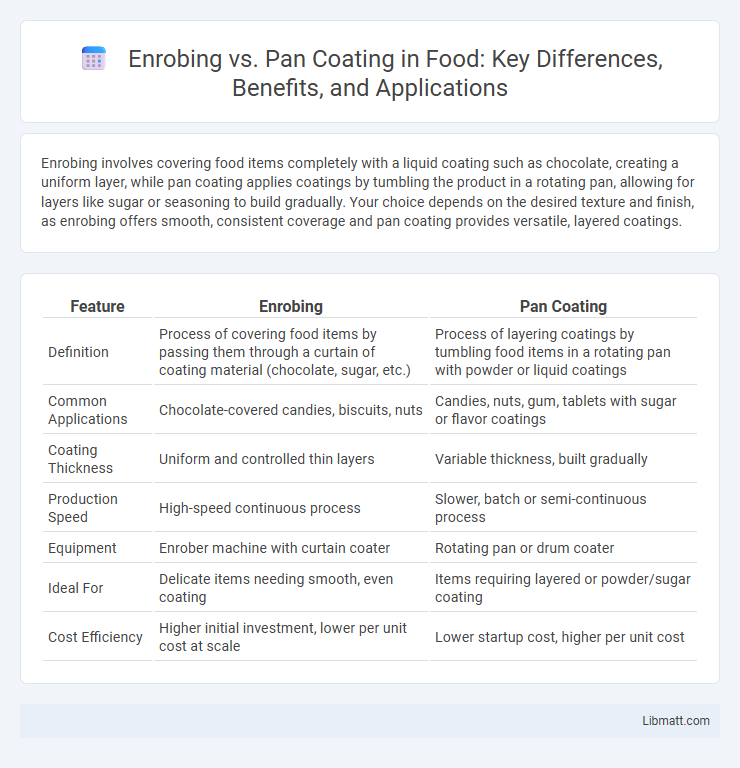
Enrobing involves covering food items completely with a liquid coating such as chocolate, creating a uniform layer, while pan coating applies coatings by tumbling the product in a rotating pan, allowing for layers like sugar or seasoning to build gradually. Your choice depends on the desired texture and finish, as enrobing offers smooth, consistent coverage and pan coating provides versatile, layered coatings.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Enrobing | Pan Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of covering food items by passing them through a curtain of coating material (chocolate, sugar, etc.) | Process of layering coatings by tumbling food items in a rotating pan with powder or liquid coatings |
| Common Applications | Chocolate-covered candies, biscuits, nuts | Candies, nuts, gum, tablets with sugar or flavor coatings |
| Coating Thickness | Uniform and controlled thin layers | Variable thickness, built gradually |
| Production Speed | High-speed continuous process | Slower, batch or semi-continuous process |
| Equipment | Enrober machine with curtain coater | Rotating pan or drum coater |
| Ideal For | Delicate items needing smooth, even coating | Items requiring layered or powder/sugar coating |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial investment, lower per unit cost at scale | Lower startup cost, higher per unit cost |
Introduction to Enrobing and Pan Coating
Enrobing involves coating products with a continuous layer of chocolate or other coatings, achieved by passing items under a curtain of liquid coating for even coverage. Pan coating, on the other hand, utilizes a rotating drum where products are tumbled and gradually coated with layers of candy, chocolate, or sugar to build up a smooth, polished finish. Both techniques serve to enhance visual appeal, texture, and flavor profile in confectionery manufacturing.
Definition and Overview of Enrobing
Enrobing is a confectionery process where food items are completely covered with a coating of chocolate or other compound coatings by passing them through a curtain of liquid coating. This technique ensures an even layer around each piece, providing a smooth and glossy finish essential for chocolates, nuts, and confectionery products. Unlike pan coating, which involves tumbling ingredients in a rotating pan to gradually build layers, enrobing applies a continuous, uniform coating in a controlled production line setting.
Definition and Overview of Pan Coating
Pan coating is a confectionery process where products are rotated in a pan while a coating substance, such as chocolate or sugar syrup, is gradually applied to build a smooth, even layer. This technique allows for controlled thickness and a glossy finish, improving texture and appearance. Unlike enrobing, which involves dipping products into liquid coatings, pan coating relies on tumbling and layering for uniform coverage.
Key Differences Between Enrobing and Pan Coating
Enrobing involves coating products entirely by passing them through a curtain of molten chocolate or coating material, resulting in a smooth, uniform layer ideal for bars and centers. Pan coating uses a rotating drum to tumble products while coating is gradually applied, creating a thicker, often textured shell suitable for nuts, candies, or snack clusters. Understanding these differences helps you select the right technique to achieve desired texture, appearance, and coating thickness for your confectionery or snack products.
Applications of Enrobing in Food and Pharmaceuticals
Enrobing is widely used in the food industry for coating chocolates, candies, nuts, and bakery products to enhance flavor, texture, and appearance while ensuring an even, protective layer. In pharmaceuticals, enrobing applies to tablets and pills, providing controlled release, taste masking, and protection from environmental factors. Your production process benefits from enrobing's precision and efficiency, delivering consistent quality across diverse applications.
Applications of Pan Coating in Various Industries
Pan coating is widely used in the confectionery, pharmaceutical, and nut industries due to its ability to uniformly coat products like candies, tablets, and nuts with sugar, chocolate, or other coatings. This process enhances product appearance, taste, and shelf life, making it essential for creating appealing and protective layers on diverse items. Your products benefit from pan coating by achieving consistent coating thickness and improved quality control in large-scale manufacturing.
Advantages of Enrobing Process
The enrobing process offers precise and uniform coating, ensuring consistent coverage of products with chocolate or other coatings, which enhances product appearance and taste. Enrobing minimizes waste due to controlled flow and efficient use of coating materials, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact. This method also allows for customization in thickness and texture, improving the overall sensory experience and extending shelf life.
Advantages of Pan Coating Process
Pan coating offers precise control over coating thickness, resulting in consistent product quality ideal for confectionery and pharmaceutical applications. The process allows for efficient layering of flavors and textures, enhancing product appeal while minimizing ingredient waste. Its versatility in coating various shapes and sizes improves manufacturing scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Coating Method
When selecting between enrobing and pan coating, consider factors such as product type, desired coating thickness, and production speed. Enrobing suits items requiring a uniform chocolate layer and high-volume output, while pan coating is ideal for creating textured, layered finishes on smaller batches. Cost efficiency, equipment availability, and product sensitivity to heat also influence the choice of coating method.
Conclusion: Enrobing vs Pan Coating—Which to Choose?
Enrobing offers precise control over chocolate thickness and uniform coverage, ideal for delicate confections and mass production with consistent quality. Pan coating is better suited for larger items and products requiring multiple coating layers, providing versatility in texture and appearance. The choice depends on product size, production scale, and desired finish, with enrobing favored for smooth consistency and pan coating chosen for layered coatings.
enrobing vs pan coating Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com