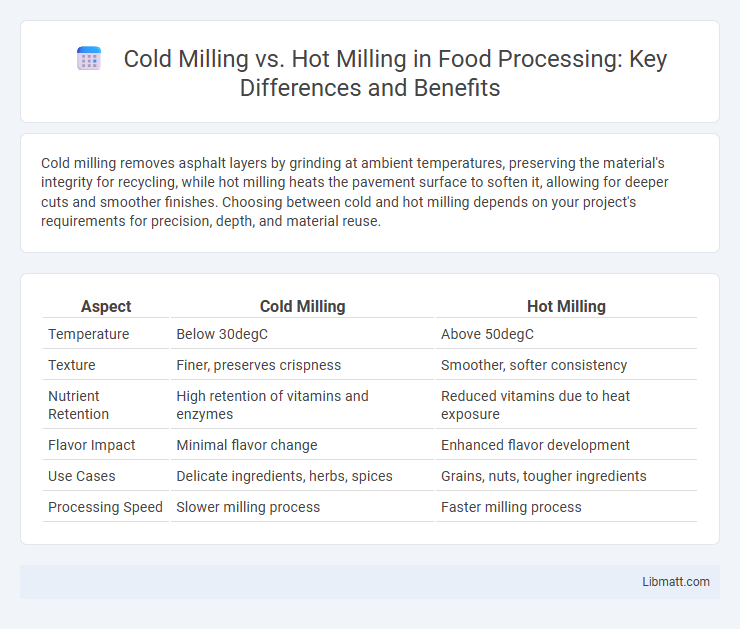
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Cold Milling | Hot Milling |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Below 30degC | Above 50degC |
| Texture | Finer, preserves crispness | Smoother, softer consistency |
| Nutrient Retention | High retention of vitamins and enzymes | Reduced vitamins due to heat exposure |
| Flavor Impact | Minimal flavor change | Enhanced flavor development |
| Use Cases | Delicate ingredients, herbs, spices | Grains, nuts, tougher ingredients |
| Processing Speed | Slower milling process | Faster milling process |
Introduction to Cold Milling and Hot Milling
Cold milling involves removing asphalt pavement layers using specialized milling machines at ambient temperatures, ensuring precise surface profiling and recycling capabilities. Hot milling, conversely, heats the asphalt before milling, which can improve removal efficiency and material quality but requires additional energy input. Your choice between cold and hot milling depends on project goals, environmental considerations, and material reuse plans.
Key Differences Between Cold Milling and Hot Milling
Cold milling involves removing existing pavement surface at low temperatures using a milling machine, preserving the underlying layers, while hot milling heats the pavement before milling to soften the material for easier removal. Your choice depends on project requirements, as cold milling is ideal for surface leveling and minor repairs, whereas hot milling suits heavy-duty pavement rehabilitation. Efficiency in material removal, temperature control, and impact on pavement integrity are the primary factors distinguishing cold milling from hot milling.
Process Overview: How Cold Milling Works
Cold milling involves the removal of damaged asphalt layers or concrete surfaces using a rotating drum equipped with carbide-tipped cutting bits, preserving the underlying pavement structure. The process generates minimal heat as the material is cut at ambient temperatures, reducing thermal stress and preventing distortion of the road base. Milling machines precisely control depth and profile, allowing for efficient surface rehabilitation and preparation for repaving or resurfacing projects.
Process Overview: How Hot Milling Works
Hot milling involves heating the material to a high temperature before or during the milling process, which softens the metal and reduces its brittleness, allowing for easier shaping and cutting. This thermal activation enhances the machinability of hard or tough metals, resulting in smoother surface finishes and prolonged tool life. The process is particularly favored in industries dealing with high-strength alloys where conventional cold milling would cause excessive tool wear and material fatigue.
Equipment Used in Cold vs Hot Milling
Cold milling employs specialized milling machines equipped with large rotating drums and carbide teeth designed to remove asphalt layers efficiently without heating. Hot milling utilizes heaters and infrared technology combined with milling machines to soften the pavement surface before milling, enabling smoother removal at elevated temperatures. The choice between cold and hot milling equipment hinges on project requirements, surface conditions, and temperature control capabilities.
Advantages of Cold Milling
Cold milling offers precise surface removal with minimal thermal damage, preserving pavement integrity and reducing distresses like cracking and rutting. It enables faster project completion due to lower cooling times and improved dust control, enhancing worker safety and environmental compliance. Cost-effective and versatile, cold milling supports effective recycling of reclaimed asphalt pavement, promoting sustainable road construction practices.
Advantages of Hot Milling
Hot milling offers advantages such as faster material removal rates and improved surface finish due to the elevated temperatures reducing material hardness during the process. It enhances cutting tool life by minimizing wear and allows better control over material properties in metals with high thermal sensitivity. Your production efficiency can significantly increase with hot milling in applications requiring precision and durability.
Applications Suited for Cold Milling
Cold milling is ideal for removing asphalt or concrete pavement layers, making it suitable for road rehabilitation and surface preparation before repaving. This method excels in applications requiring precise depth control and minimal heat generation, preserving underlying layers and reducing environmental impact. Your pavement maintenance projects benefit from cold milling's efficiency in extracting defective materials without compromising structural integrity.
Applications Suited for Hot Milling
Hot milling is best suited for applications involving heavy asphalt layers, thick concrete pavements, and surface leveling where deeper cuts are required for efficient removal. Your project benefits from hot milling when precise surface profiles and smooth finishes are essential for subsequent paving or repair work. This method excels in high-temperature environments to enhance milling machine efficiency and asphalt recycling quality.
Choosing the Right Milling Method: Factors to Consider
Selecting the appropriate milling method depends on factors such as material type, desired surface finish, and project scale. Cold milling is ideal for removing asphalt layers without damaging the underlying pavement, offering precision and minimal heat distortion. Hot milling suits materials requiring softening through heat for easier removal, enhancing efficiency but potentially affecting the material properties due to thermal exposure.
Cold Milling vs Hot Milling Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com