Defrosting refers to the process of removing ice or frost from frozen items, often using heat, while thawing describes the gradual warming of frozen food to a temperature where it becomes soft or fully unfrozen. Understanding the difference helps you handle frozen goods safely, ensuring proper preparation and preventing spoilage.
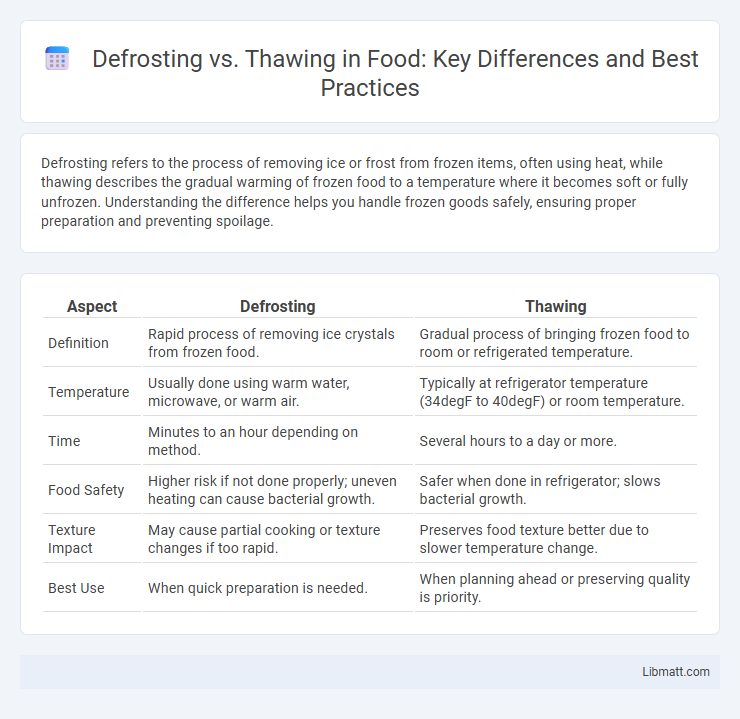
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Defrosting | Thawing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rapid process of removing ice crystals from frozen food. | Gradual process of bringing frozen food to room or refrigerated temperature. |
| Temperature | Usually done using warm water, microwave, or warm air. | Typically at refrigerator temperature (34degF to 40degF) or room temperature. |
| Time | Minutes to an hour depending on method. | Several hours to a day or more. |
| Food Safety | Higher risk if not done properly; uneven heating can cause bacterial growth. | Safer when done in refrigerator; slows bacterial growth. |
| Texture Impact | May cause partial cooking or texture changes if too rapid. | Preserves food texture better due to slower temperature change. |
| Best Use | When quick preparation is needed. | When planning ahead or preserving quality is priority. |
Understanding Defrosting and Thawing: Key Differences
Defrosting involves actively using external heat, such as a microwave or warm water, to rapidly convert frozen food from ice to a usable state, while thawing refers to the natural, gradual warming process at room temperature or in the refrigerator. Defrosting typically reduces preparation time for frozen items, but improper techniques may lead to uneven temperatures and bacterial growth. Thawing preserves texture and safety by allowing even temperature increase, especially for meats and seafood, making it the preferred method for maintaining food quality and preventing contamination.
Scientific Principles Behind Defrosting and Thawing
Defrosting involves applying controlled heat to ice crystals in frozen food, causing them to convert directly from solid to liquid through phase change, while thawing primarily relies on ambient temperature increasing the thermal energy of frozen tissues, returning them to a softer, malleable state. The scientific principle behind defrosting centers on heat transfer and latent heat absorption, whereas thawing is governed by the gradual increase in molecular motion and fluidity within the frozen material. Understanding these thermal dynamics ensures food safety and texture preservation during preparation.
Common Methods for Defrosting Food
Common methods for defrosting food include using a microwave's defrost setting, placing food in the refrigerator for slow thawing, and submerging sealed packages in cold water to expedite the process. Microwaving offers fast results but may partially cook edges if not monitored closely, while refrigeration ensures safe, even thawing over several hours to days depending on the item size. Cold water thawing requires changing water every 30 minutes to maintain temperature and prevent bacterial growth, making it ideal for quicker defrosting of meats and seafood.
Safe Techniques for Thawing
Safe techniques for thawing include refrigerating food at temperatures below 40degF (4degC) to prevent bacterial growth and thawing in cold water that is changed every 30 minutes to maintain safety. Using a microwave's defrost setting is effective for smaller portions, but food must be cooked immediately afterward to avoid bacterial proliferation. Avoid thawing food at room temperature as it increases the risk of contamination and foodborne illnesses.
Defrosting vs Thawing: Impact on Food Quality
Defrosting typically involves using external heat sources such as microwaves or warm water, which can cause uneven temperature distribution and partially cook food, negatively affecting texture and taste. Thawing, especially when done gradually in a refrigerator, preserves cellular structure and moisture, maintaining the original food quality and safety. Proper thawing enhances flavor retention and reduces the risk of bacterial growth compared to rapid defrosting methods.
Food Safety Concerns: Defrosting vs Thawing
Defrosting and thawing differ in how they impact food safety, with defrosting often done using controlled methods like refrigeration or microwave, reducing bacterial growth risks. Thawing at room temperature can elevate the risk of foodborne illnesses because bacteria multiply rapidly in the danger zone between 40degF and 140degF. Ensuring Your food is defrosted properly helps maintain safety and prevents contamination.
Best Practices for Quick Defrosting
Quick defrosting is best achieved using the microwave's defrost setting or placing sealed food in cold water, changing the water every 30 minutes to prevent bacterial growth. Avoid defrosting at room temperature to reduce the risk of contamination and uneven thawing. For optimal food safety and texture, plan defrosting times based on food weight and type, utilizing a temperature-safe method that maintains consistent cold conditions.
Thawing Tips to Preserve Flavor and Texture
Thawing frozen foods slowly in the refrigerator preserves flavor and texture by maintaining a consistent, safe temperature that minimizes moisture loss. Using cold water thawing in sealed bags speeds the process while preventing bacterial growth and retaining food quality. Avoid microwave thawing when possible, as it can cause uneven heating and degrade texture or flavor in delicate items.
Appliances and Tools for Effective Defrosting
Microwave ovens and refrigerator freezer compartments are common appliances designed for effective defrosting, providing controlled environments to safely lower frozen food temperatures. Defrosting trays made from conductive materials like aluminum speed up ice melting by transferring heat efficiently. Your ability to choose the right tool impacts food safety and quality, preventing harmful bacteria growth during the thawing process.
Frequently Asked Questions about Defrosting and Thawing
Defrosting and thawing often refer to similar processes of warming frozen food, but defrosting typically involves faster methods like using a microwave or cold water, while thawing usually occurs gradually in the refrigerator. Common questions include the safest ways to defrost meat, how long thawed food can be stored, and whether refreezing thawed items affects quality. Understanding these distinctions helps ensure food safety and maintain optimal texture and taste during preparation.
Defrosting vs Thawing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com